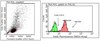
Neuroprotective effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in brain injury is mediated by preservation of mitochondrial membrane properties.
Eilam Palzur,Menashe Zaaroor,Eugene Vlodavsky,Felix Milman,Jean F Soustiel
Brain research
1221
2008
Show Abstract
Recent experimental data have shown that hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) was associated increased Bcl-2 expression at the injury site that correlated with reduced apoptosis. We hypothesized that HBOT mediated enhancement of Bcl-2 expression and increased intracellular oxygen bio-availability may both contribute to preserve mitochondrial integrity and reduce the activation of the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. For this purpose, a cortical lesion was created in the parietal cortex of Sprague-Dawley rats by dynamic cortical deformation (DCD) and outcome measures in non-treated animals were compared with that of HBOT treated rats. Morphological analysis showed a profound reduction in neuronal counts in the perilesional area and a marked rarefaction of the density of the axonal-dendritic network. In treated animals, however, there was a significant attenuation of the impact of DCD over perilesional neurons, characterized by significantly higher cell counts and denser axonal network. In mitochondria isolated from injured brain tissue, there was a profound loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential (Deltapsi(M)) that proved to be substantially reversed by HBOT. This finding correlated with a significant reduction of caspases 3 and 9 activation in HBOT treated animals but not of caspase 8, indicating a selective effect over the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis. All together, our results indicate that the neuroprotective effect of HBOT may represent the consequence of preserved mitochondrial integrity and subsequent inhibition of the mPTP and reduction of the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. | 18561900
 |
A conserved coronavirus epitope, critical in virus neutralization, mimicked by internal-image monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibodies.
C Suñé,C Smerdou,I M Antón,P Abril,J Plana,L Enjuanes
Journal of virology
65
1991
Show Abstract
Monoclonal antibody (MAb) 6A.C3 neutralizes transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus (TGEV) and is specific for a conserved epitope within subsite Ac of the spike (S) glycoprotein of TGEV. Six hybridomas secreting anti-idiotypic (Ab2) MAbs specific for MAb 6A.C3 (Ab1) have been selected. All six MAbs inhibited the binding of Ab1 to TGEV and specifically cross-linked MAb1-6A.C3. Four of these hybridomas secreted gamma-type anti-idiotypic MAbs. The other two Ab2s (MAbs 9A.G3 and 9C.E11) were recognized by TGEV-specific antiserum induced in two species. This binding was inhibited by viruses of the TGEV group but not by serologically unrelated coronaviruses. These results indicate that MAb2-9A.G3 and MAb2-9C.E11 mimic an antigenic determinant present on the TGEV surface, and they were classified as beta-type (internal-image) MAbs. TGEV-binding Ab3 antiserum was induced in 100% of mice immunized with the two beta-type MAb2s and in 25 to 50% of mice immunized with gamma-type MAb2. Both beta- and gamma-type Ab2s induced neutralizing Ab3 antibodies in mice that were mainly directed to antigenic subsite Ac of the S protein. Full Text Article | 1719237
 |