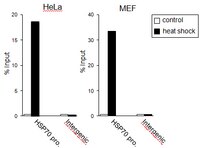
RPA assists HSF1 access to nucleosomal DNA by recruiting histone chaperone FACT.
Fujimoto, Mitsuaki, et al.
Mol. Cell, 48: 182-94 (2012)
2011
Mostra il sommario
Transcription factor access to regulatory elements is prevented by the nucleosome. Heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) is a winged helix transcription factor that plays roles in control and stressed conditions by gaining access to target elements, but mechanisms of HSF1 access are not well known in mammalian cells. Here, we show the physical interaction between the wing motif of human HSF1 and replication protein A (RPA), which is involved in DNA metabolism. Depletion of RPA1 abolishes HSF1 access to the promoter of HSP70 in unstressed condition and delays its rapid activation in response to heat shock. The HSF1-RPA complex leads to preloading of RNA polymerase II and opens the chromatin structure by recruiting a histone chaperone, FACT. Furthermore, this interaction is required for melanoma cell proliferation. These results provide a mechanism of constitutive HSF1 access to nucleosomal DNA, which is important for both basal and inducible gene expression. | 22940245
 |
Heat shock factor 2 is required for maintaining proteostasis against febrile-range thermal stress and polyglutamine aggregation.
Shinkawa, Toyohide, et al.
Mol. Biol. Cell, 22: 3571-83 (2011)
2010
Mostra il sommario
Heat shock response is characterized by the induction of heat shock proteins (HSPs), which facilitate protein folding, and non-HSP proteins with diverse functions, including protein degradation, and is regulated by heat shock factors (HSFs). HSF1 is a master regulator of HSP expression during heat shock in mammals, as is HSF3 in avians. HSF2 plays roles in development of the brain and reproductive organs. However, the fundamental roles of HSF2 in vertebrate cells have not been identified. Here we find that vertebrate HSF2 is activated during heat shock in the physiological range. HSF2 deficiency reduces threshold for chicken HSF3 or mouse HSF1 activation, resulting in increased HSP expression during mild heat shock. HSF2-null cells are more sensitive to sustained mild heat shock than wild-type cells, associated with the accumulation of ubiquitylated misfolded proteins. Furthermore, loss of HSF2 function increases the accumulation of aggregated polyglutamine protein and shortens the lifespan of R6/2 Huntington's disease mice, partly through αB-crystallin expression. These results identify HSF2 as a major regulator of proteostasis capacity against febrile-range thermal stress and suggest that HSF2 could be a promising therapeutic target for protein-misfolding diseases. | 21813737
 |