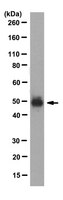
Differential expression of functional protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR-2) in human vascular smooth muscle cells.
Molino, M, et al.
Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 18: 825-32 (1998)
1998
显示摘要
The protease-activated family of G protein-coupled receptors includes PAR-1 and PAR-3, which are activated by thrombin, and PAR-2, which is activated by trypsin and tryptase. PAR-2 has recently been shown to be expressed in human endothelial cells. In the present studies, we have examined the expression of PAR-2 in other cells, particularly vascular smooth muscle, and tested whether the receptors are functional. The results show that PAR-2 is present in human aorta and coronary artery smooth muscle cells, as well as in arteries traversing the walls of the small intestine. It was also detected in human keratinocytes, sweat glands, intestinal smooth muscle, and intestinal epithelium, but not at all in myocardial smooth muscle and only inconsistently in intestinal veins and venules. Activation of aortic smooth muscle cells in culture with PAR-2 peptide agonists caused a transient increase in the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration. In contrast, PAR-2 mRNA could not be detected in saphenous vein smooth muscle cells, and the same cells placed in culture showed little, if any, response to the PAR-2 agonist peptides. These observations show that PAR-2 is widely distributed in human vascular smooth muscle, particularly in arteries. However, this is not a universal finding and at least some venous smooth muscle cells, including those in saphenous veins, apparently do not express the receptor in detectable amounts. | 9598843
 |
Endothelial cell thrombin receptors and PAR-2. Two protease-activated receptors located in a single cellular environment.
Molino, M, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 272: 11133-41 (1997)
1997
显示摘要
Human endothelial cells express thrombin receptors and PAR-2, the two known members of the family of protease-activated G protein-coupled receptors. Because previous studies have shown that the biology of the human thrombin receptor varies according to the cell in which it is expressed, we have taken advantage of the presence of both receptors in endothelial cells to examine the enabling and disabling interactions with candidate proteases likely to be encountered in and around the vascular space to compare the responses elicited by the two receptors when they are present in the same cell and to compare the mechanisms of thrombin receptor and PAR-2 clearance and replacement in a common cellular environment. Of the proteases that were tested, only trypsin activated both receptors. Cathepsin G, which disables thrombin receptors, had no effect on PAR-2, while urokinase, kallikrein, and coagulation factors IXa, Xa, XIa, and XIIa neither substantially activated nor noticeably disabled either receptor. Like thrombin receptors, activation of PAR-2 caused pertussis toxin-sensitive phospholipase C activation as well as activation of phospholipase A2, leading to the release of PGI2. Concurrent activation of both receptors caused a greater response than activation of either alone. It also abolished a subsequent response to the PAR-2 agonist peptide, SLIGRL, while only partially inhibiting the response to the agonist peptide, SFLLRN, which activates both receptors. After proteolytic or nonproteolytic activation, PAR-2, like thrombin receptors, was cleared from the endothelial cell surface and then rapidly replaced with new receptors by a process that does not require protein synthesis. Selective activation of either receptor had no effect on the clearance of the other. These results suggest that the expression of both thrombin receptors and PAR-2 on endothelial cells serves more to extend the range of proteases to which the cells can respond than it does to extend the range of potential responses. The results also show that proteases that can disable these receptors can distinguish between them, just as do most of the proteases that activate them. Finally, the residual response to SFLLRN after activation of thrombin receptors and PAR-2 raises the possibility that a third, as yet unidentified member of this family is expressed on endothelial cells, one that is activated by neither thrombin nor trypsin. | 9111010
 |