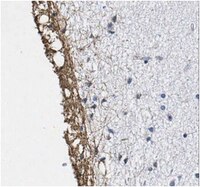
Dual immunofluorescence study of citrullinated proteins in Parkinson diseased substantia nigra.
Nicholas, Anthony P
Neurosci. Lett., 495: 26-9 (2011)
2010
Kivonat megmutatása
Deimination is a post-translational modification of proteins in which selected arginine amino acids are enzymatically converted to citrullines. Using dual-color immunofluorescence and an established monoclonal antibody (F95) against peptidyl-citrulline moieties, the present study is the first to compare immunohistochemical staining patterns for deiminated proteins in human substantia nigra (SN) from patients with Parkinson disease (PD) versus similar control specimens supplied by the Harvard Brain Bank. In control SN sections, many tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-immunoreactive dopamine neurons were seen surrounded either by small fibers immunoreactive for deiminated proteins, or large reactive astrocytes, co-localized with glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). However, in SN specimens from PD patients, immunoreactivity for deiminated proteins was also demonstrated within the cytoplasm of many surviving dopamine neurons that were also immunoreactive for TH, but this staining was not specifically restricted to Lewy bodies. Although the identity of neuronal deiminated proteins in these SN dopamine neurons is unknown, the present study provides evidence that the anatomical expression of these proteins in PD is altered and thus suggests that deimination may be involved in the pathophysiology of this disease. | 21414385
 |
Expression of citrullinated proteins in murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
Nicholas, Anthony P, et al.
J. Comp. Neurol., 486: 254-66 (2005)
2004
Kivonat megmutatása
In this study, we demonstrate for the first time the immunohistochemical expression of citrullinated proteins in the central nervous system (CNS) of mice with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). By using an established monoclonal antibody (F95) against natural and synthetic citrullinated proteins (Nicholas and Whitaker [2002] Glia 37:328-336), numerous, small, previously unrecognized "patches" of citrullinated proteins were discovered throughout EAE brains, whereas EAE spinal cords showed similar but much larger lesions. On dual color immunofluorescence, these lesions were found to contain citrullinated myelin basic protein (MBP) and were surrounded by astrocytes immunoreactive for both glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and F95. These lesions became evident about the time when EAE mice became symptomatic and increased in size and number with increasing disease severity. In some sections of spinal cord but not brains of severely debilitated EAE mice, a widespread gliotic response was seen, with astrocytes containing citrullinated GFAP spread throughout the gray and white matter. Western blot analysis of acidic proteins from the brains and spinal cords of EAE mice had higher levels of multiple citrullinated GFAP isoforms compared with controls, with more F95-positive bands in the EAE brains vs. spinal cords. These results raise the possibility that citrullination of both GFAP and MBP may contribute to the pathophysiology of EAE and that the brains of EAE mice may contain more pathology than previously realized. | 15844173
 |
Preparation of a monoclonal antibody to citrullinated epitopes: its characterization and some applications to immunohistochemistry in human brain.
Nicholas, Anthony P and Whitaker, John N
Glia, 37: 328-36 (2002)
2002
Kivonat megmutatása
Using hybridoma technology, an IgM monoclonal antibody (mAb), designated as F95, was developed against a deca-citrullinated peptide (DCP) consisting of 10 citrulline residues and a carboxyl Gly-Gly-Cys through which DCP was covalently linked to an activated carrier protein, keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH). Clones were selected on the basis of not reacting with human unmodified and noncitrullinated myelin basic protein (MBP), MBP-C1, but reacting well with human citrullinated MBP (MBP-C8). When tested by ELISA, this mAb demonstrated minimal reactivity with human MBP-C1, varying reactivity with the C2-C5 isomers of human MBP, moderate binding with guinea pig MBP-C8, and strong reactivity with human MBP-C8. By ELISA, mAb F95 was directed predominantly against citrulline, not MBP, as revealed by its binding to DCP linked with activated KLH, bovine serum albumin (BSA), or ovalbumin (OA), but not with KLH, BSA, or OA alone. Immunohistochemistry of normal human brain demonstrated that F95 stained central nervous system myelin and a subset of astrocytes. Given the citrulline-directed features of mAb F95, this immunohistochemical pattern suggests that certain astroglial filaments expressing glial fibrillary acidic protein also contain citrulline-bearing components. These potentially implicate citrullinated proteins, notably in astroglial filaments, in a variety of normal and pathological neurobiological processes. | 11870872
 |