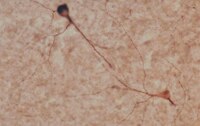
Prolonged acetylsalicylic-acid-supplementation-induced gastritis affects the chemical coding of the stomach innervating vagal efferent neurons in the porcine dorsal motor vagal nucleus (DMX).
Gańko, M; Całka, J
Journal of molecular neuroscience : MN
54
188-98
2014
Kivonat megmutatása
The main goal of our research was to study the possible alterations of the chemical coding of the dorsal motor vagal nucleus (DMX) neurons projecting to the porcine stomach prepyloric region following prolonged acetylsalicylic acid supplementation. Fast Blue (FB) was injected into the studied area of the stomach. Since the seventh day following the FB injection, acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) was given orally to the experimental gilts. All animals were euthanized on the 28th day after FB injection. Medulla oblongata sections were then processed for double-labeling immunofluorescence for choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP), vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), nitric oxide synthase (NOS), galanin (GAL), substance P (SP), leu enkephalin (LENK), and cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART). In the control DMX, only PACAP was observed in 30.08 ± 1.97 % of the FB-positive neurons, while VIP, NOS, GAL, SP, LENK, and CART were found exclusively in neuronal processes running between FB-labeled perikarya. In the ASA DMX, PACAP was revealed in 49.53 ± 5.73 % of traced vagal perikarya. Moreover, we found de novo expression of VIP in 40.32 ± 7.84 %, NOS in 25.02 ± 6.08 %, and GAL in 3.37 ± 0.85 % of the FB-labeled neurons. Our results suggest that neuronal PACAP, VIP, NOS, and GAL are mediators of neural response to aspirin-induced stomach inflammatory state. | Immunohistochemistry | Porcine | 24643520
 |
Characterization of neuronal populations in the human trigeminal ganglion and their association with latent herpes simplex virus-1 infection.
Flowerdew, SE; Wick, D; Himmelein, S; Horn, AK; Sinicina, I; Strupp, M; Brandt, T; Theil, D; Hüfner, K
PloS one
8
e83603
2013
Kivonat megmutatása
Following primary infection Herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) establishes lifelong latency in the neurons of human sensory ganglia. Upon reactivation HSV-1 can cause neurological diseases such as facial palsy, vestibular neuritis or encephalitis. Certain populations of sensory neurons have been shown to be more susceptible to latent infection in the animal model, but this has not been addressed in human tissue. In the present study, trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons expressing six neuronal marker proteins were characterized, based on staining with antibodies against the GDNF family ligand receptor Ret, the high-affinity nerve growth factor receptor TrkA, neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), the antibody RT97 against 200 kDa neurofilament, calcitonin gene-related peptide and peripherin. The frequencies of marker-positive neurons and their average neuronal sizes were assessed, with TrkA-positive (61.82%) neurons being the most abundant, and Ret-positive (26.93%) the least prevalent. Neurons positive with the antibody RT97 (1253 µm(2)) were the largest, and those stained against peripherin (884 µm(2)) were the smallest. Dual immunofluorescence revealed at least a 4.5% overlap for every tested marker combination, with overlap for the combinations TrkA/Ret, TrkA/RT97 and Ret/nNOS lower, and the overlap between Ret/CGRP being higher than would be expected by chance. With respect to latent HSV-1 infection, latency associated transcripts (LAT) were detected using in situ hybridization (ISH) in neurons expressing each of the marker proteins. In contrast to the mouse model, co-localization with neuronal markers Ret or CGRP mirrored the magnitude of these neuron populations, whereas for the other four neuronal markers fewer marker-positive cells were also LAT-ISH+. Ret and CGRP are both known to label neurons related to pain signaling. | | | 24367603
 |
Morphological, immunocytochemical, and functional characterization of esophageal enteric neurons in primary culture.
