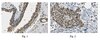
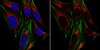
BRCA1 and FancJ cooperatively promote interstrand crosslinker induced centrosome amplification through the activation of polo-like kinase 1.
Zou, J; Zhang, D; Qin, G; Chen, X; Wang, H; Zhang, D
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.)
13
3685-97
2014
Show Abstract
DNA damage response (DDR) and the centrosome cycle are 2 of the most critical cellular processes affecting the genome stability in animal cells. Yet the cross-talks between DDR and the centrosome are poorly understood. Here we showed that deficiency of the breast cancer 1, early onset gene (BRCA1) induces centrosome amplification in non-stressed cells as previously reported while attenuating DNA damage-induced centrosome amplification (DDICA) in cells experiencing prolonged genotoxic stress. Mechanistically, the function of BRCA1 in promoting DDICA is through binding and recruiting polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) to the centrosome. In a recent study, we showed that FancJ also suppresses centrosome amplification in non-stressed cells while promoting DDICA in both hydroxyurea and mitomycin C treated cells. FancJ is a key component of the BRCA1 B-complex. Here, we further demonstrated that, in coordination with BRCA1, FancJ promotes DDICA by recruiting both BRCA1 and PLK1 to the centrosome in the DNA damaged cells. Thus, we have uncovered a novel role of BRCA1 and FancJ in the regulation of DDICA. Dysregulation of DDR or centrosome cycle leads to aneuploidy, which is frequently seen in both solid and hematological cancers. BRCA1 and FancJ are known tumor suppressors and have well-recognized functions in DNA damage checkpoint and DNA repair. Together with our recent findings, we demonstrated here that BRCA1 and FancJ also play an important role in centrosome cycle especially in DDICA. DDICA is thought to be an alternative fail-safe mechanism to prevent cells experiencing severe DNA damage from becoming carcinogenic. Therefore, BRCA1 and FancJ are potential liaisons linking early DDR with the DDICA. We propose that together with their functions in DDR, the role of BRCA1 and FancJ in the activation of DDICA is also crucial for their tumor suppression functions in vivo. | | 25483079
 |
FancJ regulates interstrand crosslinker induced centrosome amplification through the activation of polo-like kinase 1.
Zou, J; Tian, F; Li, J; Pickner, W; Long, M; Rezvani, K; Wang, H; Zhang, D
Biology open
2
1022-31
2013
Show Abstract
DNA damage response (DDR) and the centrosome cycle are two of the most critical processes for maintaining a stable genome in animals. Sporadic evidence suggests a connection between these two processes. Here, we report our findings that six Fanconi Anemia (FA) proteins, including FancI and FancJ, localize to the centrosome. Intriguingly, we found that the localization of FancJ to the mother centrosome is stimulated by a DNA interstrand crosslinker, Mitomycin C (MMC). We further show that, in addition to its role in interstrand crosslinking (ICL) repair, FancJ also regulates the normal centrosome cycle as well as ICL induced centrosome amplification by activating the polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1). We have uncovered a novel function of FancJ in centrosome biogenesis and established centrosome amplification as an integral part of the ICL response. | | 24167712
 |
Leukemia-associated RhoGEF (LARG) is a novel RhoGEF in cytokinesis and required for the proper completion of abscission.
Martz, MK; Grabocka, E; Beeharry, N; Yen, TJ; Wedegaertner, PB
Molecular biology of the cell
24
2785-94
2013
Show Abstract
Proper completion of mitosis requires the concerted effort of multiple RhoGEFs. Here we show that leukemia-associated RhoGEF (LARG), a RhoA-specific RGS-RhoGEF, is required for abscission, the final stage of cytokinesis, in which the intercellular membrane is cleaved between daughter cells. LARG colocalizes with α-tubulin at the spindle poles before localizing to the central spindle. During cytokinesis, LARG is condensed in the midbody, where it colocalizes with RhoA. HeLa cells depleted of LARG display apoptosis during cytokinesis with unresolved intercellular bridges, and rescue experiments show that expression of small interfering RNA-resistant LARG prevents this apoptosis. Moreover, live cell imaging of LARG-depleted cells reveals greatly delayed fission kinetics in abscission in which a population of cells with persistent bridges undergoes apoptosis; however, the delayed fission kinetics is rescued by Aurora-B inhibition. The formation of a Flemming body and thinning of microtubules in the intercellular bridge of cells depleted of LARG is consistent with a defect in late cytokinesis, just before the abscission event. In contrast to studies of other RhoGEFs, particularly Ect2 and GEF-H1, LARG depletion does not result in cytokinetic furrow regression nor does it affect internal mitotic timing. These results show that LARG is a novel and temporally distinct RhoGEF required for completion of abscission. | Immunofluorescence | 23885121
 |
Polo-like kinase 2 is a mediator of hedgehog survival signaling in cholangiocarcinoma.
