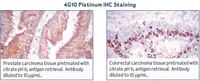
Platelet actin nodules are podosome-like structures dependent on Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein and ARP2/3 complex.
Poulter, NS; Pollitt, AY; Davies, A; Malinova, D; Nash, GB; Hannon, MJ; Pikramenou, Z; Rappoport, JZ; Hartwig, JH; Owen, DM; Thrasher, AJ; Watson, SP; Thomas, SG
Nature communications
6
7254
2015
Mostrar resumen
The actin nodule is a novel F-actin structure present in platelets during early spreading. However, only limited detail is known regarding nodule organization and function. Here we use electron microscopy, SIM and dSTORM super-resolution, and live-cell TIRF microscopy to characterize the structural organization and signalling pathways associated with nodule formation. Nodules are composed of up to four actin-rich structures linked together by actin bundles. They are enriched in the adhesion-related proteins talin and vinculin, have a central core of tyrosine phosphorylated proteins and are depleted of integrins at the plasma membrane. Nodule formation is dependent on Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASp) and the ARP2/3 complex. WASp(-/-) mouse blood displays impaired platelet aggregate formation at arteriolar shear rates. We propose actin nodules are platelet podosome-related structures required for platelet-platelet interaction and their absence contributes to the bleeding diathesis of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. | | | 26028144
 |
Digital microfluidic assay for protein detection.
Mok, J; Mindrinos, MN; Davis, RW; Javanmard, M
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
111
2110-5
2014
Mostrar resumen
Global studies of the human proteome have revealed a plethora of putative protein biomarkers. However, their application for early disease detection remains at a standstill without suitable methods to realize their utility in the clinical setting. There thus continues to be tremendous interest in developing new technology for sensitive protein detection that is both low in cost and carries a small footprint to be able to be used at the point of care. The current gold standard method for protein biomarker detection is the ELISA, which measures protein abundance using bulky fluorescent scanners that lack portability. Here, we present a digital microfluidic platform for protein biomarker detection that is low in cost compared with standard optical detection methods, without any compromise in sensitivity. This platform furthermore makes use of simple electronics, enabling its translation into a portable handheld device, and has been developed in a manner that can easily be adapted to assay different types of proteomic biomarkers. We demonstrate its utility in quantifying not only protein abundance, but also activity. Interleukin-6 abundance could be assayed from concentrations as low as 50 pM (an order of magnitude lower than that detectable by a comparable laboratory designed ELISA) using less than 5 μL of sample, and Abelson tyrosine kinase activity was detectable in samples containing 100 pM of kinase. | | | 24449893
 |
SILAC-based quantitative proteomic analysis of human lung cell response to copper oxide nanoparticles.
Edelmann, MJ; Shack, LA; Naske, CD; Walters, KB; Nanduri, B
PloS one
9
e114390
2014
Mostrar resumen
Copper (II) oxide (CuO) nanoparticles (NP) are widely used in industry and medicine. In our study we evaluated the response of BEAS-2B human lung cells to CuO NP, using Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC)-based proteomics and phosphoproteomics. Pathway modeling of the protein differential expression showed that CuO NP affect proteins relevant in cellular function and maintenance, protein synthesis, cell death and survival, cell cycle and cell morphology. Some of the signaling pathways represented by BEAS-2B proteins responsive to the NP included mTOR signaling, protein ubiquitination pathway, actin cytoskeleton signaling and epithelial adherens junction signaling. Follow-up experiments showed that CuO NP altered actin cytoskeleton, protein phosphorylation and protein ubiquitination level. | Western Blotting | | 25470785
 |
Angiotensin II induces membrane trafficking of natively expressed transient receptor potential vanilloid type 4 channels in hypothalamic 4B cells.
