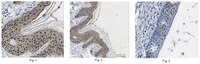
Galectin-7 acts as an adhesion molecule during implantation and increased expression is associated with miscarriage.
Menkhorst, EM; Gamage, T; Cuman, C; Kaitu'u-Lino, TJ; Tong, S; Dimitriadis, E
Placenta
35
195-201
2014
Kivonat megmutatása
Galectins are expressed at the fetal-maternal interface and have multiple roles including during blastocyst implantation. The expression of galectin-7 however has not been investigated in the uterus. We aimed to localise galectin-7 to the endometrium of women with normal fertility and with a history of miscarriage and prospectively determine whether serum levels are altered in women who subsequently miscarry. We also investigated the role of galectin-7 on trophoblast-endometrial epithelial cell adhesion.Immunohistochemistry localised galectin-7 to endometrium throughout the menstrual cycle in women (normal fertility or with history of miscarriage) and in first trimester implantation sites. Galectin-7 serum levels were determined by ELISA. We used both endometrial epithelial-trophoblast cell lines and primary cells for cell-cell adhesion experiments.Galectin-7 immunolocalized to endometrial luminal and glandular epithelium in normally fertile women and was upregulated in epithelium and stroma of women with a history of miscarriage. Similarly, galectin-7 serum levels were elevated at 6 weeks gestation in women who subsequently miscarried compared to gestation matched controls. Exogenous galectin-7 reduced endometrial epithelial-trophoblast adhesion in cell-line and primary cell assays. However, when endometrial epithelial cells were isolated from women with endometrial disorders, galectin-7 increased epithelial-trophoblast adhesion.Galectin-7 is produced by endometrial epithelium and is abnormally elevated in the endometrium of women with a history of miscarriage. Serum levels may be useful as a predictive biomarker of miscarriage. Our data suggests that galectin-7 facilitates adhesion of the embryo to the endometrium and elevated galectin-7 may result in abnormal adhesion. | 24522232
 |
Ras inhibition boosts galectin-7 at the expense of galectin-1 to sensitize cells to apoptosis.
Barkan, B; Cox, AD; Kloog, Y
Oncotarget
4
256-68
2013
Kivonat megmutatása
Galectins are a family of β-galactoside-binding lectins that exert diverse extracellular and intracellular effects. Galectin-7 and galectin-1 show opposing effects on proliferation and survival in different cell types. Galectin-7 is a p53-induced gene and an enhancer of apoptosis, whereas galectin-1 induces tumorigenicity and resistance to apoptosis in several types of cancers. We show here that in cells derived from neurofibromin-deficient (Nf1(-/-)) malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs), Ras inhibition by S-trans,trans-farnesylthiosalicylic-acid (FTS; Salirasib) shifts the pattern of galectin expression. Whereas FTS decreased levels of both active Ras and galectin-1 expression, it dramatically increased both the mRNA and protein expression levels of galectin-7. Galectin-7 accumulation was mediated through JNK inhibition presumably resulting from the observed induction of p53, and was negatively regulated by the AP-1 inhibitor JDP2. Expression of galectin-7 by itself decreased Ras activation in ST88-14 cells and rendered them sensitive to apoptosis. This observed shift in galectin expression pattern together with the accompanying shift from cell proliferation to apoptosis represents a novel pattern of Ras inhibition by FTS. This seems likely to be an important phenomenon in view of the fact that both enhanced cell proliferation and defects of apoptosis constitute major hallmarks of human cancers and play a central role in the resistance of MPNSTs to anti-cancer treatments. These findings suggest that FTS, alone or in combination with chemotherapy agents, may be worth developing as a possible treatment for MPNSTs. | 23530091
 |
Galectin-7 overexpression is associated with the apoptotic process in UVB-induced sunburn keratinocytes.
Bernerd, F; Sarasin, A; Magnaldo, T
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
96
11329-34
1998
Kivonat megmutatása
Galectin-7 is a beta-galactoside binding protein specifically expressed in stratified epithelia and notably in epidermis, but barely detectable in epidermal tumors and absent from squamous carcinoma cell lines. Galectin-7 gene is an early transcriptional target of the tumor suppressor protein P53 [Polyak, K., Xia, Y., Zweier, J., Kinzler, K. & Vogelstein, B. (1997) Nature (London) 389, 300-305]. Because p53 transcriptional activity is increased by genotoxic stresses we have examined the possible effects of ultraviolet radiations (UVB) on galectin-7 expression in epidermal keratinocytes. The amounts of galectin-7 mRNA and protein are increased rapidly after UVB irradiation of epidermal keratinocytes. The increase of galectin-7 is parallel to P53 stabilization. UVB irradiation of skin reconstructed in vitro and of human skin ex vivo demonstrates that galectin-7 overexpression is associated with sunburn/apoptotic keratinocytes. Transfection of a galectin-7 expression vector results in a significant increase in terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated UTP end labeling-positive keratinocytes. The present findings demonstrate a keratinocyte-specific protein involved in the UV-induced apoptosis, an essential process in the maintenance of epidermal homeostasis. | 10500176
 |