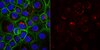
Functional Characterization of ABCB4 Mutations Found in Low Phospholipid-Associated Cholelithiasis (LPAC).
Kim, TH; Park, HJ; Choi, JH
The Korean journal of physiology & pharmacology : official journal of the Korean Physiological Society and the Korean Society of Pharmacology
17
525-30
2013
Kivonat megmutatása
Multidrug resistance 3 (MDR3) is expressed on the canalicular membrane of the hepatocytes and plays an important role in protecting the liver from bile acids. Altered ABCB4 gene expression can lead to a rare hepatic disease, low phospholipid-associated cholelithiasis (LPAC). In this study, we characterized 3 ABCB4 mutations in LPAC patients using various in vitro assay systems. We first measured the ability of each mutant to transport paclitaxel and then the mechanisms by which these mutations might change MDR3 transport activity were determined using immunoblotting, cell surface protein biotinylation, and immunofluorescence. Through a membrane vesicular transport assay, we observed that the uptake of paclitaxel was significantly reduced in membrane vesicles expressing 2 ABCB4 mutations, F165I and S320F. Both mutants showed significantly decreased total and cell surface MDR3 expression. These data suggest two missense mutations of ABCB4 may alter function of MDR3 and ultimately can be determined as LPAC-causing mutations. | Western Blotting | 24381502
 |
Significance of aquaporins and sodium potassium ATPase subunits for expansion of the early equine conceptus.
Budik, S; Walter, I; Tschulenk, W; Helmreich, M; Deichsel, K; Pittner, F; Aurich, C
Reproduction (Cambridge, England)
135
497-508
2008
Kivonat megmutatása
Expansion of the equine conceptus can be divided into blastocoel and yolk sac phases. The endodermal layer transforming the blastocoel into the yolk sac is completed around day 8 of pregnancy. From that time, the size of the spherical conceptus increases tremendously due mainly to the accumulation of fluid rather than cell multiplication. In this study, we have investigated the abundance and localisation of Na(+)/K(+)-ATPases and aquaporins (AQP) in the equine conceptus on days 8, 10, 12, 14 and 16 by multiplex reverse transcriptase PCR, Western blot and immunohistochemistry. During conceptus expansion, the ectoderm of the yolk sac exhibited basolateral abundance of alpha1ATPase, apical localisation of AQP5, and membrane and cytoplasmic expression of AQP3. With increasing conceptus size its cells showed an extensive enlargement of the apical membrane surface by microvilli. From day 14 onwards, the yolk sac endoderm forms arc-like structures with attaching sites to the ectodermal layer and shows intensive staining for alpha1ATPase, AQP5 and AQP3 in the membrane as well as in the cytoplasm. In the yolk sac ectoderm, the arrangement of these proteins is comparable with the collecting ducts of kidney with AQP2 being replaced by the closely related AQP5. The detection of phosphorylation sites for protein kinase A suggests a similar AQP5 traffic and regulation as known for AQP2 in the collecting ducts of the kidney. The arrangement of these proteins in equine embryos indicates at least partially the mechanism of conceptus expansion. | | 18367510
 |
R7-binding protein targets the G protein beta 5/R7-regulator of G protein signaling complex to lipid rafts in neuronal cells and brain.