Saxena, A; Bachelor, M; Park, YH; Carreno, FR; Nedungadi, TP; Cunningham, JT
American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology
307
R945-55
2014
Mostrar resumen
Transient receptor potential vanilloid family type 4 (TRPV4) channels are expressed in central neuroendocrine neurons and have been shown to be polymodal in other systems. We previously reported that in the rodent, a model of dilutional hyponatremia associated with hepatic cirrhosis, TRPV4 expression is increased in lipid rafts from the hypothalamus and that this effect may be angiotensin dependent. In this study, we utilized the immortalized neuroendocrine rat hypothalamic 4B cell line to more directly test the effects of angiotensin II (ANG II) on TRPV4 expression and function. Our results demonstrate the expression of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) transcripts, for sex-determining region Y (SRY) (male genotype), arginine vasopressin (AVP), TRPV4, and ANG II type 1a and 1b receptor in 4B cells. After a 1-h incubation in ANG II (100 nM), 4B cells showed increased TRPV4 abundance in the plasma membrane fraction, and this effect was prevented by the ANG II type 1 receptor antagonist losartan (1 μM) and by a Src kinase inhibitor PP2 (10 μM). Ratiometric calcium imaging experiments demonstrated that ANG II incubation potentiated TRPV4 agonist (GSK 1016790A, 20 nM)-induced calcium influx (control 18.4 ± 2.8% n = 5 and ANG II 80.5 ± 2.4% n = 5). This ANG II-induced increase in calcium influx was also blocked by 1 μM losartan and 10 μM PP2 (losartan 26.4 ± 3.8% n = 5 and PP2 19.7 ± 3.9% n = 5). Our data suggests that ANG II can increase TRPV4 channel membrane expression in 4B cells through its action on AT1R involving a Src kinase pathway. | | | 25080500
 |
Involvement of de novo synthesized palmitate and mitochondrial EGFR in EGF induced mitochondrial fusion of cancer cells.
Bollu, LR; Ren, J; Blessing, AM; Katreddy, RR; Gao, G; Xu, L; Wang, J; Su, F; Weihua, Z
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.)
13
2415-30
2014
Mostrar resumen
Increased expressions of fatty acid synthase (FASN) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are common in cancer cells. De novo synthesis of palmitate by FASN is critical for the survival of cancer cells via mechanisms independent of its role as an energy substrate. Besides the plasma membrane and the nucleus, EGFR can also localize at the mitochondria; however, signals that can activate mitochondrial EGFR (mtEGFR) and the functions of mtEGFR of cancer cells remain unknown. The present study characterizes mtEGFR in the mitochondria of cancer cells (prostate and breast) and reveals that mtEGFR can promote mitochondrial fusion through increasing the protein levels of fusion proteins PHB2 and OPA1. Activation of plasma membranous EGFR (pmEGFR) stimulates the de novo synthesis of palmitate through activation of FASN and ATP-citrate lyase (ACLy). In vitro kinase assay with isolated mitochondria shows that palmitate can activate mtEGFR. Inhibition of FASN blocks the mtEGFR phosphorylation and palmitoylation induced by EGF. Mutational studies show that the cysteine 797 is important for mtEGFR activation and palmitoylation. Inhibition of FASN can block EGF induced mitochondrial fusion and increased the sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor. In conclusion, these results suggest that mtEGFR can be activated by pmEGFR through de novo synthesized palmitate to promote mitochondrial fusion and survival of cancer cells. This mechanism may serve as a novel target to improve EGFR-based cancer therapy. | | | 25483192
 |
Mer or Axl receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition promotes apoptosis, blocks growth and enhances chemosensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer.
