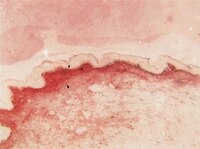
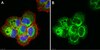
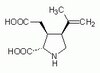
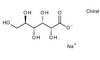
Biological Effects Induced by Specific Advanced Glycation End Products in the Reconstructed Skin Model of Aging.
Pageon, H; Zucchi, H; Dai, Z; Sell, DR; Strauch, CM; Monnier, VM; Asselineau, D
BioResearch open access
4
54-64
2015
Abstract anzeigen
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) accumulate in the aging skin. To understand the biological effects of individual AGEs, skin reconstructed with collagen selectively enriched with N(ɛ)-(carboxymethyl)-lysine (CML), N(ɛ)-(carboxyethyl)-lysine (CEL), methylglyoxal hydroimidazolone (MG-H1), or pentosidine was studied. Immunohistochemistry revealed increased expression of α6 integrin at the dermal epidermal junction by CEL and CML (pless than 0.01). Laminin 5 was diminished by CEL and MG-H1 (pless than 0.05). Both CML and CEL induced a robust increase (pless than 0.01) in procollagen I. In the culture medium, IL-6, VEGF, and MMP1 secretion were significantly decreased (pless than 0.05) by MG-H1. While both CEL and CML decreased MMP3, only CEL decreased IL-6 and TIMP1, while CML stimulated TIMP1 synthesis significantly (pless than 0.05). mRNA expression studies using qPCR in the epidermis layer showed that CEL increased type 7 collagen (COL7A1), β1, and α6 integrin, while CML increased only COL7A1 (pless than 0.05). MG-H1-modified collagen had no effect. Importantly, in the dermis layer, MMP3 mRNA expression was increased by both CML and MG-H1. CML also significantly increased the mRNAs of MMP1, TIMP1, keratinocyte growth factor (KGF), IL-6, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1) (pless than 0.05). Mixed effects were present in CEL-rich matrix. Minimally glycoxidized pentosidine-rich collagen suppressed most mRNAs of the genes studied (pless than 0.05) and decreased VEGF and increased MCP1 protein expression. Taken together, this model of the aging skin suggests that a combination of AGEs tends to counterbalance and thus minimizes the detrimental biological effects of individual AGEs. | | 26309782
 |
Caveolin-1 regulates chemokine receptor 5-mediated contribution of bone marrow-derived cells to dermal fibrosis.
Lee, R; Perry, B; Heywood, J; Reese, C; Bonner, M; Hatfield, CM; Silver, RM; Visconti, RP; Hoffman, S; Tourkina, E
Frontiers in pharmacology
5
140
2014
Abstract anzeigen
In fibrotic diseases caveolin-1 underexpression in fibroblasts results in collagen overexpression and in monocytes leads to hypermigration. These profibrotic behaviors are blocked by the caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide (CSD) which compensates for caveolin-1 deficiency. Monocytes and fibroblasts are related in that monocytes are the progenitors of fibrocytes (CD45+/Collagen I+ cells) that, in turn, are the progenitors of many fibroblasts in fibrotic tissues. In an additional anti-fibrotic activity, CSD blocks monocyte differentiation into fibrocytes. We studied a mouse fibrosis model (Pump Model) involving systemic bleomycin delivery that closely models scleroderma (SSc) in several ways, the most important of which for this study is that fibrosis is observed in the lungs, skin, and internal organs. We show here that dermal thickness is increased 2-fold in the Pump Model and that this effect is almost completely blocked by CSD (p less than 0.001). Concomitantly, the subcutaneous fat layer becomes greater than 80% thinner. This effect is also blocked by CSD (p less than 0.001). Even in mice receiving vehicle instead of bleomycin, CSD increases the thickness of the fat layer. To study the mechanisms of action of bleomycin and CSD, we examined the accumulation of the chemokine receptor CCR5 and its ligands MIP1α and MIP1β in fibrotic tissue and their roles in monocyte migration. Fibrocytes and other leukocytes expressing CCR5 and its ligands were present at high levels in the fibrotic dermis of SSc patients and Pump Model mice while CSD blocked their accumulation in mouse dermis. Migration toward CCR5 ligands of SSc monocytes and Pump Model bone marrow cells was 3-fold greater than cells from control subjects. This enhanced migration was almost completely blocked by CSD. These results suggest that low monocyte caveolin-1 promotes fibrosis by enhancing the recruitment of fibrocytes and their progenitors into affected tissue. | | 24966836
 |
Fibrocytes in the fibrotic lung: altered phenotype detected by flow cytometry.
