508509 Sigma-AldrichNS309 - CAS 18711-16-5 - Calbiochem
A potent activator of Ca2+ -activated K+ channels of SK and IK types, but not BK type channels. It is at least 1000 times more potent than 1-EBIO.
More>> A potent activator of Ca2+ -activated K+ channels of SK and IK types, but not BK type channels. It is at least 1000 times more potent than 1-EBIO. Less<<Sinónimos: Ca2+ -activated K+ Channels Activator, NS309, NS-309, NS 309
Productos recomendados
Descripción
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Tabla espec. clave
| CAS # | Empirical Formula |
|---|---|
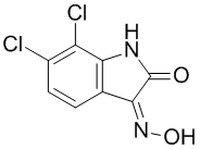
| 18711-16-5 | C₈H₄Cl₂N₂O₂ |
Products
| Número de referencia | Embalaje | Cant./Env. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5085090001 | Frasco de vidrio | 10 mg |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| CAS number | 18711-16-5 |
| Form | Yellow solid |
| Hill Formula | C₈H₄Cl₂N₂O₂ |
| Chemical formula | C₈H₄Cl₂N₂O₂ |
| Structure formula Image | |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Applications |
|---|
| Biological Information | |
|---|---|
| Primary Target | Ca2+-activated K+ channels |
| Purity | ≥98% by HPLC |
| Physicochemical Information |
|---|
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Product Usage Statements |
|---|
| Packaging Information |
|---|
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Número de referencia | GTIN |
| 5085090001 | 04055977262025 |
Documentation
NS309 - CAS 18711-16-5 - Calbiochem Ficha datos de seguridad (MSDS)
| Título |
|---|
Referencias bibliográficas
| Visión general referencias |
|---|
| Leurangue, V. et al. 2008. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 377, 101. Morimura, K. et al. 2006. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 100, 237. Strobaek, D. et al. 2004. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1665, 1. |