420127 Sigma-AldrichInSolution™ Jasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni - Calbiochem
InSolution™ Jasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni, CAS 102396-24-7, is a 1 mM solution of Jasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni in DMSO. Acts as a potent inducer of actin polymerization and stabilization.
More>> InSolution™ Jasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni, CAS 102396-24-7, is a 1 mM solution of Jasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni in DMSO. Acts as a potent inducer of actin polymerization and stabilization. Less<<Productos recomendados
Descripción
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Tabla espec. clave
| Empirical Formula |
|---|
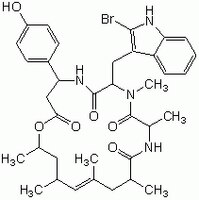
| C₃₆H₄₅BrN₄O₆ |
Products
| Número de referencia | Embalaje | Cant./Env. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 420127-50UG | Ampolla de plást. | 50 μg |
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | 420127 |
| Brand Family | Calbiochem® |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| ATP Competitive | N |
| Form | Liquid |
| Formulation | A 1 mM (50 µg/71 µl) solution of Jasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni (Cat. No. 420107) in DMSO. |
| Hill Formula | C₃₆H₄₅BrN₄O₆ |
| Chemical formula | C₃₆H₄₅BrN₄O₆ |
| Hygroscopic | Hygroscopic |
| Reversible | N |
| Structure formula Image | |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Biological Information | |
|---|---|
| Primary Target | F-actin |
| Primary Target IC<sub>50</sub> | Kd = 15 nM for actin binding |
| Purity | ≥90% by HPLC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
|---|---|
| Cell permeable | N |
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Product Usage Statements |
|---|
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Packaged under inert gas | Packaged under inert gas |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Número de referencia | GTIN |
| 420127-50UG | 04055977188059 |
Documentation
InSolution™ Jasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni - Calbiochem Ficha datos de seguridad (MSDS)
| Título |
|---|
InSolution™ Jasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni - Calbiochem Certificados de análisis
| Cargo | Número de lote |
|---|---|
| 420127 |
Referencias bibliográficas
| Visión general referencias |
|---|
| Rosado, J.A., et al. 2000. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 7527. Posey, S.C., and Bierer, B.E. 1999. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 4259. Senderowicz, A.M., et al. 1995. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 87, 46. Bubb, M.R., et al. 1994. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 14869. Scott, V.R., et al. 1988. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 32, 1154. |
Citas
| Título | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Ficha técnica | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Note that this data sheet is not lot-specific and is representative of the current specifications for this product. Please consult the vial label and the certificate of analysis for information on specific lots. Also note that shipping conditions may differ from storage conditions.
|