Reese, C; Lee, R; Bonner, M; Perry, B; Heywood, J; Silver, RM; Tourkina, E; Visconti, RP; Hoffman, S
Frontiers in pharmacology
5
141
2014
Abstract anzeigen
Fibrocytes are bone marrow hematopoietic-derived cells that also express a mesenchymal cell marker (commonly collagen I) and participate in fibrotic diseases of multiple organs. Given their origin, they or their precursors must be circulating cells before recruitment into target tissues. While most previous studies focused on circulating fibrocytes, here we focus on the fibrocyte phenotype in fibrotic tissue. The study's relevance to human disease is heightened by use of a model in which bleomycin is delivered systemically, recapitulating several features of human scleroderma including multi-organ fibrosis not observed when bleomycin is delivered directly into the lungs. Using flow cytometry, we find in the fibrotic lung a large population of CD45(high) fibrocytes (called Region I) rarely found in vehicle-treated control mice. A second population of CD45+ fibrocytes (called Region II) is observed in both control and fibrotic lung. The level of CD45 in circulating fibrocytes is far lower than in either Region I or II lung fibrocytes. The chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CCR5 are expressed at higher levels in Region I than in Region II and are present at very low levels in all other lung cells including CD45+/collagen I- leucocytes. The collagen chaperone HSP47 is present at similar high levels in both Regions I and II, but at a higher level in fibrotic lung than in control lung. There is also a major population of HSP47(high)/CD45- cells in fibrotic lung not present in control lung. CD44 is present at higher levels in Region I than in Region II and at much lower levels in all other cells including CD45+/collagen I- leucocytes. When lung fibrosis is inhibited by restoring caveolin-1 activity using a caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide (CSD), a strong correlation is observed between fibrocyte number and fibrosis score. In summary, the distinctive phenotype of fibrotic lung fibrocytes suggests that fibrocyte differentiation occurs primarily within the target organ. | | 24999331
 |
Calcipotriol counteracts betamethasone-induced decrease in extracellular matrix components related to skin atrophy.
Norsgaard, H; Kurdykowski, S; Descargues, P; Gonzalez, T; Marstrand, T; Dünstl, G; Røpke, M
Archives of dermatological research
306
719-29
2014
Abstract anzeigen
The calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate fixed-combination gel is widely used for topical treatment of psoriasis vulgaris. It has been hypothesized that calcipotriol counteracts glucocorticoid-induced skin atrophy which is associated with changes in the extracellular matrix (ECM). To elucidate the combined effects of calcipotriol and betamethasone on key ECM components, a comparative study to the respective mono-treatments was carried out. The effect on collagen I synthesis, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) secretion, and hyaluronic acid (HA) production was investigated in primary human fibroblast and keratinocyte cultures as well as in a human skin explant model. We show that calcipotriol counteracts betamethasone-induced suppression of collagen I synthesis. Similarly, calcipotriol and betamethasone have opposing effects on MMP expression in both fibroblasts and keratinocytes. Moreover, calcipotriol is able to restore betamethasone-impaired HA synthesis in keratinocytes and prevent betamethasone-induced epidermal thinning in minipigs upon treatment with the calcipotriol/betamethasone gel. In summary, our results show for the first time in primary human skin cultures that calcipotriol reduces early signs of betamethasone-induced skin atrophy by modulation of key ECM components. These results indicate that the calcipotriol component of the fixed-combination gel counteracts the atrophogenic effects of betamethasone on the skin. | | 25027750
 |
Platelet-rich fibrin versus albumin in surgical wound repair: a randomized trial with paired design.
