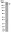NLRC5 interacts with RIG-I to induce a robust antiviral response against influenza virus infection.
Ranjan, P; Singh, N; Kumar, A; Neerincx, A; Kremmer, E; Cao, W; Davis, WG; Katz, JM; Gangappa, S; Lin, R; Kufer, TA; Sambhara, S
European journal of immunology
2014
Show Abstract
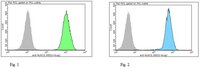
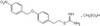
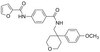
The NLR protein, NLRC5, is an important regulator of MHC I gene expression, however, the role of NLRC5 in other innate immune responses is less well defined. In the present study, we report that NLRC5 binds RIG-I and that this interaction is critical for robust antiviral responses against influenza virus. Overexpression of NLRC5 in the human lung epithelial cell line, A549, and normal human bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cells resulted in impaired replication of influenza virus A/Puerto Rico/8/34 virus (PR8) and enhanced IFN-β expression. Influenza virus leads to induction of IFN-β that drives RIG-I and NLRC5 expression in host cells. Our results suggest that NLRC5 extends and stabilizes influenza virus-induced RIG-I expression and delays expression of the viral inhibitor protein NS1. We show that NS1 binds to NLRC5 to suppress its function. Interaction domain mapping revealed that NLRC5 interacts with RIG-I via its N-terminal death domain and that NLRC5 enhanced antiviral activity in a LRR-domain-independent manner. Taken together, our findings identify a novel role for NLRC5 in RIG-I-mediated antiviral host responses against influenza virus infection, distinguished from the role of NLRC5 in MHC class I gene regulation. This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved. | 25404059
 |
NLRC5 controls basal MHC class I gene expression in an MHC enhanceosome-dependent manner.
Neerincx, Andreas, et al.
J. Immunol., 188: 4940-50 (2012)
2012
Show Abstract
Nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat (NLR) proteins play important roles in innate immune responses as pattern-recognition receptors. Although most NLR proteins act in cell autonomous immune pathways, some do not function as classical pattern-recognition receptors. One such NLR protein is the MHC class II transactivator, the master regulator of MHC class II gene transcription. In this article, we report that human NLRC5, which we recently showed to be involved in viral-mediated type I IFN responses, shuttles to the nucleus and activates MHC class I gene expression. Knockdown of NLRC5 in different human cell lines and primary dermal fibroblasts leads to reduced MHC class I expression, whereas introduction of NLRC5 into cell types with very low expression of MHC class I augments MHC class I expression to levels comparable to those found in lymphocytes. Expression of NLRC5 positively correlates with MHC class I expression in human tissues. Functionally, we show that both the N-terminal effector domain of NLRC5 and its C-terminal leucine-rich repeat domain are needed for activation of MHC class I expression. Moreover, nuclear shuttling and function depend on a functional Walker A motif. Finally, we identified a promoter sequence in the MHC class I promoter, the X1 box, to be involved in NLRC5-mediated MHC class I gene activation. Taken together, this suggested that NLRC5 acts in a manner similar to class II transactivator to drive MHC expression and revealed NLRC5 as an important regulator of basal MHC class I expression. | 22490867
 |
A role for the human nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich repeat-containing family member NLRC5 in antiviral responses.
Neerincx, Andreas, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 285: 26223-32 (2010)
2010
Show Abstract
Proteins of the nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich repeat (NLR)-containing family recently gained attention as important components of the innate immune system. Although over 20 of these proteins are present in humans, only a few members including the cytosolic pattern recognition receptors NOD1, NOD2, and NLRP3 have been analyzed extensively. These NLRs were shown to be pivotal for mounting innate immune response toward microbial invasion. Here we report on the characterization of human NLRC5 and provide evidence that this NLR has a function in innate immune responses. We found that NLRC5 is a cytosolic protein expressed predominantly in hematopoetic cells. NLRC5 mRNA and protein expression was inducible by the double-stranded RNA analog poly(I.C) and Sendai virus. Overexpression of NLRC5 failed to trigger inflammatory responses such as the NF-kappaB or interferon pathways in HEK293T cells. However, knockdown of endogenous NLRC5 reduced Sendai virus- and poly(I.C)-mediated type I interferon pathway-dependent responses in THP-1 cells and human primary dermal fibroblasts. Taken together, this defines a function for NLRC5 in anti-viral innate immune responses. | 20538593
 |