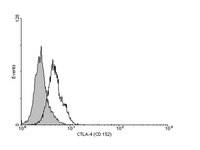
04-963 Sigma-AldrichAnti-CTLA4 (CD152) Antibody, clone 9H10
Anti-CTLA4 (CD152) Antibody, clone 9H10 is an antibody against CTLA4 (CD152) for use in WB, FC & IP.
More>> Anti-CTLA4 (CD152) Antibody, clone 9H10 is an antibody against CTLA4 (CD152) for use in WB, FC & IP. Less<<Anti-CTLA4 (CD152) Antibody, clone 9H10 MSDS (material safety data sheet) or SDS, CoA and CoQ, dossiers, brochures and other available documents.
Recommended Products
概述
| Replacement Information |
|---|
重要规格表
| Species Reactivity | Key Applications | Host | Format | Antibody Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | WB, FC, IP | Ht | Purified | Monoclonal Antibody |
| References |
|---|
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Format | Purified |
| Control |
|
| Presentation | Purified hamster monoclonal IgG in buffer containing 0.1 M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4) with 150 mM NaCl and 0.05% sodium azide. |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Physicochemical Information |
|---|
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Storage and Shipping Information | |
|---|---|
| Storage Conditions | Stable at 2-8°C for 1 year from date of receipt. |
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Material Size | 100 µg |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| 产品目录编号 | GTIN |
| 04-963 | 04053252671722 |
Documentation
Anti-CTLA4 (CD152) Antibody, clone 9H10 MSDS
| 职位 |
|---|
Anti-CTLA4 (CD152) Antibody, clone 9H10 分析证书
小册子
| 标题 |
|---|
| Advancing cancer research: From hallmarks & biomarkers to tumor microenvironment progression |