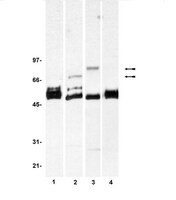
Human fibroblast growth factor receptor 1-IIIb is a functional fibroblast growth factor receptor expressed in the pancreas and involved in proliferation and movement of pancreatic ductal cells.
Zhanbing Liu, Toshiyuki Ishiwata, Shaxia Zhou, Susanne Maier, Doris Henne-Bruns, Murray Korc, Max Bachem, Marko Kornmann
Pancreas
35
147-57
2007
Kivonat megmutatása
OBJECTIVES: The possible functions of the human IIIb-messenger RNA splice variant of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor 1 (FGFR-1 IIIb) are yet to be delineated. In this study, the expression and functionality of the human FGFR-1 IIIb were characterized in the pancreas. METHODS: In situ hybridization with a specific FGFR-1 IIIb probe in human pancreatic tissues demonstrated that FGFR-1 IIIb localized in normal pancreatic acinar and in ductal-like pancreatic cancer cells. To further assess the potential role of this receptor, a full-length human FGFR-1 IIIb was stably expressed in TAKA-1 pancreatic ductal cells not expressing endogenous FGFR-1. RESULTS: The FGFR-1 IIIb-expressing TAKA-1 cells synthesized a glycosylated 110-kd protein capable of inducing proliferation on incubation with exogenous FGF-1, -2, and -4. These effects were paralleled by tyrosine phosphorylation of FGFR substrate 2 and association of FGFR substrate 2 with FGFR-1 IIIb. The FGF-1, -2, and -10 induced the activation of p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), p38 MAPK, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Pharmacological inhibition revealed that FGF-induced proliferation was dependent on the concomitant activation of p44/42 MAPK and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. The FGFR-1 IIIb expression enhanced single-cell movement and plating efficacy. CONCLUSIONS: Our results demonstrate that the human FGFR-1 IIIb variant is a functional FGFR expressed in the pancreas that can alter pancreatic functions that regulate proliferation, adhesion, and movement. | 17632321
 |
The signaling adapter FRS-2 competes with Shc for binding to the nerve growth factor receptor TrkA. A model for discriminating proliferation and differentiation.
Meakin, S O, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 274: 9861-70 (1999)
1998
Kivonat megmutatása
We have isolated a human cDNA for the signaling adapter molecule FRS-2/suc1-associated neurotrophic factor target and shown that it is tyrosine-phosphorylated in response to nerve growth factor (NGF) stimulation. Importantly, we demonstrate that the phosphotyrosine binding domain of FRS-2 directly binds the Trk receptors at the same phosphotyrosine residue that binds the signaling adapter Shc, suggesting a model in which competitive binding between FRS-2 and Shc regulates differentiation versus proliferation. Consistent with this model, FRS-2 binds Grb-2, Crk, the SH2 domain containing tyrosine phosphatase SH-PTP-2, the cyclin-dependent kinase substrate p13(suc1), and the Src homology 3 (SH3) domain of Src, providing a functional link between TrkA, cell cycle, and multiple NGF signaling effectors. Importantly, overexpression of FRS-2 in cells expressing an NGF nonresponsive TrkA receptor mutant reconstitutes the ability of NGF to stop cell cycle progression and to stimulate neuronal differentiation. | 10092678
 |
Binding of Shp2 tyrosine phosphatase to FRS2 is essential for fibroblast growth factor-induced PC12 cell differentiation.
Hadari, Y R, et al.
Mol. Cell. Biol., 18: 3966-73 (1998)
1998
Kivonat megmutatása
FRS2 is a lipid-anchored docking protein that plays an important role in linking fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and nerve growth factor receptors with the Ras/mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase signaling pathway. In this report, we demonstrate that FRS2 forms a complex with the N-terminal SH2 domain of the protein tyrosine phosphatase Shp2 in response to FGF stimulation. FGF stimulation induces tyrosine phosphorylation of Shp2, leading to the formation of a complex containing Grb2 and Sos1 molecules. In addition, a mutant FRS2 deficient in both Grb2 and Shp2 binding induces a weak and transient MAP kinase response and fails to induce PC12 cell differentiation in response to FGF stimulation. Furthermore, FGF is unable to induce differentiation of PC12 cells expressing an FRS2 point mutant deficient in Shp2 binding. Finally, we demonstrate that the catalytic activity of Shp2 is essential for sustained activation of MAP kinase and for potentiation of FGF-induced PC12 cell differentiation. These experiments demonstrate that FRS2 recruits Grb2 molecules both directly and indirectly via complex formation with Shp2 and that Shp2 plays an important role in FGF-induced PC12 cell differentiation. | 9632781
 |
Novel recognition motif on fibroblast growth factor receptor mediates direct association and activation of SNT adapter proteins.
Xu, H, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 273: 17987-90 (1998)
1998
Kivonat megmutatása
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) stimulate tyrosine phosphorylation of a membrane-anchored adapter protein, FRS2/SNT-1, promoting its association with Shp-2 tyrosine phosphatase and upstream activators of Ras. Using the yeast two-hybrid protein-protein interaction assay, we show that FRS2/SNT-1 and a newly isolated SNT-2 protein directly bind to FGF receptor-1 (FGFR-1). A juxtamembrane segment of FGFR-1 and the phosphotyrosine-binding domain of SNTs are both necessary and sufficient for interaction in yeast and in vitro, and FGFR-mediated SNT tyrosine phosphorylation in vivo requires these segments of receptor and SNT. Our findings establish SNTs as direct protein links between FGFR-1 and multiple downstream pathways. The SNT binding motif of FGFR-1 is distinct from previously described phosphotyrosine-binding domain recognition motifs, lacking both tyrosine and asparagine residues. | 9660748
 |