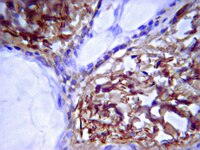
Changes in calpain activity, muscle structure, and function after eccentric exercise.
Raastad T, Owe SG, Paulsen G, Enns D, Overgaard K, Crameri R, Kiil S, Belcastro A, Bergersen L, Hallén J
Medicine and science in sports and exercise
42
86-95
2009
Afficher le résumé
PURPOSE: The aim of this study was to investigate changes in muscle function, muscle structure, and calpain activity after high-force eccentric exercise. METHODS: Eleven healthy males performed 300 maximal voluntary eccentric actions with knee extensors in one leg. Maximal force-generating capacity was measured before exercise and regularly during the next 7 d. Biopsies from musculus vastus lateralis were taken in both control and exercised legs 0.5, 4, 8, 24, 96, and 168 h after exercise for evaluation of myofibrillar structure, extracellular matrix proteins, and calpain activity. RESULTS: In the exercised leg, peak torque was reduced by 47 +/- 5% during exercise and was still 22 +/- 5% lower than baseline 4 d after the exercise. Calpain activity was three times higher in the exercised leg compared with the control leg 30 min after exercise. Myofibrillar disruptions were observed in 36 +/- 6% of all fibers in exercised muscle and in 2 +/- 1% of fibers in control muscle. The individual reductions in peak torque correlated with the proportion of fibers with myofibrillar disruptions (r = 0.89). The increase in calpain activity was not correlated to the proportion of fibers with myofibrillar disruptions. Nevertheless, the characteristics of the myofibrillar disruptions mimicked calpain-mediated degradation of myofibrils. Tenascin-C and the N-terminal propeptide of procollagen type III showed increased staining intensity on cross-sections 4-7 d after the exercise. CONCLUSIONS: Myofibrillar disruptions seem to be a main cause for the long-lasting reduction in force-generating capacity after high-force eccentric exercise. The increase in calpain activity, but the lack of a relationship between calpain activity and the amount of muscle damage, suggests multiple roles of calpain in the damage and repair process. | | 20010126
 |
Expression and activation of TGF-beta isoforms in acute allergen-induced remodelling in asthma.
Torrego, A; Hew, M; Oates, T; Sukkar, M; Fan Chung, K
Thorax
62
307-13
2007
Afficher le résumé
Airway wall remodelling and inflammation are features of chronic asthma. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) has been implicated in these processes.To determine the effect of allergen challenge on airway inflammation and remodelling and whether TGF-beta isoforms and the Smad signalling pathways are involved.Thirteen patients with atopic asthma underwent inhalational challenge with 0.9% saline, followed by allergen 3-4 weeks later. After both challenges, fibreoptic bronchoscopy was undertaken to obtain bronchial biopsies and tissue samples were processed for immunohistochemistry and examined by microscopy.Forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV(1)) fell after allergen challenge (mean (SE) -28.1 (0.9)% at 30 min with a late response at 7 hours (-23.0 (1.2)%). Allergen challenge caused an increase in neutrophils and eosinophils in the bronchial mucosa compared with saline. Sub-basement membrane (SBM) thickness did not change after allergen, but tenascin deposition in SBM was increased. Intranuclear (activated) Smad 2/3 and Smad 4 detected by immunohistochemistry were increased after allergen challenge in epithelial and subepithelial cells of bronchial biopsies. No inhibitory Smad (Smad 7) protein was detected. TGF-beta isoforms 1, 2 and 3 were expressed predominantly in bronchial epithelium after saline and allergen challenges, but only TGF-beta(2) expression was increased after allergen. Double immunostaining showed an increase in TGF-beta(2) positive eosinophils and neutrophils but not in TGF-beta(1) positive eosinophils and neutrophils after allergen challenge.TGF-beta(2) may contribute to the remodelling changes in allergic asthma following single allergen exposure. Article en texte intégral | Immunohistochemistry | 17251317
 |