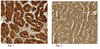
Curcumin attenuates brain edema in mice with intracerebral hemorrhage through inhibition of AQP4 and AQP9 expression.
Wang, BF; Cui, ZW; Zhong, ZH; Sun, YH; Sun, QF; Yang, GY; Bian, LG
Acta pharmacologica Sinica
36
939-48
2015
Zobrazit abstrakt
Aquaporins (AQPs) are the water-channels that play important roles in brain water homeostasis and in cerebral edema induced by brain injury. In this study we investigated the relationship between AQPs and a neuroprotective agent curcumin that was effective in the treatment of brain edema in mice with intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH).ICH was induced in mice by autologous blood infusion. The mice immediately received curcumin (75, 150, 300 mg/kg, ip). The Rotarod test scores, brain water content and brain expression of AQPs were measured post ICH. Cultured primary mouse astrocytes were used for in vitro experiments. The expression of AQP1, AQP4 and AQP9 and NF-κB p65 were detected using Western blotting or immunochemistry staining.Curcumin administration dose-dependently reduced the cerebral edema at d 3 post ICH, and significantly attenuated the neurological deficits at d 5 post ICH. Furthermore, curcumin dose-dependently decreased the gene and protein expression of AQP4 and AQP9, but not AQP1 post ICH. Treatment of the cultured astrocytes with Fe(2+) (10-100 μmol/L) dose-dependently increased the expression and nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 and the expression of AQP4 and AQP9, which were partly blocked by co-treatment with curcumin (20 μmol/L) or the NF-κB inhibitor PDTC (10 μmol/L).Curcumin effectively attenuates brain edema in mice with ICH through inhibition of the NF-κB pathway and subsequently the expression of AQP4 and AQP9. Curcumin may serve as a potential therapeutic agent for ICH. | | | 26119880
 |
Connexin 43 stabilizes astrocytes in a stroke-like milieu to facilitate neuronal recovery.
Wu, LY; Yu, XL; Feng, LY
Acta pharmacologica Sinica
36
928-38
2015
Zobrazit abstrakt
Connexin 43 (Cx43) is a member of connexin family mainly expressed in astrocytes, which forms gap junctions and hemichannels and maintains the normal shape and function of astrocytes. In this study we investigated the role of Cx43 in astrocytes in facilitating neuronal recovery during ischemic stroke.Primary culture of astrocytes or a mixed culture of astrocytes and cortical neurons was subjected to oxygen glucose deprivation and reperfusion (OGD/R). The expression of Cx43 and Ephrin-A4 in astrocytes was detected using immunocytochemical staining and Western blot assays. Intercellular Ca(2+) concentration was determined with Fluo-4 AM fluorescent staining. Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model rats were used for in vivo studies.OGD/R treatment of cultured astrocytes caused a decrement of Cx43 expression and translocation of Cx43 from cell membrane to cytoplasm, accompanied by cell retraction. Furthermore, OGD/R increased intracellular Ca(2+) concentration, activated CaMKII/CREB pathways and upregulated expression of Ephrin-A4 in the astrocytes. All these changes in OGD/R-treated astrocytes were alleviated by overexpression of Cx43. In the cortical neurons cultured with astrocytes, OGD/R inhibited the neurite growth, whereas overexpression of Cx43 or knockdown of Ephrin-A4 in astrocytes restored the neurite growth. In MCAO model rats, neuronal recovery was found to be correlated with the recuperation of Cx43 and Ephrin-A4 in astrocytes.Cx43 can stabilize astrocytes and facilitate the resistance to the deleterious effects of a stroke-like milieu and promote neuronal recovery. | | | 26095039
 |
Early pro-inflammatory cytokine elevations in the DBA/2J mouse model of glaucoma.