Danielsen, Patricia L, et al.
Ann. Surg., 251: 825-31 (2010)
2009
Abstract anzeigen
To study the effects of autologous platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) versus human albumin on incisional wound breaking strength and subcutaneous collagen deposition in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy in a randomized trial. | | 20395860
 |
Cancer-associated fibroblasts are positively correlated with metastatic potential of human gastric cancers.
Zhi, K; Shen, X; Zhang, H; Bi, J
Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR
29
66
2009
Abstract anzeigen
The prognosis of gastric cancer patients is difficult to predict because of defects in establishing the surgical-pathological features. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) have been found to play prominent role in promoting tumor growth, invasion and metastasis. Thus raises the hypothesis that the extent of CAFs prevalence may help to establish the prognosis of gastric cancer patients.Immunochemistry and realtime-PCR experiments were carried out to compare the expression of proteins which are specific markers of CAFs or secreted by CAFs in the tumor and normal tissue specimens. The extent of CAFs' prevalence was graded according to immunochemical staining, and correlation was further analyzed between CAFs' prevalence and other tumor characteristics which may influence the prognosis of gastric cancer patients.Nearly 80 percent of normal gastric tissues were negative or weak positive for CAFs staining, while more than 60 percent of gastric cancer tissues were moderate or strong positive for CAFs staining. Realtime-PCR results also showed significant elevated expression of FAP, SDF-1 and TGF-beta1 in gastric cancer tissues compared to normal gastric tissues. Further analysis showed that CAFs' prevalence was correlated with tumor size, depth of the tumor, lymph node metastasis, liver metastasis or peritoneum metastasis.Reactive cancer associated fibroblasts (CAFs) were frequently accumulated in gastric cancer tissues, and the prevalence of CAFs was correlated with tumor size, depth of the tumor and tumor metastasis, thus give some supports for establishing the prognosis of the gastric cancer patients. | | 20529313
 |
Keratinocyte-derived chemokine induces prostate epithelial hyperplasia and reactive stroma in a novel transgenic mouse model.
Isaiah G Schauer, Steven J Ressler, David R Rowley, Isaiah G Schauer, Steven J Ressler, David R Rowley, Isaiah G Schauer, Steven J Ressler, David R Rowley, Isaiah G Schauer, Steven J Ressler, David R Rowley
The Prostate
69
373-84
2009
Abstract anzeigen
BACKGROUND: Interleukin-8 (IL-8) is upregulated in fibrotic and malignant diseases and is a key mediator of proliferative responses. Elevated IL-8 was recently correlated with benign prostatic hyperplasia epithelium and a myofibroblast reactive stroma. Thus, we sought to determine whether overexpressed IL-8 and keratinocyte-derived chemokine (KC), the functional murine homolog of IL-8, induce prostate epithelial hyperplasia and a reactive phenotype. METHODS: Transgenic mice that overexpress KC within prostate epithelia and xenograft models with engineered human cells that overexpress IL-8 were developed. RESULTS: Overexpression of KC in transgenic mice produced hyperplastic prostate epithelial acini associated with a periacinar reactive stroma. KC induced an altered epithelial/stroma proliferation index ratio, increased acini diameter, epithelial infolding, and expression of prototypical reactive stroma markers. Overexpression of IL-8 in normal human prostate epithelial xenografts correlated with elevated epithelial proliferation index and altered morphology. Elevated human prostate stromal and epithelial cell proliferation, nodule-like morphology and increased xenograft survival were observed in IL-8-overexpressing orthotopic xenografts. CONCLUSIONS: Together, these data demonstrate that overexpression of IL-8/KC results in a prostate epithelial hyperplasia with an associated reactive stroma phenotype. The novel transgenic mouse and human xenograft models described here may be useful in dissecting key mechanisms of IL-8 induced prostate hyperplasia and reactive stroma. Volltextartikel | | 19021203
 |
Validation of the cardiosphere method to culture cardiac progenitor cells from myocardial tissue.