Nini, L; Waheed, AA; Panicker, LM; Czapiga, M; Zhang, JH; Simonds, WF
BMC biochemistry
8
18
2007
Kivonat megmutatása
Heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins), composed of G alpha, G beta, and G gamma subunits, are positioned at the inner face of the plasma membrane and relay signals from activated G protein-coupled cell surface receptors to various signaling pathways. G beta 5 is the most structurally divergent G beta isoform and forms tight heterodimers with regulator of G protein signalling (RGS) proteins of the R7 subfamily (R7-RGS). The subcellular localization of G beta 5/R7-RGS protein complexes is regulated by the palmitoylation status of the associated R7-binding protein (R7BP), a recently discovered SNARE-like protein. We investigate here whether R7BP controls the targeting of G beta 5/R7-RGS complexes to lipid rafts, cholesterol-rich membrane microdomains where conventional heterotrimeric G proteins and some effector proteins are concentrated in neurons and brain.We show that endogenous G beta 5/R7-RGS/R7BP protein complexes are present in native neuron-like PC12 cells and that a fraction is targeted to low-density, detergent-resistant membrane lipid rafts. The buoyant density of endogenous raft-associated G beta 5/R7-RGS protein complexes in PC12 cells was similar to that of lipid rafts containing the palmitoylated marker proteins PSD-95 and LAT, but distinct from that of the membrane microdomain where flotillin was localized. Overexpression of wild-type R7BP, but not its palmitoylation-deficient mutant, greatly enriched the fraction of endogenous G beta 5/R7-RGS protein complexes in the lipid rafts. In HEK-293 cells the palmitoylation status of R7BP also regulated the lipid raft targeting of co-expressed G beta 5/R7-RGS/R7BP proteins. A fraction of endogenous G beta 5/R7-RGS/R7BP complexes was also present in lipid rafts in mouse brain.A fraction of G beta 5/R7-RGS/R7BP protein complexes is targeted to low-density, detergent-resistant membrane lipid rafts in PC12 cells and brain. In cultured cells, the palmitoylation status of R7BP regulated the lipid raft targeting of endogenous or co-expressed G beta 5/R7-RGS proteins. Taken together with recent evidence that the kinetic effects of the G beta 5 complex on GPCR signaling are greatly enhanced by R7BP palmitoylation through a membrane-anchoring mechanism, our data suggest the targeting of the G beta 5/R7-RGS/R7BP complex to lipid rafts in neurons and brain, where G proteins and their effectors are concentrated, may be central to the G protein regulatory function of the complex. Teljes cikk | Western Blotting | 17880698
 |
Intrarenal octreotide treatment prevents sodium retention in liver cirrhotic rats: evidence for direct effects within the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop.
Jonassen, TE; Christensen, S; Marcussen, N; Petersen, JS
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology
291
F537-45
2005
Kivonat megmutatása
We have previously shown that systemic treatment with the somatostatin analog octreotide has marked beneficial effects on renal function in rats with liver cirrhosis induced by common bile duct ligation (CBL; Jonassen TEN, Christensen S, Sørensen AM, Marcussen N, Flyvbjerg A, Andreasen F, and Petersen JS. Hepatology 29: 1387-1395, 1999). In the present study, we tested the hypothesis that octreotide has a direct effect on renal tubular function. Rats (CBL or Sham-CBL) were intrarenally treated with low-dose octreotide in a long-acting release formulation, which had no systemic actions (100 microg/kg body wt as a single dose). Rats receiving low-dose octreotide (sc) were used as controls. The rats were chronically instrumented, and renal function was examined 4 wk after CBL or Sham-CBL. Intrarenal octreotide administration (IROA) prevented sodium retention in CBL rats without changes in renal plasma flow, glomerular filtration rate, or circulating levels of aldosterone and vasopressin. Renal clearance studies revealed that IROA normalized the increased natriuretic efficacy of furosemide found in CBL rats. Furthermore, IROA protected against the development of hypertrophy of the inner stripe of the outer medulla and thereby the increased the volume of thick ascending limb of Henle's loop (TAL) epithelium found in CBL rats. Finally, Western blot analyses of outer medullary homogenates showed increased abundance of the furosemide-sensitive Na-K-2Cl (NKCC2) cotransporter. IROA did not affect the abundance of NCKK2 within the outer medulla. Together with the histological findings, these results indicate that IROA reduces the total number of NKCC2 within the outer medulla. In conclusion, the results indicate a direct intrarenal effect of octreotide on TAL function and morphology in cirrhotic rats. | | 16418303
 |
Na+-K+-ATPase properties in rat heart and skeletal muscle 3 mo after coronary artery ligation.
