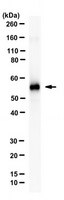
Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells to Sympathetic Neurons: A Potential Model for Understanding Neuroblastoma Pathogenesis
Jane Carr-Wilkinson 1 2 3 , Nilendran Prathalingam 2 4 , Deepali Pal 1 2 , Mohammad Moad 5 , Natalie Lee 1 , Aishwarya Sundaresh 1 , Helen Forgham 3 , Peter James 6 , Mary Herbert 2 4 7 , Majlinda Lako 2 4 , Deborah A Tweddle
Stem Cells Int
2018
4391641
2018
Afficher le résumé
Background and aims: Previous studies modelling human neural crest differentiation from stem cells have resulted in a low yield of sympathetic neurons. Our aim was to optimise a method for the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) to sympathetic neuron-like cells (SN) to model normal human SNS development. <br />Results: Using stromal-derived inducing activity (SDIA) of PA6 cells plus BMP4 and B27 supplements, the H9 hESC line was differentiated to neural crest stem-like cells and SN-like cells. After 7 days of PA6 cell coculture, mRNA expression of SNAIL and SOX-9 neural crest specifier genes and the neural marker peripherin (PRPH) increased. Expression of the pluripotency marker OCT 4 decreased, whereas TP53 and LIN28B expression remained high at levels similar to SHSY5Y and IMR32 neuroblastoma cell lines. A 5-fold increase in the expression of the catecholaminergic marker tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and the noradrenergic marker dopamine betahydroxylase (DBH) was observed by day 7 of differentiation. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting for the neural crest marker p75, enriched for cells expressing p75, DBH, TH, and PRPH, was more specific than p75 neural crest stem cell (NCSC) microbeads. On day 28 post p75 sorting, dual immunofluorescence identified sympathetic neurons by PRPH and TH copositivity cells in 20% of the cell population. Noradrenergic sympathetic neurons, identified by copositivity for both PHOX2B and DBH, were present in 9.4% ± 5.5% of cells. <br />Conclusions: We have optimised a method for noradrenergic SNS development using the H9 hESC line to improve our understanding of normal human SNS development and, in a future work, the pathogenesis of neuroblastoma. | | 30515222
 |
Preparation of mouse monoclonal antibody for RB1CC1 and its clinical application
Yusuke Hama 1 , Tokuhiro Chano, Takuma Inui, Kyoichi Matsumoto, Hidetoshi Okabe
PLos One
7(3)
e32052
2011
Afficher le résumé
RB1-inducible coiled-coil 1 (RB1CC1; also known as FIP200) plays important roles in several biological pathways such as cell proliferation and autophagy. Evaluation of RB1CC1 expression can provide useful clinical information on various cancers and neurodegenerative diseases. In order to realize the clinical applications, it is necessary to establish a stable supply of antibody and reproducible procedures for the laboratory examinations. In the present study, we have generated mouse monoclonal antibodies for RB1CC1, and four kinds of antibodies (N1-8, N1-216, N3-2, and N3-42) were found to be optimal for clinical applications such as ELISA and immunoblots and work as well as the pre-existing polyclonal antibodies. N1-8 monoclonal antibody provided the best recognition of RB1CC1 in the clinico-pathological examination of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. These monoclonal antibodies will help to generate new opportunities in scientific examinations in biology and clinical medicine. | | 28326944
 |
Peripherin is a subunit of peripheral nerve neurofilaments: implications for differential vulnerability of CNS and peripheral nervous system axons
Aidong Yuan 1 , Takahiro Sasaki, Asok Kumar, Corrinne M Peterhoff, Mala V Rao, Ronald K Liem, Jean-Pierre Julien, Ralph A Nixon
J Neurosci
32(25)
8501-8
2011
Afficher le résumé
Peripherin, a neuronal intermediate filament protein implicated in neurodegenerative disease, coexists with the neurofilament triplet proteins [neurofilament light (NFL), medium (NFM), and heavy (NFH) chain] but has an unknown function. The earlier peak expression of peripherin than the triplet during brain development and its ability to form homopolymers, unlike the triplet, which are obligate heteropolymers, have supported a widely held view that peripherin and neurofilament triplets form separate filament systems. However, here, we demonstrate that, despite a postnatal decline in expression, peripherin is as abundant as the triplet in the adult PNS and exists in a relatively fixed stoichiometry with these subunits. Peripherin exhibits a distribution pattern identical to those of triplet proteins in sciatic axons and colocalizes with NFL on single neurofilaments by immunogold electron microscopy. Peripherin also coassembles into a single network of filaments containing NFL, NFM, and NFH with and without α-internexin in quadruple- or quintuple-transfected SW13vim(-) cells. Genetically deleting NFL in mice dramatically reduces peripherin content in sciatic axons. Moreover, peripherin mutations has been shown to disrupt the neurofilament network in transfected SW13vim(-) cells. These data show that peripherin and the neurofilament proteins are functionally interdependent. The results strongly support the view that, rather than forming an independent structure, peripherin is a subunit of neurofilaments in the adult PNS. Our findings provide a basis for its close relationship with neurofilaments in PNS diseases associated with neurofilament accumulation. | Western Blotting | 22723690
 |
Syncoilin modulates peripherin filament networks and is necessary for large-calibre motor neurons
W Thomas Clarke 1 , Ben Edwards, Karl J A McCullagh, Matthew W Kemp, Catherine Moorwood, Diane L Sherman, Matthew Burgess, Kay E Davies
J Cell Sci
123(Pt 15)
2543-52
2009
Afficher le résumé
Syncoilin is an atypical type III intermediate filament (IF) protein, which is expressed in muscle and is associated with the dystrophin-associated protein complex. Here, we show that syncoilin is expressed in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. Isoform Sync1 is dominant in the brain, but isoform Sync2 is dominant in the spinal cord and sciatic nerve. Peripherin is a type III IF protein that has been shown to colocalise and interact with syncoilin. Our analyses suggest that syncoilin might function to modulate formation of peripherin filament networks through binding to peripherin isoforms. Peripherin is associated with the disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), thus establishing a link between syncoilin and ALS. A neuronal analysis of the syncoilin-null mouse (Sync(-/-)) revealed a reduced ability in accelerating treadmill and rotarod tests. This phenotype might be attributable to the impaired function of extensor digitorum longus muscle and type IIb fibres caused by a shift from large- to small-calibre motor axons in the ventral root. | | 20587592
 |