Fingas, CD; Mertens, JC; Razumilava, N; Sydor, S; Bronk, SF; Christensen, JD; Rizvi, SH; Canbay, A; Treckmann, JW; Paul, A; Sirica, AE; Gores, GJ
Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.)
58
1362-74
2013
Show Abstract
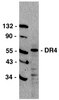
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) cells paradoxically express the death ligand tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and thus rely on potent survival signals to circumvent cell death by TRAIL. Hedgehog (Hh) signaling is an important survival pathway in CCA. Herein, we further examine the mechanisms whereby Hh signaling mediates apoptosis resistance in CCA, revealing a pivotal role for the cell division regulating serine/threonine kinase polo-like kinase 2 (PLK2). We employed 50 human CCA samples (25 intrahepatic and 25 extrahepatic CCA) as well as human KMCH-1, Mz-CHA-1, and HUCCT-1 CCA cells for these studies. In vivo experiments were conducted using a syngeneic rat orthotopic CCA model. In human samples, polo-like kinase (PLK)1/2/3-immunoreactive cancer cells were present in the preponderance of intra- and extrahepatic CCA specimens. Inhibition of Hh signaling by cyclopamine reduced PLK2, but not PLK1 or PLK3, messenger RNA and protein expression in vehicle-treated and sonic Hh-treated CCA cells, confirming our previous microarray study. PLK2 regulation by Hh signaling appears to be direct, because the Hh transcription factors, glioma-associated oncogene 1 and 2, bind to the PLK2 promotor. Moreover, inhibition of PLK2 by the PLK inhibitor, BI 6727 (volasertib), or PLK2 knockdown was proapoptotic in CCA cells. BI 6727 administration or PLK2 knockdown decreased cellular protein levels of antiapoptotic myeloid cell leukemia 1 (Mcl-1), an effect reversed by the proteasome inhibitor, MG-132. Finally, BI 6727 administration reduced Mcl-1 protein expression in CCA cells, resulting in CCA cell apoptosis and tumor suppression in vivo.PLK2 appears to be an important mediator of Hh survival signaling. These results suggest PLK inhibitors to be of therapeutic value for treatment of human CCA. | Western Blotting | 23703673
 |
BRCA1 downregulates the kinase activity of Polo-like kinase 1 in response to replication stress.
Zou, J; Rezvani, K; Wang, H; Lee, KS; Zhang, D
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.)
12
2255-65
2013
Show Abstract
In response to DNA damage or replication stress, proliferating cells are arrested at different cell cycle stages for DNA repair by downregulating the activity of both the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and other important cell cycle kinases, including Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) . The signaling pathway to inhibit CDKs is relatively well understood, and breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) and other DNA damage response (DDR) factors play a key role in this process. However, the DNA damage-induced inhibition of PLK1 is still largely a mystery. Here we show that DNA damage and replication stress stimulate the association between BRCA1 and PLK1. Most importantly, we demonstrate that BRCA1 downregulates the kinase activity of PLK1 by modulating the dynamic interactions of Aurora A, hBora, and PLK1. Together with previous findings, we propose that in response to replication stress and DNA damage, BRCA1 plays a critical role in downregulating the kinase activity of both CDKs and PLK1. | | 24067368
 |
Neuronal c-Abl activation leads to induction of cell cycle and interferon signaling pathways.
Schlatterer, SD; Suh, HS; Conejero-Goldberg, C; Chen, S; Acker, CM; Lee, SC; Davies, P
Journal of neuroinflammation
9
208
2012
Show Abstract
Expression of active c-Abl in adult mouse forebrain neurons in the AblPP/tTA mice resulted in severe neurodegeneration, particularly in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. Neuronal loss was preceded and accompanied by substantial microgliosis and astrocytosis. In contrast, expression of constitutively active Arg (Abl-related gene) in mouse forebrain neurons (ArgPP/tTA mice) caused no detectable neuronal loss or gliosis, although protein expression and kinase activity were at similar levels to those in the AblPP/tTA mice.To begin to elucidate the mechanism of c-Abl-induced neuronal loss and gliosis, gene expression analysis of AblPP/tTA mouse forebrain prior to development of overt pathology was performed. Selected results from gene expression studies were validated with quantitative reverse transcription PCR , immunoblotting and bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) labeling, and by immunocytochemistry.Two of the top pathways upregulated in AblPP/tTA mice with c-Abl expression for 2 weeks were cell cycle and interferon signaling. However, only the expression of interferon signaling pathway genes remained elevated at 4 weeks of c-Abl induction. BrdU incorporation studies confirm that, while the cell cycle pathway is upregulated in AblPP/tTA mice at 2 weeks of c-Abl induction, the anatomical localization of the pathway is not consistent with previous pathology seen in the AblPP/tTA mice. Increased expression and activation of STAT1, a known component of interferon signaling and interferon-induced neuronal excitotoxicity, is an early consequence of c-Abl activation in AblPP/tTA mice and occurs in the CA1 region of the hippocampus, the same region that goes on to develop severe neurodegenerative pathology and neuroinflammation. Interestingly, no upregulation of gene expression of interferons themselves was detected.Our data suggest that the interferon signaling pathway may play a role in the pathologic processes caused by c-Abl expression in neurons, and that the AblPP/tTA mouse may be an excellent model for studying sterile inflammation and the effects of interferon signaling in the brain. | | 22938163
 |
Female infertility in PDE3A(-/-) mice: polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) may be a target of protein kinase A (PKA) and involved in meiotic arrest of oocytes from PDE3A(-/-) mice.
