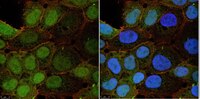
Cdk1 inhibition induces mutually inhibitory apoptosis and reactivation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.
Li, X; Chen, S; Sun, R
Journal of virology
86
6668-76
2011
Afficher le résumé
Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) cells are predominantly infected by the latent form of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), with virus reactivation occurring in a small percentage of cells. Latency enables KSHV to persist in the host cell and promotes tumorigenesis through viral gene expression, thus presenting a major barrier to the elimination of KSHV and the treatment of PEL. Therefore, it is important to identify cellular genes that are essential for PEL cell survival or the maintenance of KSHV latency. Here we report that cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1) inhibition can induce both apoptosis and KSHV reactivation in a population of PEL cells. Caspases, but not p53, are required for PEL cell apoptosis induced by Cdk1 inhibition. p38 kinase is activated by Cdk1 inhibition and mediates KSHV reactivation. Interestingly, upon Cdk1 inhibition, KSHV is reactivated predominantly in the nonapoptotic subpopulation of PEL cells. We provide evidence that this is due to mutual inhibition between apoptosis and KSHV reactivation. In addition, we found that KSHV reactivation activates protein kinase B (AKT/PKB), which promotes cell survival and facilitates KSHV reactivation. Our study thus establishes a key role for Cdk1 in PEL cell survival and the maintenance of KSHV latency and reveals a multifaceted relationship between KSHV reactivation and PEL cell apoptosis. | | | 22496227
 |
Iron-independent phosphorylation of iron regulatory protein 2 regulates ferritin during the cell cycle.
Wallander, ML; Zumbrennen, KB; Rodansky, ES; Romney, SJ; Leibold, EA
The Journal of biological chemistry
283
23589-98
2008
Afficher le résumé
Iron regulatory protein 2 (IRP2) is a key iron sensor that post-transcriptionally regulates mammalian iron homeostasis by binding to iron-responsive elements (IREs) in mRNAs that encode proteins involved in iron metabolism (e.g. ferritin and transferrin receptor 1). During iron deficiency, IRP2 binds IREs to regulate mRNA translation or stability, whereas during iron sufficiency IRP2 is degraded by the proteasome. Here, we identify an iron-independent IRP2 phosphorylation site that is regulated by the cell cycle. IRP2 Ser-157 is phosphorylated by Cdk1/cyclin B1 during G(2)/M and is dephosphorylated during mitotic exit by the phosphatase Cdc14A. Ser-157 phosphorylation during G(2)/M reduces IRP2 RNA-binding activity and increases ferritin synthesis, whereas Ser-157 dephosphorylation during mitotic exit restores IRP2 RNA-binding activity and represses ferritin synthesis. These data show that reversible phosphorylation of IRP2 during G(2)/M has a role in modulating the iron-independent expression of ferritin and other IRE-containing mRNAs during the cell cycle. | | | 18574241
 |
Phosphorylation of Plk1 at Ser326 regulates its functions during mitotic progression.
Tang, J; Yang, X; Liu, X
Oncogene
27
6635-45
2008
Afficher le résumé
Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1), the best characterized member of the mammalian polo-like kinase family, is well regulated throughout the cell cycle at the protein expression level. Moreover, it is known that Plk1 kinase activity is also regulated at the post-translational level through phosphorylation. However, the upstream kinases of Plk1 have not been identified. Although the involvement of the p38 MAP kinase pathway in cellular responses to stress has been well documented, the role of this pathway in normal cell cycle progression is unclear. Here, we show that phosphorylated p38 and MAP kinase-activated protein kinase 2 (MK2) are colocalized with Plk1 to the spindle poles during prophase and metaphase. Specific depletion of various members of the p38 MAP kinase pathway by the use of RNA interference revealed that the pathway is required for mitotic progression under normal growth conditions. Furthermore, MK2 directly phosphorylates Ser326 of Plk1. Ectopic expression of Plk1-S326A completely blocked cells at mitosis, likely due to the defect of bipolar spindle formation and subsequent activation of the spindle checkpoint. Only Plk1-S326E, but not the Plk1-S326A, efficiently rescued the p38 or MK2-depletion-induced mitotic defects, further solidifying the requirement of S326 phosphorylation during mitotic progression. Article en texte intégral | | | 18695677
 |
Plk1-dependent phosphorylation regulates functions of DNA topoisomerase IIalpha in cell cycle progression.
