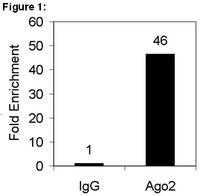
Argonaute 2 sustains the gene expression program driving human monocytic differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Iosue, I; Quaranta, R; Masciarelli, S; Fontemaggi, G; Batassa, EM; Bertolami, C; Ottone, T; Divona, M; Salvatori, B; Padula, F; Fatica, A; Lo-Coco, F; Nervi, C; Fazi, F
Cell death & disease
4
e926
2013
显示摘要
MicroRNAs are key regulators of many biological processes, including cell differentiation. These small RNAs exert their function assembled in the RNA-induced silencing complexes (RISCs), where members of Argonaute (Ago) family of proteins provide a unique platform for target recognition and gene silencing. Here, by using myeloid cell lines and primary blasts, we show that Ago2 has a key role in human monocytic cell fate determination and in LPS-induced inflammatory response of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (D3)-treated myeloid cells. The silencing of Ago2 impairs the D3-dependent miR-17-5p/20a/106a, miR-125b and miR-155 downregulation, the accumulation of their translational targets AML1, VDR and C/EBPβ and monocytic cell differentiation. Moreover, we show that Ago2 is recruited on miR-155 host gene promoter and on the upstream region of an overlapping antisense lncRNA, determining their epigenetic silencing, and miR-155 downregulation. These findings highlight Ago2 as a new factor in myeloid cell fate determination in acute myeloid leukemia cells. | 24263100
 |
Characterization of polysaccharide production of haemophilus influenzae Type b and its relationship to bacterial cell growth.
Mickie Takagi,Joaquin Cabrera-Crespo,Júlia Baruque-Ramos,Teresa Cristina Zangirolami,Isaias Raw,Martha Massako Tanizaki
Applied biochemistry and biotechnology
110
2003
显示摘要
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) causes invasive infections in infants and young children. Vaccines consisting of Hib capsular polysaccharide (polymer of ribosylribitol phosphate [PRP]) conjugated to a protein are effective in the prevention of such infections. The production of capsular polysaccharide type b was studied in three cultivation conditions: single, glucose pulse, and repeated batch. Specific polysaccharide production (Yp/x) was calculated for all experiments, showing the following values: 67 (single-batch cultivation), 71 (glucose pulse), 75 (repeated-batch cultivation, first batch), and 87 mg of PRP/g of dry cell weight (DCW) (repeated-batch cultivation, second batch). Biomass concentration reached approximately 1.8 g of DCW/L, while polysaccharide concentration was about approximately 132 mg/L in the three fermentation runs. Polysaccharide synthesis is associated with cell growth in all studied conditions as established by Kono's analysis and Luedeking-Piret's model. | 14515024
 |