Wilson, GN; Inman, DM; Dengler Crish, CM; Denger-Crish, CM; Smith, MA; Crish, SD
Journal of neuroinflammation
12
176
2015
Zobrazit abstrakt
Neuroinflammation-astrogliosis, microglial activation, and changes in cytokine signaling-is a prominent feature of neurodegenerative disorders. Glaucoma is a group of chronic neurodegenerative conditions that make up the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. Neuroinflammation has been postulated to play a significant role in the pathogenesis and progression of glaucomatous neurodegeneration. Though much is known regarding inflammation in the eye in glaucoma, little is known about cytokine activity outside of the retina where pathologies develop early.We traced the primary visual projection from the eye to the superior colliculus (SC) in DBA/2J and DBA/2J.Gpnmb (+) (control) mice using the anterograde tracer cholera toxin-B (CTB) to assay axonal transport deficits. Forty-eight hours later, visual structures were microdissected from fresh tissue based on transport outcome. Using magnetic bead multiplexing assays, we measured levels of 20 cytokines in the retina, proximal and distal optic nerves, CTB-positive and negative SC subdivisions, cerebellum, and serum at different ages representing different stages of pathology.Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine levels in mice often changed in the same direction based on strain, age, and tissue. Significant elevations in retinal pro-inflammatory cytokines were observed in young DBA/2J mice compared to controls, followed by an age-dependent decrease in the DBA/2J mice. Proximal optic nerve of young DBA/2J mice showed a 50 % or greater decrease in levels of certain cytokines compared to older DBA/2J cohorts and controls, while both proximal and distal optic nerve of DBA/2Js showed elevations in IL-1β at all ages compared to controls. Pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 levels varied in accordance with transport outcome in the SC: IL-6 was elevated 44-80 % in glaucomatous DBA/2J collicular regions deficient in anterograde transport from retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) compared to areas with intact transport.Dysregulation of cytokine signaling in the RGC projection of DBA/2J mice was evident early in distal retinal targets, well before intraocular pressure elevation or axonal degeneration begins. | | | 26376776
 |
Dopamine D1 receptor activation regulates the expression of the estrogen synthesis gene aromatase B in radial glial cells.
Xing, L; McDonald, H; Da Fonte, DF; Gutierrez-Villagomez, JM; Trudeau, VL
Frontiers in neuroscience
9
310
2015
Zobrazit abstrakt
Radial glial cells (RGCs) are abundant stem-like non-neuronal progenitors that are important for adult neurogenesis and brain repair, yet little is known about their regulation by neurotransmitters. Here we provide evidence for neuronal-glial interactions via a novel role for dopamine to stimulate RGC function. Goldfish were chosen as the model organism due to the abundance of RGCs and regenerative abilities of the adult central nervous system. A close anatomical relationship was observed between tyrosine hydroxylase-positive catecholaminergic cell bodies and axons and dopamine-D1 receptor expressing RGCs along the ventricular surface of telencephalon, a site of active neurogenesis. A primary cell culture model was established and immunofluorescence analysis indicates that in vitro RGCs from female goldfish retain their major characteristics in vivo, including expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein and brain lipid binding protein. The estrogen synthesis enzyme aromatase B is exclusively found in RGCs, but this is lost as cells differentiate to neurons and other glial types in adult teleost brain. Pharmacological experiments using the cultured RGCs established that specific activation of dopamine D1 receptors up-regulates aromatase B mRNA through a cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent molecular mechanism. These data indicate that dopamine enhances the steroidogenic function of this neuronal progenitor cell. | | | 26388722
 |
Effects of dextromethorphan and oxycodone on treatment of neuropathic pain in mice.
Yang, PP; Yeh, GC; Huang, EY; Law, PY; Loh, HH; Tao, PL
Journal of biomedical science
22
81
2015
Zobrazit abstrakt
Neuropathic pain is a very troublesome and difficult pain to treat. Although opioids are the best analgesics for cancer and surgical pain in clinic, only oxycodone among opioids shows better efficacy to alleviate neuropathic pain. However, many side effects associated with the use of oxycodone render the continued use of it in neuropathic pain treatment undesirable. Hence, we explored whether dextromethorphan (DM, a known N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist with neuroprotective properties) could potentiate the anti-allodynic effect of oxycodone and underlying mechanisms regarding to glial cells (astrocytes and microglia) activation and proinflammatory cytokines release in a spinal nerve injury (SNL) mice model.Oxycodone produced a dose-dependent anti-allodynic effect. Co-administration of DM at a dose of 10 mg/kg (i.p.) (DM10) which had no anti-allodynic effect by itself enhanced the acute oxycodone (1 mg/kg, s.c.) effect. When the chronic anti-allodynic effects were examined, co-administration of DM10 also significantly enhanced the oxycodone effect at 3 mg/kg. Furthermore, oxycodone decreased SNL-induced activation of glial cells (astrocytes and microglia) and plasma levels of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α). Co-administration of DM10 potentiated these effects of oxycodone.The combined use of DM with oxycodone may have therapeutic potential for decreasing the effective dose of oxycodone on the treatment of neuropathic pain. Attenuation of the glial activation and proinflammatory cytokines in the spinal cord may be important mechanisms for these effects of DM. | | | 26391752
 |
Buyang Huanwu decoction increases the expression of glutamate transporter-1 and glutamate synthetase in association with PACAP-38 following focal ischemia.
