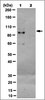
COUP-TFII orchestrates venous and lymphatic endothelial identity by homo- or hetero-dimerisation with PROX1.
Aranguren, XL; Beerens, M; Coppiello, G; Wiese, C; Vandersmissen, I; Lo Nigro, A; Verfaillie, CM; Gessler, M; Luttun, A
Journal of cell science
126
1164-75
2013
Mostrar resumen
Endothelial cell (EC) identity is in part genetically predetermined. Transcription factor NR2F2 (also known as chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor II, COUP-TFII) plays a key role in EC fate decision making; however, many of the underlying mechanisms remain enigmatic. In the present study, we demonstrate that NR2F2 differentially regulates gene expression of venous versus lymphatic ECs (LECs) and document a novel paradigm whereby NR2F2 homodimers induce a venous EC fate, while heterodimers with the LEC-specific transcription factor PROX1 instruct LEC lineage specification. NR2F2 homodimers inhibit arterial differentiation in venous ECs through direct binding to the promoter regions of the Notch target genes HEY1 and HEY2 (HEY1/2), whereas NR2F2/PROX1 heterodimers lack this inhibitory effect, resulting at least in part in non-canonical HEY1/2 expression in LECs. Furthermore, NR2F2/PROX1 heterodimers actively induce or are permissive for the expression of a major subset of LEC-specific genes. In addition to NR2F2/PROX1 heterodimerisation, the expression of HEY1 and some of these LEC-specific genes is dependent on PROX1 DNA binding. Thus, NR2F2 homodimers in venous ECs and NR2F2/PROX1 heterodimers in LECs differentially regulate EC subtype-specific genes and pathways, most prominently the Notch target genes HEY1/2. This novel mechanistic insight could pave the way for new therapeutic interventions for vascular-bed-specific disorders. | 23345397
 |
E-cadherin impairment increases cell survival through Notch-dependent upregulation of Bcl-2.
Ferreira, AC; Suriano, G; Mendes, N; Gomes, B; Wen, X; Carneiro, F; Seruca, R; Machado, JC
Human molecular genetics
21
334-43
2011
Mostrar resumen
The role of E-cadherin in tumorigenesis has been attributed to its ability to suppress invasion and metastization. However, E-cadherin impairment may have a wider impact on tumour development. We have previously shown that overexpression of mutant human E-cadherin in Drosophila produces a phenotype characteristic of downregulated Notch. Hence, we hypothesized that Notch signalling may be influenced by E-cadherin and may mediate tumour development associated with E-cadherin deficiency. De novo expression of wild-type E-cadherin in two cellular models led to a significant decrease in the activity of the Notch pathway. In contrast, the ability to inhibit Notch-1 signalling was lost in cells transfected with mutant forms of E-cadherin. Increased Notch-1 activity in E-cadherin-deficient cells correlated with increased expression of Bcl-2, and increased resistance to apoptotic stimuli. After Notch-1 inhibition, E-cadherin-deficient cells were re-sensitized to apoptosis in a similar degree to wild-type E-cadherin cells. We also show that Notch-inhibiting drugs are able to significantly inhibit the growth of E-cadherin-deficient cells xenografted into nude mice. This effect was comparable with the one observed in animals treated with the chemotherapeutic agent taxol, a chemical inducer of cell death. In conclusion, our results show that aberrant Notch-1 activation, Bcl-2 overexpression and increased cell survival are likely to play a crucial role in neoplastic transformation associated with E-cadherin impairment. These findings highlight the possibility of new targeted therapeutical strategies for the treatment of tumours associated with E-cadherin inactivation. | 21989054
 |
Expression of HES and HEY genes in infantile hemangiomas.
Adepoju, O; Wong, A; Kitajewski, A; Tong, K; Boscolo, E; Bischoff, J; Kitajewski, J; Wu, JK
Vascular cell
3
19
2010
Mostrar resumen
Infantile hemangiomas (IHs) are the most common benign tumor of infancy, yet their pathogenesis is poorly understood. IHs are believed to originate from a progenitor cell, the hemangioma stem cell (HemSC). Recent studies by our group showed that NOTCH proteins and NOTCH ligands are expressed in hemangiomas, indicating Notch signaling may be active in IHs. We sought to investigate downstream activation of Notch signaling in hemangioma cells by evaluating the expression of the basic HLH family proteins, HES/HEY, in IHs.HemSCs and hemangioma endothelial cells (HemECs) are isolated from freshly resected hemangioma specimens. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed to probe for relative gene transcript levels (normalized to beta-actin). Immunofluorescence was performed to evaluate protein expression. Co-localization studies were performed with CD31 (endothelial cells) and NOTCH3 (peri-vascular, non-endothelial cells). HemSCs were treated with the gamma secretase inhibitor (GSI) Compound E, and gene transcript levels were quantified with real-time PCR.HEY1, HEYL, and HES1 are highly expressed in HemSCs, while HEY2 is highly expressed in HemECs. Protein expression evaluation by immunofluorescence confirms that HEY2 is expressed by HemECs (CD31+ cells), while HEY1, HEYL, and HES1 are more widely expressed and mostly expressed by perivascular cells of hemangiomas. Inhibition of Notch signaling by addition of GSI resulted in down-regulation of HES/HEY genes.HES/HEY genes are expressed in IHs in cell type specific patterns; HEY2 is expressed in HemECs and HEY1, HEYL, HES1 are expressed in HemSCs. This pattern suggests that HEY/HES genes act downstream of Notch receptors that function in distinct cell types of IHs. HES/HEY gene transcripts are decreased with the addition of a gamma-secretase inhibitor, Compound E, demonstrating that Notch signaling is active in infantile hemangioma cells. Artículo Texto completo | 21834989
 |
Notch receptor and effector expression in von hippel-Lindau disease-associated central nervous system hemangioblastomas.
