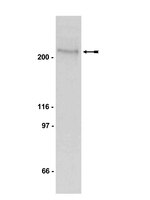
Regulation of skeletal muscle oxidative capacity and muscle mass by SIRT3.
Lin, L; Chen, K; Abdel Khalek, W; Ward, JL; Yang, H; Chabi, B; Wrutniak-Cabello, C; Tong, Q
PloS one
9
e85636
2014
Mostrar resumen
We have previously reported that the expression of mitochondrial deacetylase SIRT3 is high in the slow oxidative muscle and that the expression of muscle SIRT3 level is increased by dietary restriction or exercise training. To explore the function of SIRT3 in skeletal muscle, we report here the establishment of a transgenic mouse model with muscle-specific expression of the murine SIRT3 short isoform (SIRT3M3). Calorimetry study revealed that the transgenic mice had increased energy expenditure and lower respiratory exchange rate (RER), indicating a shift towards lipid oxidation for fuel usage, compared to control mice. The transgenic mice exhibited better exercise performance on treadmills, running 45% further than control animals. Moreover, the transgenic mice displayed higher proportion of slow oxidative muscle fibers, with increased muscle AMPK activation and PPARδ expression, both of which are known regulators promoting type I muscle fiber specification. Surprisingly, transgenic expression of SIRT3M3 reduced muscle mass up to 30%, likely through an up-regulation of FOXO1 transcription factor and its downstream atrophy gene MuRF-1. In summary, these results suggest that SIRT3 regulates the formation of oxidative muscle fiber, improves muscle metabolic function, and reduces muscle mass, changes that mimic the effects of caloric restriction. | 24454908
 |
Combinatorial interactions are required for the efficient recruitment of pho repressive complex (PhoRC) to polycomb response elements.
Kahn, TG; Stenberg, P; Pirrotta, V; Schwartz, YB
PLoS genetics
10
e1004495
2014
Mostrar resumen
Polycomb Group (PcG) proteins are epigenetic repressors that control metazoan development and cell differentiation. In Drosophila, PcG proteins form five distinct complexes targeted to genes by Polycomb Response Elements (PREs). Of all PcG complexes PhoRC is the only one that contains a sequence-specific DNA binding subunit (PHO or PHOL), which led to a model that places PhoRC at the base of the recruitment hierarchy. Here we demonstrate that in vivo PHO is preferred to PHOL as a subunit of PhoRC and that PHO and PHOL associate with PREs and a subset of transcriptionally active promoters. Although the binding to the promoter sites depends on the quality of recognition sequences, the binding to PREs does not. Instead, the efficient recruitment of PhoRC to PREs requires the SFMBT subunit and crosstalk with Polycomb Repressive Complex 1. We find that human YY1 protein, the ortholog of PHO, binds sites at active promoters in the human genome but does not bind most PcG target genes, presumably because the interactions involved in the targeting to Drosophila PREs are lost in the mammalian lineage. We conclude that the recruitment of PhoRC to PREs is based on combinatorial interactions and propose that such a recruitment strategy is important to attenuate the binding of PcG proteins when the target genes are transcriptionally active. Our findings allow the appropriate placement of PhoRC in the PcG recruitment hierarchy and provide a rationale to explain why YY1 is unlikely to serve as a general recruiter of mammalian Polycomb complexes despite its reported ability to participate in PcG repression in flies. | 25010632
 |
Effect of exercise intensity on skeletal muscle AMPK signaling in humans.
Zhi-Ping Chen, Terry J Stephens, Sid Murthy, Benedict J Canny, Mark Hargreaves, Lee A Witters, Bruce E Kemp, Glenn K McConell
Diabetes
52
2205-12
2003
Mostrar resumen
The effect of exercise intensity on skeletal muscle AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling and substrate metabolism was examined in eight men cycling for 20 min at each of three sequential intensities: low (40 +/- 2% VO(2) peak), medium (59 +/- 1% VO(2) peak), and high (79 +/- 1% VO(2) peak). Muscle free AMP/ATP ratio only increased at the two higher exercise intensities (P 0.05). AMPK alpha 1 (1.5-fold) and AMPK alpha 2 (5-fold) activities increased from low to medium intensity, with AMPK alpha 2 activity increasing further from medium to high intensity. The upstream AMPK kinase activity was substantial at rest and only increased 50% with exercise, indicating that, initially, signaling through AMPK did not require AMPK kinase posttranslational modification. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC)-beta phosphorylation was sensitive to exercise, increasing threefold from rest to low intensity, whereas neuronal NO synthase (nNOS) micro phosphorylation was only observed at the higher exercise intensities. Glucose disappearance (tracer) did not increase from rest to low intensity, but increased sequentially from low to medium to high intensity. Calculated fat oxidation increased from rest to low intensity in parallel with ACC beta phosphorylation, then declined during high intensity. These results indicate that ACC beta phosphorylation is especially sensitive to exercise and tightly coupled to AMPK signaling and that AMPK activation does not depend on AMPK kinase activation during exercise. | 12941758
 |
AMPK signaling in contracting human skeletal muscle: acetyl-CoA carboxylase and NO synthase phosphorylation.
Chen, Z P, et al.
Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab., 279: E1202-6 (2000)
1999
Mostrar resumen
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a metabolic stress-sensing protein kinase responsible for coordinating metabolism and energy demand. In rodents, exercise accelerates fatty acid metabolism, enhances glucose uptake, and stimulates nitric oxide (NO) production in skeletal muscle. AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) carboxylase (ACC) and enhances GLUT-4 translocation. It has been reported that human skeletal muscle malonyl-CoA levels do not change in response to exercise, suggesting that other mechanisms besides inhibition of ACC may be operating to accelerate fatty acid oxidation. Here, we show that a 30-s bicycle sprint exercise increases the activity of the human skeletal muscle AMPK-alpha1 and -alpha2 isoforms approximately two- to threefold and the phosphorylation of ACC at Ser(79) (AMPK phosphorylation site) approximately 8.5-fold. Under these conditions, there is also an approximately 5.5-fold increase in phosphorylation of neuronal NO synthase-mu (nNOSmu;) at Ser(1451). These observations support the concept that inhibition of ACC is an important component in stimulating fatty acid oxidation in response to exercise and that there is coordinated regulation of nNOSmu to protect the muscle from ischemia/metabolic stress. | 11052978
 |
Dealing with energy demand: the AMP-activated protein kinase.
Kemp, B E, et al.
Trends Biochem. Sci., 24: 22-5 (1999)
1998
Mostrar resumen
The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a member of a metabolite-sensing protein kinase family that is found in all eukaryotes. AMPK activity is regulated by vigorous exercise, nutrient starvation and ischemia/hypoxia, and modulates many aspects of mammalian cell metabolism. The AMPK yeast homolog, Snf1p, plays a major role in adaption to glucose deprivation. In mammals, AMPK also has diverse roles that extend from energy metabolism through to transcriptional control. | 10087918
 |