Ding, W; Yu, P; Liu, W; Zhou, L; Guan, LI; Lin, R
Biomedical reports
3
651-656
2015
Zobrazit abstrakt
The neuroprotective role of Buyang Huanwu decoction (BYHWD) in focal ischemia is associated with decreasing glutamate concentration. However, the mechanisms are not fully understood. The present study aimed to explore whether glutamate transporter-1 (GLT-1) and glutamine synthetase (GS) participated in the decreased level of glutamate and whether pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide-38 (PACAP-38) was involved in this process. BYHWD was found to significantly upregulate the expression of GLT-1 and GS in the hippocampal CA1 area compared to the ischemia group, with the difference on day 3 being most significant. BYHWD increased the level of PACAP-38, and PACAP-(6-38) (PACAP receptor antagonist) significantly attenuated the effect of BYHWD on GLT-1 and GS, suggesting that PACAP-38 was involved in the upregulation of GLT-1 and GS induced by BYHWD. In addition, as GLT-1 and GS are mainly located in astrocytes, the changes of astrocytes were detected by glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP; an astrocytic marker) immunostaining. The results showed that BYHWD inhibited the expression of GFAP compared with the ischemia group, however, co-administration with PACAP-(6-38), which inhibited the effect of BYHWD on GLT-1 and GS in astrocytes, attenuated this effect, indicating that astrocytes participated in the protective role of BYHWD following focal ischemia. These results provided the evidence for the first time that not only neurons but also astrocytes contribute to the protective role of BYHWD, which opposes previous studies and may be a starting point for traditional medicine. | | | 26405540
 |
Identification of Spinal Cord MicroRNA and Gene Signatures in a Model of Chronic Stress-Induced Visceral Hyperalgesia in Rat.
Bradesi, S; Karagiannides, I; Bakirtzi, K; Joshi, SM; Koukos, G; Iliopoulos, D; Pothoulakis, C; Mayer, EA
PloS one
10
e0130938
2015
Zobrazit abstrakt
Animal studies have shown that stress could induce epigenetic and transcriptomic alterations essential in determining the balance between adaptive or maladaptive responses to stress. We tested the hypothesis that chronic stress in rats deregulates coding and non-coding gene expression in the spinal cord, which may underline neuroinflammation and nociceptive changes previously observed in this model.Male Wistar rats were exposed to daily stress or handled, for 10 days. At day 11, lumbar spinal segments were collected and processed for mRNA/miRNA isolation followed by expression profiling using Agilent SurePrint Rat Exon and Rat miRNA Microarray platforms. Differentially expressed gene lists were generated using the dChip program. Microarrays were analyzed using the Ingenuity Pathways Analysis (IPA) tool from Ingenuity Systems. Multiple methods were used for the analysis of miRNA-mRNA functional modules. Quantitative real time RT-PCR for Interleukin 6 signal transducer (gp130), the Signal Transducer And Activator Of Transcription 3 (STAT3), glial fibrillary acidic protein and mir-17-5p were performed to confirm levels of expression.Gene network analysis revealed that stress deregulated different inflammatory (IL-6, JAK/STAT, TNF) and metabolic (PI3K/AKT) signaling pathways. MicroRNA array analysis revealed a signature of 39 deregulated microRNAs in stressed rats. MicroRNA-gene network analysis showed that microRNAs are regulators of two gene networks relevant to inflammatory processes. Specifically, our analysis of miRNA-mRNA functional modules identified miR-17-5p as an important regulator in our model. We verified miR-17-5p increased expression in stress using qPCR and in situ hybridization. In addition, we observed changes in the expression of gp130 and STAT3 (involved in intracellular signaling cascades in response to gp130 activation), both predicted targets for miR-17-5p. A modulatory role of spinal mir17-5p in the modulation of visceral sensitivity was confirmed in vivo.Using an integrative high throughput approach, our findings suggest a link between miR-17-5p increased expression and gp130/STAT3 activation providing new insight into the possible mechanisms mediating the effect of chronic stress on neuroinflammation in the spinal cord. | | | 26222740
 |
Expression of progerin in aging mouse brains reveals structural nuclear abnormalities without detectible significant alterations in gene expression, hippocampal stem cells or behavior.
