Essential role of lncRNA binding for WDR5 maintenance of active chromatin and embryonic stem cell pluripotency.
Yang, YW; Flynn, RA; Chen, Y; Qu, K; Wan, B; Wang, KC; Lei, M; Chang, HY
eLife
3
e02046
2014
Show Abstract
The WDR5 subunit of the MLL complex enforces active chromatin and can bind RNA; the relationship between these two activities is unclear. Here we identify a RNA binding pocket on WDR5, and discover a WDR5 mutant (F266A) that selectively abrogates RNA binding without affecting MLL complex assembly or catalytic activity. Complementation in ESCs shows that WDR5 F266A mutant is unable to accumulate on chromatin, and is defective in gene activation, maintenance of histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation, and ESC self renewal. We identify a family of ESC messenger and lncRNAs that interact with wild type WDR5 but not F266A mutant, including several lncRNAs known to be important for ESC gene expression. These results suggest that specific RNAs are integral inputs into the WDR5-MLL complex for maintenance of the active chromatin state and embryonic stem cell fates. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02046.001. | | 24521543
 |
Crosstalk between NSL histone acetyltransferase and MLL/SET complexes: NSL complex functions in promoting histone H3K4 di-methylation activity by MLL/SET complexes.
Zhao, X; Su, J; Wang, F; Liu, D; Ding, J; Yang, Y; Conaway, JW; Conaway, RC; Cao, L; Wu, D; Wu, M; Cai, Y; Jin, J
PLoS genetics
9
e1003940
2013
Show Abstract
hMOF (MYST1), a histone acetyltransferase (HAT), forms at least two distinct multiprotein complexes in human cells. The male specific lethal (MSL) HAT complex plays a key role in dosage compensation in Drosophila and is responsible for histone H4K16ac in vivo. We and others previously described a second hMOF-containing HAT complex, the non-specific lethal (NSL) HAT complex. The NSL complex has a broader substrate specificity, can acetylate H4 on K16, K5, and K8. The WD (tryptophan-aspartate) repeat domain 5 (WDR5) and host cell factor 1 (HCF1) are shared among members of the MLL/SET (mixed-lineage leukemia/set-domain containing) family of histone H3K4 methyltransferase complexes. The presence of these shared subunits raises the possibility that there are functional links between these complexes and the histone modifications they catalyze; however, the degree to which NSL and MLL/SET influence one another's activities remains unclear. Here, we present evidence from biochemical assays and knockdown/overexpression approaches arguing that the NSL HAT promotes histone H3K4me2 by MLL/SET complexes by an acetylation-dependent mechanism. In genomic experiments, we identified a set of genes including ANKRD2, that are affected by knockdown of both NSL and MLL/SET subunits, suggested they are co-regulated by NSL and MLL/SET complexes. In ChIP assays, we observe that depletion of the NSL subunits hMOF or NSL1 resulted in a significant reduction of both H4K16ac and H3K4me2 in the vicinity of the ANKRD2 transcriptional start site proximal region. However, depletion of RbBP5 (a core component of MLL/SET complexes) only reduced H3K4me2 marks, but not H4K16ac in the same region of ANKRD2, consistent with the idea that NSL acts upstream of MLL/SET to regulate H3K4me2 at certain promoters, suggesting coordination between NSL and MLL/SET complexes is involved in transcriptional regulation of certain genes. Taken together, our results suggest a crosstalk between the NSL and MLL/SET complexes in cells. | | 24244196
 |
Glucagon regulates gluconeogenesis through KAT2B- and WDR5-mediated epigenetic effects.
Ravnskjaer, K; Hogan, MF; Lackey, D; Tora, L; Dent, SY; Olefsky, J; Montminy, M
The Journal of clinical investigation
123
4318-28
2013
Show Abstract
Circulating pancreatic glucagon is increased during fasting and maintains glucose balance by stimulating hepatic gluconeogenesis. Glucagon triggering of the cAMP pathway upregulates the gluconeogenic program through the phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) and the dephosphorylation of the CREB coactivator CRTC2. Hormonal and nutrient signals are also thought to modulate gluconeogenic gene expression by promoting epigenetic changes that facilitate assembly of the transcriptional machinery. However, the nature of these modifications is unclear. Using mouse models and in vitro assays, we show that histone H3 acetylation at Lys 9 (H3K9Ac) was elevated over gluconeogenic genes and contributed to increased hepatic glucose production during fasting and in diabetes. Dephosphorylation of CRTC2 promoted increased H3K9Ac through recruitment of the lysine acetyltransferase 2B (KAT2B) and WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5), a core subunit of histone methyltransferase (HMT) complexes. KAT2B and WDR5 stimulated the gluconeogenic program through a self-reinforcing cycle, whereby increases in H3K9Ac further potentiated CRTC2 occupancy at CREB binding sites. Depletion of KAT2B or WDR5 decreased gluconeogenic gene expression, consequently breaking the cycle. Administration of a small-molecule KAT2B antagonist lowered circulating blood glucose concentrations in insulin resistance, suggesting that this enzyme may be a useful target for diabetes treatment. | | 24051374
 |
Crosstalk between leukemia-associated proteins MOZ and MLL regulates HOX gene expression in human cord blood CD34+ cells.