Dong, H; Jiang, Y; Srinivasan, S; Mittal, RK
American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology
305
G129-38
2013
Kivonat megmutatása
The enteric nervous system of the esophagus plays an important role in its sensory and motor functions. Although the esophagus contains enteric neurons, they have never been isolated and characterized in primary culture. We isolated and cultured enteric neurons of the rat esophagus and determined their morphological appearance, chemical coding for neurotransmitters, and functional characteristics. After primary culture for 2 wk, dendrites and axons appeared in the enteric neurons, which usually have one axon and several dendrites. Although the size of neuronal bodies varied from Dogiel type I to type II, their average size was 39 ± 1.8 μm in length and 23 ± 1.4 μm in width. Immmunocytochemical studies revealed that over 95% of these cells were positively stained for two general neuronal markers, PGP 9.5 or Milli-Mark Fluoro. Chemical coding showed that the neurons were positively stained for choline acetyltransferease (53 ± 6%) or nNOS (66 ± 13%). In functional studies, membrane depolarization and stimulation of several G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) induced Ca²⁺ signaling in the esophageal enteric neurons. The GPCR stimulation was found to induce both intracellular Ca²⁺ release and extracellular Ca²⁺ entry. The functional expressions of Ca²⁺ channels (voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels and store-operated channels) and Ca²⁺ pump (sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca²⁺-ATPase) were also demonstrated on these neurons. We have grown, for the first time, esophageal enteric neurons in primary culture, and these contain excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters. The functional integrity of GPCRs, Ca²⁺ channels, and Ca²⁺ pump in these neurons makes them a useful cell model for further studies. | | | 23660501
 |
Effects of nitric oxide synthase-3 overexpression on post-translational modifications and cell survival in HepG2 cells.
P Aguilar-Melero,G Ferrín,J Muntané
Journal of proteomics
75
2011
Kivonat megmutatása
Hepatocarcinoma is the fifth most common neoplasm and the third cause of cancer-related death. The development of genetic- and/or molecular-based therapies is urgently required. The administration of high doses of nitric oxide (NO) promotes cell death in hepatocytes. NO contributes to cell signaling by inducing oxidative/nitrosative-dependent post-translational modifications. The aim of the present study was to investigate protein modifications and its relation with alteration of cell proliferation and death in hepatoma cells. Increased intracellular NO production was achieved by stable nitric oxide synthase-3 (NOS-3) overexpression in HepG2 cells. We assessed the pattern of nitration, nitrosylation and carbonylation of proteins by proteomic analysis. The results showed that NOS-3 cell overexpression increased oxidative stress, which affected proteins mainly involved in cell protein folding. Carbonylation also altered metabolism, as well as immune and antioxidant responses. The interaction of nitrosative and oxidative stress generated tyrosine nitration, which affected the tumor marker Serpin B3, ATP synthesis and cytoskeleton. All these effects were associated with a decrease in chaperone activity, a reduction in cell proliferation and an increased cell death. Our study showed that alteration of nitration, nitrosylation and carbonylation pattern of proteins by NO-dependent oxidative/nitrosative stress was related to a reduction of cell survival in a hepatoma cell line. | | | 21968428
 |
Reticular groove of the domestic ruminants: histochemical and immunocytochemical study.
G Scala,L Maruccio
Anatomia, histologia, embryologia
41
2011
Kivonat megmutatása
The reticular groove mucosa of adult cattle, buffalo and sheep was investigated by histochemical and immunocytochemical techniques. Intense NADPH-d staining was observed in the folds of the epithelium mucosa and at the bottom of the reticular groove in all domestic ruminants studied. The NADPH-d staining showed that the innervations of the tunica muscularis of the reticular groove lip were composed of nerve corpuscles, nerve fibres and nerve cells of the mucosa epithelium. SEM analysis showed an intense nitric oxide synthase (NOS) I immunoreactivity in deep and medium cellular layers. It is interesting to note that the same morphologies were observed in samples of the mucosa epithelium, and of the tunica muscularis processed by NADPH-d and in those processed by immunogold techniques. This study has demonstrated that nitric oxide (NO) is involved in the rumination activity and that it plays a double role in this activity in the reticular groove of all domestic ruminants studied: (1) NO plays a role similar to the one it has in the mucosa epithelium of all the other compartments of the ruminant forestomach, (2) The lip sections of the reticular groove has shown abundant innervations that may indirectly coordinate and control the forestomach motility through the direct activation of the nitrergic (nitroxidergic) nerve cells and nerve fibres. | | | 22506730
 |
Role of neural NO synthase (nNOS) uncoupling in the dysfunctional nitrergic vasorelaxation of penile arteries from insulin-resistant obese Zucker rats.