Baek, JH; Schmidt, E; Viceconte, N; Strandgren, C; Pernold, K; Richard, TJ; Van Leeuwen, FW; Dantuma, NP; Damberg, P; Hultenby, K; Ulfhake, B; Mugnaini, E; Rozell, B; Eriksson, M
Human molecular genetics
24
1305-21
2015
Zobrazit abstrakt
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) is a segmental progeroid syndrome with multiple features suggestive of premature accelerated aging. Accumulation of progerin is thought to underlie the pathophysiology of HGPS. However, despite ubiquitous expression of lamin A in all differentiated cells, the HGPS mutation results in organ-specific defects. For example, bone and skin are strongly affected by HGPS, while the brain appears to be unaffected. There are no definite explanations as to the variable sensitivity to progeria disease among different organs. In addition, low levels of progerin have also been found in several tissues from normal individuals, but it is not clear if low levels of progerin contribute to the aging of the brain. In an attempt to clarify the origin of this phenomenon, we have developed an inducible transgenic mouse model with expression of the most common HGPS mutation in brain, skin, bone and heart to investigate how the mutation affects these organs. Ultrastructural analysis of neuronal nuclei after 70 weeks of expression of the LMNA c.1824Cgreater than T mutation showed severe distortion with multiple lobulations and irregular extensions. Despite severe distortions in the nuclei of hippocampal neurons of HGPS animals, there were only negligible changes in gene expression after 63 weeks of transgenic expression. Behavioral analysis and neurogenesis assays, following long-term expression of the HGPS mutation, did not reveal significant pathology. Our results suggest that certain tissues are protected from functional deleterious effects of progerin. | | | 25343989
 |
miR-26a and miR-384-5p are required for LTP maintenance and spine enlargement.
Gu, QH; Yu, D; Hu, Z; Liu, X; Yang, Y; Luo, Y; Zhu, J; Li, Z
Nature communications
6
6789
2015
Zobrazit abstrakt
Long-term potentiation (LTP) is a form of synaptic plasticity that results in enhanced synaptic strength. It is associated with the formation and enlargement of dendritic spines-tiny protrusions accommodating excitatory synapses. Both LTP and spine remodelling are crucial for brain development, cognition and the pathophysiology of neurological disorders. The role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in the maintenance of LTP, however, is not well understood. Using next-generation sequencing to profile miRNA transcriptomes, we demonstrate that miR-26a and miR-384-5p specifically affect the maintenance, but not induction, of LTP and different stages of spine enlargement by regulating the expression of RSK3. Using bioinformatics, we also examine the global effects of miRNA transcriptome changes during LTP on gene expression and cellular activities. This study reveals a novel miRNA-mediated mechanism for gene-specific regulation of translation in LTP, identifies two miRNAs required for long-lasting synaptic and spine plasticity and presents a catalogue of candidate 'LTP miRNAs'. | | | 25858512
 |
Evidence for a novel functional role of astrocytes in the acute homeostatic response to high-fat diet intake in mice.
Buckman, LB; Thompson, MM; Lippert, RN; Blackwell, TS; Yull, FE; Ellacott, KL
Molecular metabolism
4
58-63
2015
Zobrazit abstrakt
Introduction of a high-fat diet to mice results in a period of voracious feeding, known as hyperphagia, before homeostatic mechanisms prevail to restore energy intake to an isocaloric level. Acute high-fat diet hyperphagia induces astrocyte activation in the rodent hypothalamus, suggesting a potential role of these cells in the homeostatic response to the diet. The objective of this study was to determine physiologic role of astrocytes in the acute homeostatic response to high-fat feeding.We bred a transgenic mouse model with doxycycline-inducible inhibition of NFkappaB (NFκB) signaling in astrocytes to determine the effect of loss of NFκB-mediated astrocyte activation on acute high-fat hyperphagia. ELISA was used to measure the levels of markers of astrocyte activation, glial-fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and S100B, in the medial basal hypothalamus.Inhibition of NFκB signaling in astrocytes prevented acute high-fat diet-induced astrocyte activation and resulted in a 15% increase in caloric intake (P less than 0.01) in the first 24 h after introduction of the diet.These data reveal a novel homeostatic role for astrocytes in the acute physiologic regulation of food intake in response to high-fat feeding. | | | 25685690
 |