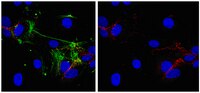
Cellular sources of MMP-7, MMP-13 and MMP-28 in ulcerative colitis.
Timo Rath,Martin Roderfeld,Jörg Michael Halwe,Annette Tschuschner,Elke Roeb,Jürgen Graf
Scandinavian journal of gastroenterology
45
2010
Show Abstract
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are considered the predominant proteases in the pathogenesis of mucosal ulcerations associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Whether the malignancy associated MMP-7 and MMP-13 or the recently cloned MMP-28 convey a certain meaning for intestinal homeostasis and pathogenesis of IBD is currently unknown. We therefore set off to analyze regulation patterns and cellular origins of these MMPs in mucosal tissues of patients with ulcerative colitis (UC). | 20568971
 |
Flow-conditioned HUVECs support clustered leukocyte adhesion by coexpressing ICAM-1 and E-selectin.
Burns, MP; DePaola, N
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology
288
H194-204
2005
Show Abstract
Endothelial sequestration of circulating monocytes is a key event in early atherosclerosis. Hemodynamics is proposed to regulate monocyte-endothelial cell interactions by direct cell activation and establishment of flow environments that are conducive or prohibitive to cell-cell interaction. We investigated fluid shear regulation of monocyte-endothelial cell adhesion in vitro using a disturbed laminar shear system that models in vivo hemodynamics characteristic of lesion-prone vascular regions. Human endothelial cell monolayers were flow conditioned for 6 h before evaluation of monocyte adhesion under static and dynamic flow conditions. Results revealed a distinctive clustered cell pattern of monocyte adhesion that strongly resembles in vivo leukocyte adhesion in early- and late-stage atherosclerosis. Clustered monocyte cell adhesion correlated with endothelial cells coexpressing intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and E-selectin as result of a flow-induced, selective upregulation of E-selectin expression in a subset of ICAM-1-expressing cells. Clustered monocyte cell adhesion assayed under static conditions exhibited a spatial variation in size and frequency of occurrence, which demonstrates differential regulation of endothelial cell adhesiveness by the local flow environment. Dynamic adhesion studies conducted with circulating monocytes resulted in clustered cell adhesion only within the disturbed flow region, where the monocyte rate of motion is sufficiently low for cell-cell interaction. These studies provide evidence and reveal mechanisms of local hemodynamic regulation of endothelial adhesiveness and endothelial monocyte interaction that lead to localized monocyte adhesion and potentially contribute to the focal origin of arterial diseases such as atherosclerosis. | 15331359
 |
Synergistic induction of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 by the human cytomegalovirus transactivators IE2p86 and pp71 is mediated via an Sp1-binding site.
Martina Kronschnabl, Thomas Stamminger
The Journal of general virology
84
61-73
2003
Show Abstract
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection of transplant recipients is frequently associated with allograft vasculopathy and rejection. One potential mechanism is vascular injury from HCMV-triggered, immunologically mediated processes. HCMV infection has been shown to increase the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). The objective of this study was to determine the molecular basis of HCMV-enhanced ICAM-1 gene expression. Transient transfection experiments identified the IE2p86 protein as a potent activator of the ICAM-1 promoter. The tegument protein pp71 showed a strong synergistic effect on IE2p86-mediated ICAM-1 promoter activation. Mutagenesis experiments defined a DNA element from -110 to -42 relative to the transcription start site as responsive for IE2p86. Further point mutations within this DNA element identified an Sp1-binding site that was essential for strong synergistic activation by IE2p86 and pp71. To confirm the activation of ICAM-1 gene expression, human fibroblasts (HFF) as well as endothelial cells (HUVEC) were infected with recombinant IE2p86- and pp71-expressing baculoviruses, respectively. In FACS analysis, a synergistic induction of ICAM-1 was detectable when cells were co-infected with the two recombinant baculoviruses. These findings clearly demonstrate that IE2p86 and pp71 are crucial regulatory factors for HCMV-induced ICAM-1 upregulation. | 12533701
 |