Linger, RM; Cohen, RA; Cummings, CT; Sather, S; Migdall-Wilson, J; Middleton, DH; Lu, X; Barón, AE; Franklin, WA; Merrick, DT; Jedlicka, P; DeRyckere, D; Heasley, LE; Graham, DK
Oncogene
32
3420-31
2013
Mostrar resumen
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a prevalent and devastating disease that claims more lives than breast, prostate, colon and pancreatic cancers combined. Current research suggests that standard chemotherapy regimens have been optimized to maximal efficiency. Promising new treatment strategies involve novel agents targeting molecular aberrations present in subsets of NSCLC. We evaluated 88 human NSCLC tumors of diverse histology and identified Mer and Axl as receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) overexpressed in 69% and 93%, respectively, of tumors relative to surrounding normal lung tissue. Mer and Axl were also frequently overexpressed and activated in NSCLC cell lines. Ligand-dependent Mer or Axl activation stimulated MAPK, AKT and FAK signaling pathways indicating roles for these RTKs in multiple oncogenic processes. In addition, we identified a novel pro-survival pathway-involving AKT, CREB, Bcl-xL, survivin, and Bcl-2-downstream of Mer, which is differentially modulated by Axl signaling. We demonstrated that short hairpin RNA (shRNA) knockdown of Mer or Axl significantly reduced NSCLC colony formation and growth of subcutaneous xenografts in nude mice. Mer or Axl knockdown also improved in vitro NSCLC sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents by promoting apoptosis. When comparing the effects of Mer and Axl knockdown, Mer inhibition exhibited more complete blockade of tumor growth while Axl knockdown more robustly improved chemosensitivity. These results indicate that Mer and Axl have complementary and overlapping roles in NSCLC and suggest that treatment strategies targeting both RTKs may be more effective than singly-targeted agents. Our findings validate Mer and Axl as potential therapeutic targets in NSCLC and provide justification for development of novel therapeutic compounds that selectively inhibit Mer and/or Axl. | | | 22890323
 |
Antibodies against low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 induce myasthenia gravis.
Shen, C; Lu, Y; Zhang, B; Figueiredo, D; Bean, J; Jung, J; Wu, H; Barik, A; Yin, DM; Xiong, WC; Mei, L
The Journal of clinical investigation
123
5190-202
2013
Mostrar resumen
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is the most common disorder affecting the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). MG is frequently caused by autoantibodies against acetylcholine receptor (AChR) and a kinase critical for NMJ formation, MuSK; however, a proportion of MG patients are double-negative for anti-AChR and anti-MuSK antibodies. Recent studies in these subjects have identified autoantibodies against low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 (LRP4), an agrin receptor also critical for NMJ formation. LRP4 autoantibodies have not previously been implicated in MG pathogenesis. Here we demonstrate that mice immunized with the extracellular domain of LRP4 generated anti-LRP4 antibodies and exhibited MG-associated symptoms, including muscle weakness, reduced compound muscle action potentials (CMAPs), and compromised neuromuscular transmission. Additionally, fragmented and distorted NMJs were evident at both the light microscopic and electron microscopic levels. We found that anti-LRP4 sera decreased cell surface LRP4 levels, inhibited agrin-induced MuSK activation and AChR clustering, and activated complements, revealing potential pathophysiological mechanisms. To further confirm the pathogenicity of LRP4 antibodies, we transferred IgGs purified from LRP4-immunized rabbits into naive mice and found that they exhibited MG-like symptoms, including reduced CMAP and impaired neuromuscular transmission. Together, these data demonstrate that LRP4 autoantibodies induce MG and that LRP4 contributes to NMJ maintenance in adulthood. | | | 24200689
 |
Themis sets the signal threshold for positive and negative selection in T-cell development.
Fu, G; Casas, J; Rigaud, S; Rybakin, V; Lambolez, F; Brzostek, J; Hoerter, JA; Paster, W; Acuto, O; Cheroutre, H; Sauer, K; Gascoigne, NR
Nature
504
441-5
2013
Mostrar resumen
Development of a self-tolerant T-cell receptor (TCR) repertoire with the potential to recognize the universe of infectious agents depends on proper regulation of TCR signalling. The repertoire is whittled down during T-cell development in the thymus by the ability of quasi-randomly generated TCRs to interact with self-peptides presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins. Low-affinity TCR interactions with self-MHC proteins generate weak signals that initiate 'positive selection', causing maturation of CD4- or CD8αβ-expressing 'single-positive' thymocytes from CD4(+)CD8αβ(+) 'double-positive' precursors. These develop into mature naive T cells of the secondary lymphoid organs. TCR interaction with high-affinity agonist self-ligands results in 'negative selection' by activation-induced apoptosis or 'agonist selection' of functionally differentiated self-antigen-experienced T cells. Here we show that positive selection is enabled by the ability of the T-cell-specific protein Themis to specifically attenuate TCR signal strength via SHP1 recruitment and activation in response to low- but not high-affinity TCR engagement. Themis acts as an analog-to-digital converter translating graded TCR affinity into clear-cut selection outcome. By dampening mild TCR signals Themis increases the affinity threshold for activation, enabling positive selection of T cells with a naive phenotype in response to low-affinity self-antigens. | Immunoprecipitation | | 24226767
 |
Localization and identification of sumoylated proteins in human sperm: excessive sumoylation is a marker of defective spermatozoa.