Shen, W; Ahmad, F; Hockman, S; Ma, J; Omi, H; Raghavachari, N; Manganiello, V
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.)
9
4720-34
2010
Show Abstract
Mechanisms of cAMP/PKA-induced meiotic arrest in oocytes are not completely identified. In cultured, G2/M-arrested PDE3A(-/-) murine oocytes, elevated PKA activity was associated with inactivation of Cdc2 and Plk1, and inhibition of phosphorylation of histone H3 (S10) and of dephosphorylation of Cdc25B (S323) and Cdc2 (Thr14/Tyr15). In cultured WT oocytes, PKA activity was transiently reduced and then increased to that observed in PDE3A(-/-) oocytes; Cdc2 and Plk1 were activated, phosphorylation of histone H3 (S10) and dephosphorylation of Cdc25B (S323) and Cdc2 (Thr14/Tyr15) were observed. In WT oocytes, PKAc were rapidly translocated into nucleus, and then to the spindle apparatus, but in PDE3A(-/-) oocytes, PKAc remained in the cytosol. Plk1 was reactivated by incubation of PDE3A(-/-) oocytes with PKA inhibitor, Rp-cAMPS. PDE3A was co-localized with Plk1 in WT oocytes, and co-immunoprecipitated with Plk1 in WT ovary and Hela cells. PKAc phosphorylated rPlk1 and Hela cell Plk1 and inhibited Plk1 activity in vitro. Our results suggest that PKA-induced inhibition of Plk1 may be critical in oocyte meiotic arrest and female infertility in PDE3A(-/-) mice. | | 21099356
 |
14-3-3 theta binding to cell cycle regulatory factors is enhanced by HIV-1 Vpr.
Bolton, DL; Barnitz, RA; Sakai, K; Lenardo, MJ
Biology direct
3
17
2008
Show Abstract
Despite continuing advances in our understanding of AIDS pathogenesis, the mechanism of CD4+ T cell depletion in HIV-1-infected individuals remains unclear. The HIV-1 Vpr accessory protein causes cell death, likely through a mechanism related to its ability to arrest cells in the G2,M phase. Recent evidence implicated the scaffold protein, 14-3-3, in Vpr cell cycle blockade.We found that in human T cells, 14-3-3 plays an active role in mediating Vpr-induced cell cycle arrest and reveal a dramatic increase in the amount of Cdk1, Cdc25C, and CyclinB1 bound to 14-3-3 theta during Vprv-induced G2,M arrest. By contrast, a cell-cycle-arrest-dead Vpr mutant failed to augment 14-3-3 theta association with Cdk1 and CyclinB1. Moreover, G2,M arrest caused by HIV-1 infection strongly correlated with a disruption in 14-3-3 theta binding to centrosomal proteins, Plk1 and centrin. Finally, Vpr caused elevated levels of CyclinB1, Plk1, and Cdk1 in a complex with the nuclear transport and spindle assembly protein, importin beta.Thus, our data reveal a new facet of Vpr-induced cell cycle arrest involving previously unrecognized abnormal rearrangements of multiprotein assemblies containing key cell cycle regulatory proteins. | | 18445273
 |
The family of polo-like kinases.
Golsteyn, R M, et al.
Prog Cell Cycle Res, 2: 107-14 (1996)
1996
Show Abstract
Here we discuss members of a new family of serine/threonine protein kinases with a likely role in cell cycle control. These kinases are referred to as polo-like kinases, after the prototypic founding member of the family, the polo gene product of Drosophila melanogaster. The polo kinase was originally identified in mutants that display abnormal mitotic spindle organization. Subsequently, potential homologues of Drosophila polo have been identified in yeasts (Cdc5p in Saccharomyces cerevisiae; plo1+ in Schizosaccharmoyces pombe) and in mammals (polo-like kinase 1; Plk1). Genetic and biochemical studies suggest that polo, Cdc5p and plo1+ may be required for mitotic spindle organization and, possibly, for cytokinesis. Likewise, the patterns of expression, activity and subcellular localization of Plk1 strongly suggest that this mammalian kinase functions also during mitosis, possibly in spindle assembly and function. In addition to Plk1, however, more distantly related members of the polo-like kinase family have been identified in mammalian cells, and the available data are consistent with the idea that some of these may act earlier in the cell cycle, possibly during G1. If this hypothesis is correct, different members of the polo-like kinase family would act at several points during the cell cycle, reminiscent of the behaviour of Cdk/cyclin complexes. | | 9552388
 |