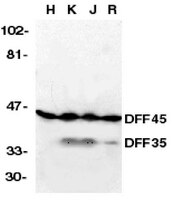
Cleavage of CAD inhibitor in CAD activation and DNA degradation during apoptosis.
Sakahira, H, et al.
Nature, 391: 96-9 (1998)
1998
Abstract anzeigen
Various molecules such as cytokines and anticancer drugs, as well as factor deprivation, rapidly induce apoptosis (programmed cell death), which is morphologically characterized by cell shrinkage and the blebbing of plasma membranes and by nuclear condensation. Caspases, particularly caspase 3, are proteases that are activated during apoptosis and which cleave substrates such as poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, actin, fodrin, and lamin. Apoptosis is also accompanied by the internucleosomal degradation of chromosomal DNA. In the accompanying Article, we have identified and molecularly cloned a caspase-activated deoxyribonuclease (CAD) and its inhibitor (ICAD). Here we show that caspase 3 cleaves ICAD and inactivates its CAD-inhibitory effect. We identified two caspase-3 cleavage sites in ICAD by site-directed mutagenesis. When human Jurkat cells were transformed with ICAD-expressing plasmid, occupation of the receptor Fas, which normally triggers apoptosis, did not result in DNA degradation. The ICAD transformants were also resistant to staurosporine-induced DNA degradation, although staurosporine still killed the cells by activating caspase. Our results indicate that activation of CAD downstream of the caspase cascade is responsible for internucleosomal DNA degradation during apoptosis, and that ICAD works as an inhibitor of this process. | 9422513
 |
Involvement of an ICE-like protease in Fas-mediated apoptosis.
Enari, M, et al.
Nature, 375: 78-81 (1995)
1994
Abstract anzeigen
Fas is a type-I membrane protein that transduces an apoptotic signal. Binding of Fas ligand or agonistic anti-Fas antibody to Fas kills the cells by apoptosis. Studies in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans have suggested that proteases such as interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme (ICE) or the product of the C. elegans cell-death gene ced-3 are involved in apoptotic signal transduction. The activity of ICE can be inhibited by the product of crmA, a cytokine-response modifier gene encoded by cowpox virus. We report here that expression of crmA inhibits cytotoxicity induced by anti-Fas antibody or tumour necrosis factor (TNF). We have found a specific ICE inhibitor tetrapeptide (acetyl-Tyr-Val-Ala-Asp-chloromethylketone) that also prevents apoptosis induced by anti-Fas antibody. These results suggest an involvement of an ICE-like protease in Fas-mediated apoptosis and TNF-induced cytotoxicity. | 7536900
 |