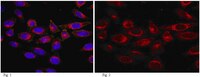
MABT100 Sigma-AldrichAnti-Girdin Antibody, CT, clone 10E6.1
This Anti-Girdin, C-terminus Antibody, clone 10E6.1 is validated for use in Western Blotting, IHC(P), ICC, Immunoprecipitation for the detection of Girdin, C-terminus, clone 10E6.1.
More>> This Anti-Girdin, C-terminus Antibody, clone 10E6.1 is validated for use in Western Blotting, IHC(P), ICC, Immunoprecipitation for the detection of Girdin, C-terminus, clone 10E6.1. Less<<Recommended Products
Overview
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Key Spec Table
| Species Reactivity | Key Applications | Host | Format | Antibody Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | WB, IH(P), ICC, IP | M | Purified | Monoclonal Antibody |
| References |
|---|
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Format | Purified |
| Control |
|
| Presentation | Purified mouse monoclonal IgG1κ in buffer containing 0.1 M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl with 0.05% sodium azide. |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Physicochemical Information |
|---|
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Storage and Shipping Information | |
|---|---|
| Storage Conditions | Stable for 1 year at 2-8°C from date of receipt. |
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Material Size | 100 µL |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | GTIN |
| MABT100 | 04053252643422 |
Documentation
Anti-Girdin Antibody, CT, clone 10E6.1 SDS
| Title |
|---|
Anti-Girdin Antibody, CT, clone 10E6.1 Certificates of Analysis
Newsletters / Publications
| Title |
|---|
| Research Focus - Volume 4 - 2012 |