Li, H; Wang, Y; Liu, X
The Journal of biological chemistry
283
6209-21
2008
Afficher le résumé
Plk1 (Polo-like kinase 1) has been documented as a critical regulator of many mitotic events. However, increasing evidence supports the notion that Plk1 might also have functions outside of mitosis. Using biochemical fractionation and RNA interference approaches, we found that Plk1 was required for both G(1)/S and G(2)/M phases and that DNA topoisomerase IIalpha (topoIIalpha) was a potential target for Plk1 in both interphase and mitosis. Plk1 phosphorylates Ser(1337) and Ser(1524) of topoIIalpha. Overexpression of an unphosphorylatable topoIIalpha mutant led to S phase arrest, suggesting that Plk1-associated phosphorylation first occurs in S phase. Moreover, overexpression of the unphosphorylatable topoIIalpha mutant activated the ATM/R-dependent DNA damage checkpoint, probably due to reduced catalytic activity of topoIIalpha, and resulted in accumulation of catenated DNA. Finally, we showed that wild type topoIIalpha, but not the unphosphorylatable mutant, was able to rescue topoIIalpha depletion-induced defects in sister chromatid segregation, indicating that Plk1-associated phosphorylation is essential for the functions of topoIIalpha in mitosis. | | | 18171681
 |
An essential role for Cdk1 in S phase control is revealed via chemical genetics in vertebrate cells.
Hochegger, H; Dejsuphong, D; Sonoda, E; Saberi, A; Rajendra, E; Kirk, J; Hunt, T; Takeda, S
The Journal of cell biology
178
257-68
2007
Afficher le résumé
In vertebrates Cdk1 is required to initiate mitosis; however, any functionality of this kinase during S phase remains unclear. To investigate this, we generated chicken DT40 mutants, in which an analog-sensitive mutant cdk1 as replaces the endogenous Cdk1, allowing us to specifically inactivate Cdk1 using bulky ATP analogs. In cells that also lack Cdk2, we find that Cdk1 activity is essential for DNA replication initiation and centrosome duplication. The presence of a single Cdk2 allele renders S phase progression independent of Cdk1, which suggests a complete overlap of these kinases in S phase control. Moreover, we find that Cdk1 inhibition did not induce re-licensing of replication origins in G2 phase. Conversely, inhibition during mitosis of Cdk1 causes rapid activation of endoreplication, depending on proteolysis of the licensing inhibitor Geminin. This study demonstrates essential functions of Cdk1 in the control of S phase, and exemplifies a chemical genetics approach to target cyclin-dependent kinases in vertebrate cells. | Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) | | 17635936
 |
Up-regulation of 14-3-3zeta in lung cancer and its implication as prognostic and therapeutic target.