Sánchez, A; Contreras, C; Martínez, MP; Climent, B; Benedito, S; García-Sacristán, A; Hernández, M; Prieto, D
PloS one
7
e36027
2011
Kivonat megmutatása
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is considered as an early sign of vascular disease due to its high prevalence in patients with cardiovascular risk factors. Endothelial and neural dysfunction involving nitric oxide (NO) are usually implicated in the pathophysiology of the diabetic ED, but the underlying mechanisms are unclear. The present study assessed the role of oxidative stress in the dysfunctional neural vasodilator responses of penile arteries in the obese Zucker rat (OZR), an experimental model of metabolic syndrome/prediabetes.Electrical field stimulation (EFS) under non-adrenergic non-cholinergic (NANC) conditions evoked relaxations that were significantly reduced in penile arteries of OZR compared with those of lean Zucker rats (LZR). Blockade of NO synthase (NOS) inhibited neural relaxations in both LZR and OZR, while saturating concentrations of the NOS substrate L-arginine reversed the inhibition and restored relaxations in OZR to levels in arteries from LZR. nNOS expression was unchanged in arteries from OZR compared to LZR and nNOS selective inhibition decreased the EFS relaxations in LZR but not in OZR, while endothelium removal did not alter these responses in either strain. Superoxide anion production and nitro-tyrosine immunostaining were elevated in the erectile tissue from OZR. Treatment with the NADPH oxidase inhibitor apocynin or acute incubation with the NOS cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) restored neural relaxations in OZR to levels in control arteries, while inhibition of the enzyme of BH4 synthesis GTP-cyclohydrolase (GCH) reduced neural relaxations in arteries from LZR but not OZR. The NO donor SNAP induced decreases in intracellular calcium that were impaired in arteries from OZR compared to controls.The present study demonstrates nitrergic dysfunction and impaired neural NO signalling due to oxidative stress and nNOS uncoupling in penile arteries under conditions of insulin resistance. This dysfunction likely contributes to the metabolic syndrome-associated ED, along with the endothelial dysfunction also involving altered NO signalling. | | | 22540017
 |
Mice overexpressing wild-type human alpha-synuclein display alterations in colonic myenteric ganglia and defecation.
Wang, L; Magen, I; Yuan, PQ; Subramaniam, SR; Richter, F; Chesselet, MF; Taché, Y
Neurogastroenterology and motility : the official journal of the European Gastrointestinal Motility Society
24
e425-36
2011
Kivonat megmutatása
Prevalent non-motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease (PD) include gastrointestinal motor impairments and advanced stage PD displays pathological aggregates of α-synuclein in colonic enteric neurons. We previously showed that 12 months old mice overexpressing human wild type (WT) α-synuclein under the Thy1 promoter (Thy1-aSyn) displayed colonic motor dysfunction. We investigated functional gut alterations at earlier ages and histological correlates.Defecation, gastric emptying (GE), and immunostaining for α-synuclein, peripheral choline acetyltransferase (pChAT), tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) in distal colon myenteric plexuses were assessed in male Thy1-aSyn compared to littermate WT mice.Thy1-aSyn mice aged 2.5-3 or 7-8 months old had 81% and 55% reduction in fecal pellet output, respectively, in the first 15 min of exposure to a novel environment. The reduction remained significant in the older group for 2-h, and subsequent refeeding resulted also in a 60% and 69% reduction of defecation in the first hour, respectively. Thy1-aSyn mice (8-10 months) displayed increased α-synuclein in the myenteric plexuses with abundant varicose terminals surrounding pChAT-immunoreactive (ir) neurons, and only a few, nNOS-ir neurons. There were no conspicuous changes in pChAT- and nNOS-ir neurons, or TH- and VIP-ir nerve fibers. Thy1-aSyn mice aged 4-18 months had normal GE.The occurrence of over-production of pre-synaptic α-synuclein in colonic myenteric ganglia several months before the loss of striatal dopamine may provide an anatomical basis for interference with cholinergic neuronal activation, causing an early impairment in defecation to stimuli. | | | 22779732
 |
A blueprint for the spatiotemporal origins of mouse hippocampal interneuron diversity.