Barr, DJ; Green, HJ; Lounsbury, DS; Rush, JW; Ouyang, J
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985)
99
656-64
2004
Kivonat megmutatása
This study was designed to determine whether chronic heart failure (CHF) results in changes in Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase properties in heart and skeletal muscles of different fiber-type composition. Adult rats were randomly assigned to a control (Con; n = 8) or CHF (n = 8) group. CHF was induced by ligation of the left main coronary artery. Examination of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase activity (means +/- SE) 12 wk after the ligation measured, using the 3-O-methylfluorescein phosphatase assay (3-O-MFPase), indicated higher (P less than 0.05) levels in soleus (Sol) (250 +/- 13 vs. 179 +/- 18 nmol.mg protein(-1).h(-1)) and lower (P less than 0.05) levels in diaphragm (Dia) (200 +/- 12 vs. 272 +/- 27 nmol.mg protein(-1).h(-1)) and left ventricle (LV) (760 +/- 62 vs. 992 +/- 16 nmol.mg protein(-1).h(-1)) in CHF compared with Con, respectively. Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase protein content, measured by the [(3)H]ouabain binding technique, was higher (P less than 0.05) in white gastrocnemius (WG) (166 +/- 12 vs. 135 +/- 7.6 pmol/g wet wt) and lower (P less than 0.05) in Sol (193 +/- 20 vs. 260 +/- 8.6 pmol/g wet wt) and LV (159 +/- 10 vs. 221 +/- 10 pmol/g wet wt) in CHF compared with Con, respectively. Isoform content in CHF, measured by Western blot techniques, showed both increases (WG; P less than 0.05) and decreases (Sol; P less than 0.05) in alpha(1). For alpha(2), only increases [red gastrocnemius (RG), Sol, and Dia; P less than 0.05] occurred. The beta(2)-isoform was decreased (LV, Sol, RG, and WG; P less than 0.05) in CHF, whereas the beta(1) was both increased (WG and Dia; P less than 0.05) and decreased (Sol and LV; P less than 0.05). For beta(3), decreases (P less than 0.05) in RG were observed in CHF, whereas no differences were found in Sol and WG between CHF and Con. It is concluded that CHF results in alterations in Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase that are muscle specific and property specific. Although decreases in Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase content would appear to explain the lower 3-O-MFPase in the LV, such does not appear to be the case in skeletal muscles where a dissociation between these properties was observed. | | 15817721
 |
Magnesium depletion enhances cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity.
H Lajer, M Kristensen, H H Hansen, S Nielsen, J Frøkiaer, L F Ostergaard, S Christensen, G Daugaard, T E N Jonassen
Cancer chemotherapy and pharmacology
56
535-42
2004
Kivonat megmutatása
PURPOSE: Nephrotoxicity and magnesium (Mg)-depletion are well-known side effects to cisplatin (CP) treatment. The purpose of this present study was to investigate the role of Mg on CP induced changes in renal function. CP induced renal dysfunction was achieved by treatment with CP or vehicle (2.5 mg/kg) once weekly for 3 weeks. Since the CP-induced renal damage, including tubular reabsorption defects, is most prominent within the outer medulla (OM), changes in the expression pattern of OM aquaporins and sodium transporters including the Na,K-ATPase (alpha-subunit), type III Na,H-exchanger (NHE3), aquaporin 1 (AQP1) and 2 (AQP2) and the Na,K,2Cl-cotransporter (NKCC2) were investigated by semi-quantitative Western blotting. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Rats had access to either a diet with standard Mg or to a Mg-depleted diet. Cisplatin was administered to female Wistar rats once a week for 3 weeks according to four regimens: (1) Cisplatin 2.5 mg/kg body weight i.p., to rats on a diet with standard Mg, (2) Cisplatin 2.5 mg/kg body weight i.p., to rats on a diet with low Mg, (3) Isotonic NaCl 2.5 ml/kg body weight i.p., to rats on a diet with standard Mg, (4) Isotonic NaCl 2.5 ml/kg body weight i.p., to rats on a diet with low Mg. RESULTS: CP had no effect on plasma creatinine or urea in rats with standard Mg intake, but the expression of all five transporters was significantly reduced when compared to vehicle treated rats on standard Mg-intake. Vehicle treated rats on low Mg-intake had a significant reduction in the expression of Na,K-ATPase, NHE3 and NKCC2, but unchanged expression levels of AQP1 or AQP2 when compared to standard treated controls. Forty percent of the CP-treated rats on low Mg-intake died during the experiment and the remaining animals had marked increased plasma creatinine and urea. Furthermore, the Western blot analysis revealed an almost complete disappearance of all four transporters, suggesting a dramatic synergistic effect of CP and Mg-depletion on renal function including the expression pattern of outer medullary sodium transporters and aquaporins. CONCLUSIONS: This study indicates a substantial additive effect of Mg-depletion on cisplatin induced renal toxicity as evidenced by significant changes in plasma creatinine and urea, renal failure induced mortality and loss of renal transporters. This should give cause for concern since the nephrotoxicity observed during cisplatin treatment might be substantiated by the known Mg-loss associated with cisplatin treatment especially in patients suffering from intense gastro-intestinal side effects. | | 15947931
 |
Effects of renal denervation on tubular sodium handling in rats with CBL-induced liver cirrhosis.