Merrill MJ, Edwards NA, Lonser RR
Journal of neurosurgery
2010
Mostrar resumen
Object Central nervous system hemangioblastomas are the most common manifestation of von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease, an autosomal dominant tumor suppressor syndrome that results in loss of VHL protein function and continuous upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factors. These tumors are composed of neoplastic stromal cells and abundant vasculature. Stromal cells express markers consistent with multipotent embryonically arrested hemangioblasts, which are precursors for hematopoietic and vascular lineages. Notch receptors are transmembrane signaling molecules that regulate multiple developmental processes including hematopoiesis and vasculogenesis. To investigate the importance of notch signaling in the development of VHL disease-associated CNS hemangioblastomas, the authors examined the presence of the four notch receptors and downstream notch effectors in this setting. Methods The authors used surgical specimens obtained from confirmed VHL-associated hemangioblastomas. Immunohistochemical analysis for the four notch receptors and the downstream effectors was performed on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections. Western blot analysis for HES1 was performed on frozen specimens. Results All four notch receptors are present in hemangioblastomas. NOTCH1 and NOTCH4 receptors were widely and prominently expressed in both the stromal and vascular cells, NOTCH2 receptor expression was limited to primarily stromal cells, and NOTCH3 receptor expression was limited to vascular cells. All 4 receptors displayed a nuclear presence. Immunohistochemical analysis also demonstrated that downstream notch effectors, HES1 and HES5, were uniformly expressed in tumor stromal and vascular cells, but HES3, HEY1, and HEY2 were not. Strong HES1 expression was confirmed by Western blot analysis. Conclusions The presence of all four notch receptors and downstream effector molecules suggests that the notch signaling pathway plays a critical role in the maintenance of the undifferentiated pluripotent phenotype of these tumors and in the associated vascular response. Moreover, the prominent expression of notch receptors in VHL-associated CNS hemangioblastomas reveals a new and possibly potent therapeutic target. | 21663414
 |
Expression of gap junction protein connexin36 in multiple subtypes of GABAergic neurons in adult rat somatosensory cortex.
Ma, Y; Hioki, H; Konno, M; Pan, S; Nakamura, H; Nakamura, KC; Furuta, T; Li, JL; Kaneko, T
Cerebral cortex (New York, N.Y. : 1991)
21
2639-49
2010
Mostrar resumen
To characterize connexin36 (Cx36)-expressing neurons of the adult rat somatosensory cortex, we examined fluorescence signals for Cx36 messenger RNA (mRNA) in 3 nonoverlapping subpopulations of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic interneurons, which showed immunoreactivity for 1) parvalbumin (PV); 2) somatostatin (SOM); and 3) either calretinin (CR), vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), cholecystokinin (CCK), or choline acetyltransferase (ChAT). About 80% of PV-, 52% of SOM-, 37% of CR/VIP/CCK/ChAT-immunoreactive cells displayed Cx36 signals across all cortical layers, and inversely 64%, 25%, and 9% of Cx36-expressing neurons were positive for PV, SOM, or CR/VIP/CCK/ChAT, respectively. Notably, although almost all Cx36-expressing neurons in layer (L) 4, L5, and L6 were positive for one of these markers, a substantial proportion of those in L1 (91%) and L2/3 (10%) were negative for the markers tested, suggesting that other types of neurons might express Cx36. We further investigated the colocalization of Cx36 mRNA and α-actinin2 immunoreactivity, as a marker for late-spiking GABAergic neurons, by using mirror-image sections. Surprisingly, more than 77% of α-actinin2-positive cells displayed Cx36 signals in L1-L3, and about 49% and 13% of Cx36-expressing neurons were positive for α-actinin2 in L1 and L2/3, respectively. These findings suggest that all the subtypes of GABAergic interneurons might form gap junctions in the neocortex. | 21467210
 |