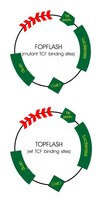
The TAK1-NLK-MAPK-related pathway antagonizes signalling between beta-catenin and transcription factor TCF.
Ishitani, T, et al.
Nature, 399: 798-802 (1999)
1998
Mostrar resumen
The Wnt signalling pathway regulates many developmental processes through a complex of beta-catenin and the T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (TCF/LEF) family of high-mobility-group transcription factors. Wnt stabilizes cytosolic beta-catenin, which then binds to TCF and activates gene transcription. This signalling cascade is conserved in vertebrates, Drosophila and Caenorhabditis elegans. In C. elegans, the proteins MOM-4 and LIT-1 regulate Wnt signalling to polarize responding cells during embryogenesis. MOM-4 and LIT-1 are homologous to TAK1 (a kinase activated by transforming growth factor-beta) mitogen-activated protein-kinase-kinase kinase (MAP3K) and MAP kinase (MAPK)-related NEMO-like kinase (NLK), respectively, in mammalian cells. These results raise the possibility that TAK1 and NLK are also involved in Wnt signalling in mammalian cells. Here we show that TAK1 activation stimulates NLK activity and downregulates transcriptional activation mediated by beta-catenin and TCF. Injection of NLK suppresses the induction of axis duplication by microinjected beta-catenin in Xenopus embryos. NLK phosphorylates TCF/LEF factors and inhibits the interaction of the beta-catenin-TCF complex with DNA. Thus, the TAK1-NLK-MAPK-like pathway negatively regulates the Wnt signalling pathway. | 10391247
 |
Two members of the Tcf family implicated in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling during embryogenesis in the mouse.
Korinek, V, et al.
Mol. Cell. Biol., 18: 1248-56 (1998)
1998
Mostrar resumen
Tcf transcription factors interact with beta-catenin and Armadillo to mediate Wnt/Wingless signaling. We now report the characterization of genes encoding two murine members of the Tcf family, mTcf-3 and mTcf-4. mTcf-3 mRNA is ubiquitously present in embryonic day 6.5 (E6.5) mouse embryos but gradually disappears over the next 3 to 4 days. mTcf-4 expression occurs first at E10.5 and is restricted to di- and mesencephalon and the intestinal epithelium during embryogenesis. The mTcf-3 and mTcf-4 proteins bind a canonical Tcf DNA motif and can complex with the transcriptional coactivator beta-catenin. Overexpression of Wnt-1 in a mammary epithelial cell line leads to the formation of a nuclear complex between beta-catenin and Tcf proteins and to Tcf reporter gene transcription. These data demonstrate a direct link between Wnt stimulation and beta-catenin/Tcf transcriptional activation and imply a role for mTcf-3 and -4 in early Wnt-driven developmental decisions in the mouse embryo. | 9488439
 |
The Xenopus Wnt effector XTcf-3 interacts with Groucho-related transcriptional repressors.
Roose, J, et al.
Nature, 395: 608-12 (1998)
1998
Mostrar resumen
Tcf/Lef transcription factors mediate signalling from Wingless/Wnt proteins by recruiting Armadillo/beta-catenin as a transcriptional co-activator. However, studies of Drosophila, Xenopus and Caenorhabditis elegans have indicated that Tcf factors may also be transcriptional repressors. Here we show that Tcf factors physically interact with members of the Groucho family of transcriptional repressors. In transient transfection assays, the Xenopus Groucho homologue XGrg-4 inhibited activation of transcription of synthetic Tcf reporter genes. In contrast, the naturally truncated Groucho-family member XGrg-5 enhanced transcriptional activation. Injection of XGrg-4 into Xenopus embryos repressed transcription of Siamois and Xnr-3, endogenous targets of beta-catenin-Tcf. Dorsal injection of XGrg-4 had a ventralizing effect on Xenopus embryos. Secondary-axis formation induced by a dominant-positive Armadillo-Tcf fusion protein was inhibited by XGrg-4 and enhanced by XGrg-5. These data indicate that expression of Tcf target genes is regulated by a balance between Armadillo and Groucho. | 9783587
 |