Fan, T; Li, R; Todd, NW; Qiu, Q; Fang, HB; Wang, H; Shen, J; Zhao, RY; Caraway, NP; Katz, RL; Stass, SA; Jiang, F
Cancer research
67
7901-6
2007
Afficher le résumé
A functional genomic approach integrating microarray and proteomic analyses done in our laboratory has identified 14-3-3zeta as a putative oncogene whose activation was common and driven by its genomic amplification in lung adenocarcinomas. 14-3-3zeta is believed to function in cell signaling, cycle control, and apoptotic death. Following our initial finding, here, we analyzed its expression in lung tumor tissues obtained from 205 patients with various histologic and stage non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) using immunohistochemistry and then explored the effects of specific suppression of the gene in vitro and in a xenograft model using small interfering RNA. The increased 14-3-3zeta expression was positively correlated with a more advanced pathologic stage and grade of NSCLCs (P = 0.001 and P = 0.006, respectively) and was associated with overall and cancer-specific survival rates of the patients (P = 0.022 and P = 0.018, respectively). Down-regulation of 14-3-3zeta in lung cancer cells led to a dose-dependent increased sensitivity to cisplatin-induced cell death, which was associated with the inhibition of cell proliferation and increased G2-M arrest and apoptosis. The result was further confirmed in the animal model, which showed that the A549 lung cancer cells with reduced 14-3-3zeta grew significantly slower than the wild-type A549 cells after cisplatin treatment (P = 0.008). Our results suggest that 14-3-3zeta is a potential target for developing a prognostic biomarker and therapeutics that can enhance the antitumor activity of cisplatin for NSCLC. | Western Blotting | Human | 17699796
 |
Quantification of cyclin B1 and p34(cdc2) in bovine cumulus-oocyte complexes and expression mapping of genes involved in the cell cycle by complementary DNA macroarrays.
Claude Robert, Isabelle Hue, Serge McGraw, Dominic Gagné, Marc-André Sirard
Biology of reproduction
67
1456-64
2002
Afficher le résumé
Although high amounts of cyclin B1 mRNA are present in bovine oocytes arrested at the germinal vesicle (GV) stage, the protein is not detectable. Furthermore, there is a depletion of the stored cyclin B1 mRNA in the oocyte as follicular growth progresses. To assess the effect of follicular growth on the accumulation of M-phase promoting factor (MPF) components, mRNA and protein levels of cyclin B1 and p34(cdc2) were measured in GV oocytes collected from diverse follicle size groups (2 mm, 3-5 mm, and >6 mm). Because oocytes collected from very small follicles have high levels of cyclin B1 mRNA, the onset of its accumulation in the oocytes was evaluated by in situ hybridization of fetal ovaries. Also, a comparative expression map of cell cycle-related genes expressed in the oocyte and cumulus cells was established using nylon-based cDNA arrays, which allowed the detection of 35 different genes transcribed mostly in oocytes. Both components of the pre-MPF complex were expressed at the mRNA level in GV oocytes, whereas p34(cdc2) was the only pre-MPF protein detected at that stage, thus indicating that meiosis resumption in bovine oocytes is differentially regulated as compared with other mammals, and meiosis resumption seems to be regulated by the translation of cyclin B1 mRNA. | | | 12390876
 |
Platelet-activating factor- and thrombin-induced stimulation of p34cdc2-cyclin histone H1 kinase activity in platelets.
Samiei, M, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 266: 14889-92 (1991)
1991
Afficher le résumé
Numerous studies of cell cycle control in dividing cells have pointed to the central role of a 34-kDa histone H1 kinase (p34cdc2) complexed with regulatory subunits known as cyclins. We now report that p34cdc2-cyclin may also participate in signal transduction in nonproliferating, terminally differentiated cells, in this instance during sheep platelet activation. Immunological evidence for the presence of a p34cdc2 cognant in sheep platelet cytosol was obtained with antipeptide antibodies raised against peptide sequences in the conserved PSTAIRE and C-terminus regions of murine cdc2. The immunoreactive 32-kDa protein was adsorbed onto p13suc1-Sepharose, which selectively binds p34cdc2. A 58-kDa protein that also bound to p13suc1-Sepharose was identified as cyclin A on the basis of its size and immunoreactivity with two different anticyclin peptide antibodies. The p34cdc2-cyclin A complex was regulated during platelet activation. Its histone H1 phosphorylating activity was stimulated 2-fold in p13suc1-Sepharose extracts from platelets that had been exposed to platelet-activating factor or thrombin for 1 min prior to harvesting. Our findings imply that the p34cdc2-cyclin complex may serve alternative functions besides control of cell division. | | | 1869529
 |
Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2
Lee, M G and Nurse, P
Nature, 327:31-5 ()
1987
| | | 3553962
 |