Paggetti, J, et al.
Oncogene, 29: 5019-31 (2010)
2010
Show Abstract
MOZ and MLL, encoding a histone acetyltransferase (HAT) and a histone methyltransferase, respectively, are targets for recurrent chromosomal translocations found in acute myeloblastic or lymphoblastic leukemia. In MOZ (MOnocytic leukemia Zinc-finger protein)/CBP- or mixed lineage leukemia (MLL)-rearranged leukemias, abnormal levels of HOX transcription factors have been found to be critical for leukemogenesis. We show that MOZ and MLL cooperate to regulate these key genes in human cord blood CD34+ cells. These chromatin-modifying enzymes interact, colocalize and functionally cooperate, and both are recruited to multiple HOX promoters. We also found that WDR5, an adaptor protein essential for lysine 4 trimethylation of histone H3 (H3K4me3) by MLL, colocalizes and interacts with MOZ. We detected the binding of the HAT MOZ to H3K4me3, thus linking histone methylation to acetylation. In CD34+ cells, depletion of MLL causes release of MOZ from HOX promoters, which is correlated to defective histone activation marks, leading to repression of HOX gene expression and alteration of commitment of CD34+ cells into myeloid progenitors. Thus, our results unveil the role of the interaction between MOZ and MLL in CD34+ cells in which both proteins have a critical role in hematopoietic cell-fate decision, suggesting a new molecular mechanism by which MOZ or MLL deregulation leads to leukemogenesis. | | 20581860
 |
Haematopoietic malignancies caused by dysregulation of a chromatin-binding PHD finger.
Wang, GG; Song, J; Wang, Z; Dormann, HL; Casadio, F; Li, H; Luo, JL; Patel, DJ; Allis, CD
Nature
459
847-51
2009
Show Abstract
Histone H3 lysine 4 methylation (H3K4me) has been proposed as a critical component in regulating gene expression, epigenetic states, and cellular identities1. The biological meaning of H3K4me is interpreted by conserved modules including plant homeodomain (PHD) fingers that recognize varied H3K4me states. The dysregulation of PHD fingers has been implicated in several human diseases, including cancers and immune or neurological disorders. Here we report that fusing an H3K4-trimethylation (H3K4me3)-binding PHD finger, such as the carboxy-terminal PHD finger of PHF23 or JARID1A (also known as KDM5A or RBBP2), to a common fusion partner nucleoporin-98 (NUP98) as identified in human leukaemias, generated potent oncoproteins that arrested haematopoietic differentiation and induced acute myeloid leukaemia in murine models. In these processes, a PHD finger that specifically recognizes H3K4me3/2 marks was essential for leukaemogenesis. Mutations in PHD fingers that abrogated H3K4me3 binding also abolished leukaemic transformation. NUP98-PHD fusion prevented the differentiation-associated removal of H3K4me3 at many loci encoding lineage-specific transcription factors (Hox(s), Gata3, Meis1, Eya1 and Pbx1), and enforced their active gene transcription in murine haematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Mechanistically, NUP98-PHD fusions act as 'chromatin boundary factors', dominating over polycomb-mediated gene silencing to 'lock' developmentally critical loci into an active chromatin state (H3K4me3 with induced histone acetylation), a state that defined leukaemia stem cells. Collectively, our studies represent, to our knowledge, the first report that deregulation of the PHD finger, an 'effector' of specific histone modification, perturbs the epigenetic dynamics on developmentally critical loci, catastrophizes cellular fate decision-making, and even causes oncogenesis during mammalian development. | Immunofluorescence | 19430464
 |
Molecular regulation of H3K4 trimethylation by Wdr82, a component of human Set1/COMPASS.
Wu, M; Wang, PF; Lee, JS; Martin-Brown, S; Florens, L; Washburn, M; Shilatifard, A
Molecular and cellular biology
28
7337-44
2008
Show Abstract
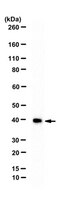
In yeast, the macromolecular complex Set1/COMPASS is capable of methylating H3K4, a posttranslational modification associated with actively transcribed genes. There is only one Set1 in yeast; yet in mammalian cells there are multiple H3K4 methylases, including Set1A/B, forming human COMPASS complexes, and MLL1-4, forming human COMPASS-like complexes. We have shown that Wdr82, which associates with chromatin in a histone H2B ubiquitination-dependent manner, is a specific component of Set1 complexes but not that of MLL1-4 complexes. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of Wdr82 results in a reduction in the H3K4 trimethylation levels, although these cells still possess active MLL complexes. Comprehensive in vitro enzymatic studies with Set1 and MLL complexes demonstrated that the Set1 complex is a more robust H3K4 trimethylase in vitro than the MLL complexes. Given our in vivo and in vitro observations, it appears that the human Set1 complex plays a more widespread role in H3K4 trimethylation than do the MLL complexes in mammalian cells. | Western Blotting | 18838538
 |