Tricoire, L; Pelkey, KA; Erkkila, BE; Jeffries, BW; Yuan, X; McBain, CJ
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
31
10948-70
2010
Kivonat megmutatása
Although vastly outnumbered, inhibitory interneurons critically pace and synchronize excitatory principal cell populations to coordinate cortical information processing. Precision in this control relies upon a remarkable diversity of interneurons primarily determined during embryogenesis by genetic restriction of neuronal potential at the progenitor stage. Like their neocortical counterparts, hippocampal interneurons arise from medial and caudal ganglionic eminence (MGE and CGE) precursors. However, while studies of the early specification of neocortical interneurons are rapidly advancing, similar lineage analyses of hippocampal interneurons have lagged. A "hippocampocentric" investigation is necessary as several hippocampal interneuron subtypes remain poorly represented in the neocortical literature. Thus, we investigated the spatiotemporal origins of hippocampal interneurons using transgenic mice that specifically report MGE- and CGE-derived interneurons either constitutively or inducibly. We found that hippocampal interneurons are produced in two neurogenic waves between E9-E12 and E12-E16 from MGE and CGE, respectively, and invade the hippocampus by E14. In the mature hippocampus, CGE-derived interneurons primarily localize to superficial layers in strata lacunosum moleculare and deep radiatum, while MGE-derived interneurons readily populate all layers with preference for strata pyramidale and oriens. Combined molecular, anatomical, and electrophysiological interrogation of MGE/CGE-derived interneurons revealed that MGE produces parvalbumin-, somatostatin-, and nitric oxide synthase-expressing interneurons including fast-spiking basket, bistratified, axo-axonic, oriens-lacunosum moleculare, neurogliaform, and ivy cells. In contrast, CGE-derived interneurons contain cholecystokinin, calretinin, vasoactive intestinal peptide, and reelin including non-fast-spiking basket, Schaffer collateral-associated, mossy fiber-associated, trilaminar, and additional neurogliaform cells. Our findings provide a basic blueprint of the developmental origins of hippocampal interneuron diversity. | | | 21795545
 |
Tetrodotoxin- and resiniferatoxin-induced changes in paracervical ganglion ChAT- and nNOS-IR neurons supplying the urinary bladder in female pigs.
Piotr Józef Burli?ski,S?awomir Gonkowski,Jaros?aw Ca?ka
Acta veterinaria Hungarica
59
2010
Kivonat megmutatása
The aim of the present study was to establish the effect of intravesical administration of resiniferatoxin (RTX) and tetrodotoxin (TTX) on the chemical coding of paracervical ganglion (PCG) neurons supplying the urinary bladder in the pig. In order to identify the PCG neurons innervating the bladder, retrograde tracer Fast Blue was injected into the bladder wall prior to intravesical RTX or TTX administration. Consequent application of immunocytochemical methods revealed that in the control group 76.82% of Fast Blue positive PCG neurons contain nitric oxide synthetase (nNOS), and 66.92% contain acetylcholine transferase (ChAT). Intravesical infusion of RTX resulted in a reduction of the nNOS-IR neurons to 57.74% and ChAT-IR to 57.05%. Alternative administration of TTX induced an increase of nNOS-IR neurons up to 79.29% and a reduction of the ChAT-IR population down to 3.73% of the Fast Blue positive PCG cells. Our data show that both neurotoxins affect the chemical coding of PCG cells supplying the porcine urinary bladder, but the effects of their action are different. Moreover, these results shed light on the possible involvement of NO-ergic and cholinergic neurons in the mechanisms of therapeutic action exerted by RTX and TTX in curing the overactive bladder disorder. | | | 22079707
 |
Immunohistochemical characterization of superior cervical ganglion neurons supplying porcine parotid salivary gland.
Joanna Wojtkiewicz,Judyta K Juranek,Ireneusz Kowalski,Marek Bladowski,Jaros?aw Ca?ka,Mariusz Majewski
Neuroscience letters
500
2010
Kivonat megmutatása
The main goal of our study was to investigate the chemical coding of the superior cervical ganglion (SCG) sympathetic neurons supplying the porcine parotid gland. Additionally, the chemical nature of the vicinal nerve fibers surrounding the parotid SCG perikarya was investigated. Fast blue (FB) retrograde tracing of the parotid gland and immunofluorescent labelling of SCG neurons were studied in juvenile female pigs. Microscopic analysis revealed that only ipsilateral SCG neurons were retrogradely labelled. The labelled neurons formed a discrete cluster in the middle and caudal region of the ganglion. Immunofluorescent labelling revealed that virtually all of the FB-positive parotid gland neurons were immunoreactive to tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), confirming their sympathetic nature. In addition to TH, the majority of the FB-positive neurons were found to be immunoreactive to calbindin (CB) and to a lesser extent for neuropeptide Y (NPY), leu-enkephalin (LENK) and galanin (GAL). In the close proximity of the FB-traced perikarya, a large number of immunoreactive (IR) vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP-IR), pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP-IR), nitric oxide synthase (NOS-IR) processes were identified. Moreover, calcitonin gene related peptide-immunoreactive (CGRP-IR), substance P-immunoreactive (SP-IR), vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT-IR), calretinin (CRT-IR), GAL-IR, LENK-IR and CB-IR protrusions were observed. The results of the present study provide a detailed characteristic of the location and neurochemical coding of sympathetic SCG neurons innervating the parotid salivary gland of the pig and lay ground for more advanced, clinical studies on salivary gland innervations. | | | 21683765
 |