Thomas E N Jonassen, Lone Brønd, Malene Torp, Martin Graebe, Søren Nielsen, Ole Skøtt, Niels Marcussen, Sten Christensen
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology
284
F555-63
2003
Kivonat megmutatása
This study was designed to examine the effect of bilateral renal denervation (DNX) on thick ascending limb of Henle's loop (TAL) function in rats with liver cirrhosis induced by common bile duct ligation (CBL). The CBL rats had, as previously shown, sodium retention associated with hypertrophy of the inner stripe of the outer medulla (ISOM) and increased natriuretic effect of furosemide in vivo, and semiquantitative immunoblotting showed increased expression of the furosemide-sensitive Na-K-2Cl cotransporter type 2 (NKCC2) in ISOM from CBL rats. DNX significantly attenuated the sodium retention in the CBL rats, which was associated with normalization of the natriuretic effect of furosemide, as well as a significant reduction in the expression of NKCC2 in the ISOM. However, the marked hypertrophy of the ISOM found in CBL rats was not reversed by DNX. Together, these data indicate that increased renal sympathetic nerve activity known to be present in CBL rats plays a significant role in the formation of sodium retention by stimulating sodium reabsorption in the TAL via increased renal abundance of NKCC2. | | 12441306
 |
Chloride, not sodium, stimulates expression of the {gamma} subunit of Na/K-ATPase and activates JNK in response to hypertonicity in mouse IMCD3 cells
Capasso, J. M., et al
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 100:6428-6433 (2003)
2003
| Immunoblotting (Western) | 12746499
 |
The mechanism by which interleukin-1 beta reduces net fluid absorption from the rat colon.
Sawsan Ibrahim Kreydiyyeh, Rana Al-Sadi, Sawsan Ibrahim Kreydiyyeh, Rana Al-Sadi
European cytokine network
13
358-63
2002
Kivonat megmutatása
IL-1beta is suspected to be involved in the diarrhea that always accompanies inflammatory bowel disease. This work was aimed at studying the in vivo effect of IL-1beta on the net absorption of fluid, Na(+) and Cl(-) from the rat colon, and at delineating its mechanism of action. Rats were injected i.p. with IL-1beta (1 mug/kg body weight) and the colon was perfused, four hours later, with Krebs-Ringer buffer. Net fluid absorption was calculated as the difference between the total volume of the buffer infused and collected per cm(2) of perfused intestine. Chloride in both buffers was determined by titration according to Mohr's method and net Cl- absorption was calculated in the same way. IL-1beta reduced the net absorption of water and chloride. The cytokine also reduced the percentage recovery of the Na(+)-K(+) ATPase activity in crude homogenates of membranes from surface and crypt colonic cells as revealed by the determination of inorganic phosphate released. In addition IL-1beta decreased the protein expression of the Na(+)-K(+) pump and increased that of the NaKCl(2) symporter. It is concluded that IL-1beta has a dual effect: it inhibits the Na(+)-K(+) pump and consequently NaCl absorption, and up-regulates the NaKCl(2) transporter and increases Cl(-) secretion. The ultimate effect of the two processes is a net decrease in Na(+)+ and Cl(-) absorption and an increase in water retention in the colon leading to the observed diarrhea in inflammatory bowel disease. | | 12231480
 |
The localization of the brain-specific inorganic phosphate transporter suggests a specific presynaptic role in glutamatergic transmission
Bellocchio, E. E., et al
J Neurosci, 18:8648-59 (1998)
1998
| Immunoblotting (Western) | 9786972
 |