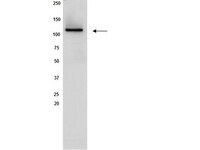
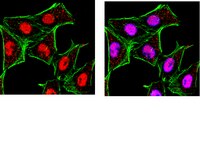
Sirt1 contributes critically to the redox-dependent fate of neural progenitors.
Prozorovski, Timour, et al.
Nat. Cell Biol., 10: 385-94 (2008)
2008
显示摘要
Repair processes that are activated in response to neuronal injury, be it inflammatory, ischaemic, metabolic, traumatic or other cause, are characterized by a failure to replenish neurons and by astrogliosis. The underlying molecular pathways, however, are poorly understood. Here, we show that subtle alterations of the redox state, found in different brain pathologies, regulate the fate of mouse neural progenitor cells (NPCs) through the histone deacetylase (HDAC) Sirt1. Mild oxidation or direct activation of Sirt1 suppressed proliferation of NPCs and directed their differentiation towards the astroglial lineage at the expense of the neuronal lineage, whereas reducing conditions had the opposite effect. Under oxidative conditions in vitro and in vivo, Sirt1 was upregulated in NPCs, bound to the transcription factor Hes1 and subsequently inhibited pro-neuronal Mash1. In utero shRNA-mediated knockdown of Sirt1 in NPCs prevented oxidation-mediated suppression of neurogenesis and caused upregulation of Mash1 in vivo. Our results provide evidence for an as yet unknown metabolic master switch that determines the fate of neural progenitors. | 18344989
 |
Sirtuins: novel targets for metabolic disease.
Elliott, Peter J and Jirousek, Michael
Current opinion in investigational drugs (London, England : 2000), 9: 371-8 (2008)
2008
显示摘要
Sirtuins represent a novel family of enzymes that are collectively well situated to help regulate nutrient sensing and utilization, metabolic rate and ultimately metabolic disease. Activation of one of these enzymes, SIRT1, leads to enhanced activity of multiple proteins, including peroxisome-proliferator activated receptor coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1alpha), which helps to mediate some of the in vitro and in vivo effects of sirtuins. As such, enhanced SIRT1 activity decreases glucose levels, improves insulin sensitivity, increases mitochondrial number and function, decreases adiposity, improves exercise tolerance and potentially lowers body weight. SRT-501 is a proprietary formulation of resveratrol with improved bioavailability. As such, SRT-501 represents the first in a novel class of SIRT1 activators that has proven to be safe and well-tolerated in humans. Clinical trials in type 2 diabetic patients are currently underway. | 18393104
 |
hSIR2(SIRT1) functions as an NAD-dependent p53 deacetylase.
Vaziri, H, et al.
Cell, 107: 149-59 (2001)
2001
显示摘要
DNA damage-induced acetylation of p53 protein leads to its activation and either growth arrest or apoptosis. We show here that the protein product of the gene hSIR2(SIRT1), the human homolog of the S. cerevisiae Sir2 protein known to be involved in cell aging and in the response to DNA damage, binds and deacetylates the p53 protein with a specificity for its C-terminal Lys382 residue, modification of which has been implicated in the activation of p53 as a transcription factor. Expression of wild-type hSir2 in human cells reduces the transcriptional activity of p53. In contrast, expression of a catalytically inactive hSir2 protein potentiates p53-dependent apoptosis and radiosensitivity. We propose that hSir2 is involved in the regulation of p53 function via deacetylation. | 11672523
 |