Neurodegeneration and early lethality in superoxide dismutase 2-deficient mice: a comprehensive analysis of the central and peripheral nervous systems.
Oh, SS; Sullivan, KA; Wilkinson, JE; Backus, C; Hayes, JM; Sakowski, SA; Feldman, EL
Neuroscience
212
201-13
2011
Afficher le résumé
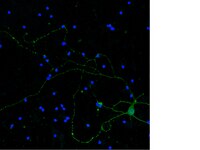
The contribution of oxidative stress to diabetic complications including neuropathy is widely known. Mitochondrial and cellular damage are associated with the overproduction of reactive oxygen species and decreased levels or function of the cellular antioxidant mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase (SOD2). We hypothesized that targeted SOD2 deletion in the peripheral nervous system using cre-lox technology under control of the nestin promoter would accelerate neuropathy in a type 2 model of diabetes, the BKS.db/db mouse. SOD2-deficient mice, however, demonstrated severe gait deformities and seizures and died by 20 days of age. Examination of SOD2 expression levels revealed that SOD2 was lost in brain and reduced in the spinal cord, but appeared normal in dorsal root ganglia and peripheral nerves in SOD2-deficient mice. These findings indicate incomplete targeted knockout of SOD2. Morphological examination revealed cortical lesions similar to spongiform encephalopathy in the brain of SOD2-deficient mice. No lesions were evident in the spinal cord, but changes in myelin within the sciatic and sural nerves including a lack of cohesion between layers of compact myelin were observed. Together, these results indicate that targeted neuronal SOD2 knockout using the nestin promoter results in severe central nervous system degeneration and perinatal lethality in mice. A specific peripheral nervous system-targeting construct is required to examine the consequences of SOD2 knockout in diabetic neuropathy. | Immunofluorescence | 22516022
 |