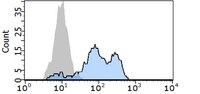
Role of S100A8 and S100A9 in neutrophil recruitment in response to monosodium urate monohydrate crystals in the air-pouch model of acute gouty arthritis.
Ryckman, Carle, et al.
Arthritis Rheum., 48: 2310-20 (2003)
2003
Zobrazit abstrakt
To examine the role of chemokines, S100A8, and S100A9 in neutrophil accumulation induced by the causative agent of gout, monosodium urate monohydrate (MSU) crystals. | 12905486
 |
The heterodimeric complex of MRP-8 (S100A8) and MRP-14 (S100A9). Antibody recognition, epitope definition and the implications for structure.
Hessian, P A and Fisher, L
Eur. J. Biochem., 268: 353-63 (2001)
2001
Zobrazit abstrakt
The S100 calcium-binding proteins MRP-8 (S100A8) and MRP-14 (S100A9) form a heterodimeric complex in the cytosol of monocyte and neutrophil cell types circulating in peripheral blood. This complex, but not the individual subunit proteins, is specifically recognized by mAb 27E10. Domains in MRP-8 and MRP-14 mediating heterodimeric complex formation have not yet been identified but it is predicted that the structure of the complex will be similar to homodimeric forms of other S100 proteins. This study makes use of the specificity of mAb 27E10, and an in vitro coupled transcription/translation system to further examine the formation and maintenance of the MRP-8/MRP-14 complex. Truncated mutants of MRP-14 that lack the N-terminal residues 1-4 or the extended C-terminal 'tail', both complex with MRP-8. These deleted domains of MRP-14 are therefore not essential for complex formation. Peptides from MRP-8 or MRP-14, used to induce the epitope recognized by mAb 27E10, show that a critical interaction in complex formation involves the N-terminal of MRP-8 interacting with MRP-14. Phage display analysis defined composite residues of the epitope recognized by mAb 27E10. The epitope is trans-subunit, composed of residues in the C-terminal ends of helix IV in MRP-14 and helix I of MRP-8. A further complex-specific mAb, named 5.5, recognizes the hydrophobic residues in helix IV of MRP-8, exposed during heterodimer formation. The definition of these two epitopes indicates that helices IV of MRP-8 and MRP-14 are also a prominent point of interaction and suggests that the subunit proteins will assume an antiparallel alignment in the heterodimer, similar in structure to the homodimeric forms of S100 proteins. | 11168370
 |
Identification of p8,14 as a highly abundant heterodimeric calcium binding protein complex of myeloid cells.
Edgeworth, J, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 266: 7706-13 (1991)
1991
Zobrazit abstrakt
In this report we describe the biochemical characterization of neutrophil and monocyte p8 and p14. Together the two proteins comprise approximately 45% of cytosolic protein in neutrophils and approximately 40-fold less in monocytes. They fractionated together in several chromatographic procedures and were found to exist as a noncovalently associated complex with a stoichiometry of 1:1, named p8,14. Cross-linking experiments showed p8,14 to form heterodimers under conditions simulating the cytosol. An apparent molecular mass of 35,000 daltons was obtained for the p8,14 complex in molecular sizing experiments which suggests the presence of modifications or distinctive structural features. Two major forms of p14 can be identified by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, both of which form heterodimers with p8. The lower molecular weight variant of p14 lacks Cys-3 (Met-Thr-Cys-Lys-Met...) suggesting that differing translational start sites account for these two forms of p14. A protocol has been devised for the rapid purification of milligram quantities of p8 and p14 from neutrophil cytosol using fast-protein liquid chromatography. | 2019594
 |
Monoclonal antibody 5.5 reacts with p8,14, a myeloid molecule associated with some vascular endothelium.
Hogg, N, et al.
Eur. J. Immunol., 19: 1053-61 (1989)
1988
Zobrazit abstrakt
The movement of mononuclear phagocytes and neutrophils from the circulation into tissues is a process which is not completely understood. Monoclonal antibody 5.5 is specific for an 8/14-kDa molecule known variously as the CF antigen, L1 molecule or MRP8 and 14. We show that this molecule, which will be named p8,14 in this study, is expressed in all circulating monocytes and neutrophils as an intracellular product (as well as some types of epithelium). Tissue staining patterns suggest that when monocytes and neutrophils adhere to vascular endothelium, they release this molecule onto the associated endothelium. This process occurs with single monocytes and when monocytes form part of an inflammatory infiltrate. Monoclonal antibody 5.5 does not react with cultured endothelial cells even when stimulated with phorbol ester, tumor necrosis factor, interferon-gamma or interleukin 1 alpha providing further evidence that myeloid cells are the source of the p8,14 in this interactive process. Monocytes which have moved further into such tissues and tissue macrophages in general are monoclonal antibody 5.5 negative, suggesting that the ability to synthesize this molecule may be lost when monocytes leave the circulation and enter tissues. These results indicate that p8,14 plays a role in the interaction between myeloid cells and the vascular endothelium to which they adhere prior to leaving the circulation. | 2666142
 |