Vigodner, M; Shrivastava, V; Gutstein, LE; Schneider, J; Nieves, E; Goldstein, M; Feliciano, M; Callaway, M
Human reproduction (Oxford, England)
28
210-23
2013
Mostrar resumen
Sumoylation is a type of post-translational modification that is implicated in the regulation of numerous cellular events. However, its role in the function of human sperm has not yet been characterized.In this study, both immunofluorescence and electron microscopy revealed that small ubiquitin-like modifiers (SUMO) SUMO1 and SUMO2/3 were highly enriched in the neck area of human sperm that is associated with the redundant nuclear envelope and were also detectable in the flagella and some head regions. Similar localization patterns of SUMO were also observed in mouse and fly sperm. Nonmotile, two-tailed, curled tailed, misshapen, microcephalic (small head) and aciphalic (no head) sperm exhibited abnormally high levels of sumoylation in their neck and tail regions relative to normal sperm. Numerous sumoylated proteins, ranging from 20 to 260 kDa, were detected via western blotting and identified by mass spectrometry, and 55 SUMO targets that were present specifically in human sperm, and not in the control fraction, corresponded to flagella proteins, proteins involved in the maturation and differentiation of sperm, heat shock proteins and important glycolytic and mitochondrial enzymes. The targets that were identified included proteins with specific functions in germ cells and sperm, such as heat shock-related 70-kDa protein 2, outer dense fiber protein 3, A-kinase anchor proteins 3 and 4, L-lactate dehydrogenase C, sperm protein associated with the nucleus on the X chromosome B/F, valosin-containing protein, seminogelins, histone H4 and ubiquitin. Coimmunoprecipitation experiments confirmed the sumoylation of semenogelin and indicated that some sperm proteins are modified by sumoylation and ubiquitination simultaneously.Numerous proteins are modified by sumoylation in human sperm; excessive sumoylation is a marker of defective spermatozoa. | Western Blotting | | 23077236
 |
Identification of a Src tyrosine kinase/SIAH2 E3 ubiquitin ligase pathway that regulates C/EBPδ expression and contributes to transformation of breast tumor cells.
Sarkar, TR; Sharan, S; Wang, J; Pawar, SA; Cantwell, CA; Johnson, PF; Morrison, DK; Wang, JM; Sterneck, E
Molecular and cellular biology
32
320-32
2011
Mostrar resumen
The transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta (C/EBPδ, CEBPD) is a tumor suppressor that is downregulated during breast cancer progression but may also promote metastasis. Here, we have investigated the mechanism(s) regulating C/EBPδ expression and its role in human breast cancer cells. We describe a novel pathway by which the tyrosine kinase Src downregulates C/EBPδ through the SIAH2 E3 ubiquitin ligase. Src phosphorylates SIAH2 in vitro and leads to tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of SIAH2 in breast tumor cell lines. SIAH2 interacts with C/EBPδ, but not C/EBPβ, and promotes its polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Src/SIAH2-mediated inhibition of C/EBPδ expression supports elevated cyclin D1 levels, phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein (Rb), motility, invasive properties, and survival of transformed cells. Pharmacological inhibition of Src family kinases by SKI-606 (bosutinib) induces C/EBPδ expression in an SIAH2-dependent manner, which is necessary for "therapeutic" responses to SKI-606 in vitro. Ectopic expression of degradation-resistant mutants of C/EBPδ, which do not interact with SIAH2 and/or cannot be polyubiquitinated, prevents full transformation of MCF-10A cells by activated Src (Src truncated at amino acid 531 [Src-531]) in vitro. These data reveal that C/EBPδ expression can be regulated at the protein level by oncogenic Src kinase signals through SIAH2, thus contributing to breast epithelial cell transformation. | | | 22037769
 |