Nature protocols
Haque, A; Tonks, NK
Nature protocols
7
2127-43
2011
Afficher le résumé
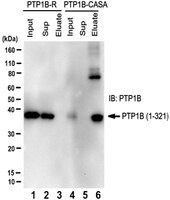
We describe a phage display approach that we have previously used to generate conformation-sensor antibodies that specifically recognize and stabilize the oxidized, inactive conformation of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B). We use a solution-based panning and screening strategy conducted in the presence of reduced active PTP1B, which enriches antibodies to epitopes unique to the oxidized form while excluding antibodies that recognize epitopes common to oxidized and reduced forms of PTP1B. This strategy avoids conventional solid-phase immobilization owing to its inherent potential for denaturation of the antigen. In addition, a functional screening strategy selects single-chain variable fragments (scFvs) directly for their capacity for both specific binding and stabilization of the target enzyme in its inactive conformation. These conformation-specific scFvs illustrate that stabilization of oxidized PTP1B is an effective strategy to inhibit PTP1B function; it is possible that this approach may be applicable to the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family as a whole. With this protocol, isolation and characterization of specific scFvs from immune responsive animals should take ~6 weeks. | 23154784
 |
Cell
Haque, A; Andersen, JN; Salmeen, A; Barford, D; Tonks, NK
Cell
147
185-98
2010
Afficher le résumé
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) plays important roles in downregulation of insulin and leptin signaling and is an established therapeutic target for diabetes and obesity. PTP1B is regulated by reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced in response to various stimuli, including insulin. The reversibly oxidized form of the enzyme (PTP1B-OX) is inactive and undergoes profound conformational changes at the active site. We generated conformation-sensor antibodies, in the form of single-chain variable fragments (scFvs), that stabilize PTP1B-OX and thereby inhibit its phosphatase function. Expression of conformation-sensor scFvs as intracellular antibodies (intrabodies) enhanced insulin-induced tyrosyl phosphorylation of the β subunit of the insulin receptor and its substrate IRS-1 and increased insulin-induced phosphorylation of PKB/AKT. Our data suggest that stabilization of the oxidized, inactive form of PTP1B with appropriate therapeutic molecules may offer a paradigm for phosphatase drug development. | 21962515
 |