Davis, DR; Zhang, Y; Smith, RR; Cheng, K; Terrovitis, J; Malliaras, K; Li, TS; White, A; Makkar, R; Marbán, E
PloS one
4
e7195
2009
Abstract anzeigen
At least four laboratories have shown that endogenous cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs) can be grown directly from adult heart tissue in primary culture, as cardiospheres or their progeny (cardiosphere-derived cells, CDCs). Indeed, CDCs are already being tested in a clinical trial for cardiac regeneration. Nevertheless, the validity of the cardiosphere strategy to generate CPCs has been called into question by reports based on variant methods. In those reports, cardiospheres are argued to be cardiomyogenic only because of retained cardiomyocytes, and stem cell activity has been proposed to reflect hematological contamination. We use a variety of approaches (including genetic lineage tracing) to show that neither artifact is applicable to cardiospheres and CDCs grown using established methods, and we further document the stem cell characteristics (namely, clonogenicity and multilineage potential) of CDCs.CPCs were expanded from human endomyocardial biopsies (n = 160), adult bi-transgenic MerCreMer-Z/EG mice (n = 6), adult C57BL/6 mice (n = 18), adult GFP(+) C57BL/6 transgenic mice (n = 3), Yucatan mini pigs (n = 67), adult SCID beige mice (n = 8), and adult Wistar-Kyoto rats (n = 80). Cellular yield was enhanced by collagenase digestion and process standardization; yield was reduced in altered media and in specific animal strains. Heparinization/retrograde organ perfusion did not alter the ability to generate outgrowth from myocardial sample. The initial outgrowth from myocardial samples was enriched for sub-populations of CPCs (c-Kit(+)), endothelial cells (CD31(+), CD34(+)), and mesenchymal cells (CD90(+)). Lineage tracing using MerCreMer-Z/EG transgenic mice revealed that the presence of cardiomyocytes in the cellular outgrowth is not required for the generation of CPCs. Rat CDCs are shown to be clonogenic, and cloned CDCs exhibit spontaneous multineage potential.This study demonstrates that direct culture and expansion of CPCs from myocardial tissue is simple, straightforward, and reproducible when appropriate techniques are used. Volltextartikel | Immunohistochemistry | 19779618
 |
SPARC-induced increase in glioma matrix and decrease in vascularity are associated with reduced VEGF expression and secretion.
Yunker, CK; Golembieski, W; Lemke, N; Schultz, CR; Cazacu, S; Brodie, C; Rempel, SA
International journal of cancer. Journal international du cancer
122
2735-43
2008
Abstract anzeigen
Glioblastomas are heterogeneous tumors displaying regions of necrosis, proliferation, angiogenesis, apoptosis and invasion. SPARC, a matricellular protein that negatively regulates angiogenesis and cell proliferation, but enhances cell deadhesion from matrix, is upregulated in gliomas (Grades II-IV). We previously demonstrated that SPARC promotes invasion while concomitantly decreasing tumor growth, in part by decreasing proliferation of the tumor cells. In other cancer types, SPARC has been shown to influence tumor growth by altering matrix production, and by decreasing angiogenesis via interfering with the VEGF-VEGFR1 signaling pathway. We therefore examined whether the SPARC-induced decrease in glioma tumor growth was also, in part, due to alterations in matrix and/or decreased vascularity, and assessed SPARC-VEGF interactions. The data demonstrate that SPARC upregulates glioma matrix, collagen I is a constituent of the matrix and SPARC promotes collagen fibrillogenesis. Furthermore, SPARC suppressed glioma vascularity, and this was accompanied by decreased VEGF expression and secretion, which was, in part, due to reduced VEGF165 transcript abundance. These data indicate that SPARC modulates glioma growth by altering the tumor microenvironment and by suppressing tumor vascularity through suppression of VEGF expression and secretion. These experiments implicate a novel mechanism, whereby SPARC regulates VEGF function by limiting the available growth factor. Because SPARC is considered to be a therapeutic target for gliomas, a further understanding of its complex signaling mechanisms is important, as targeting SPARC to decrease invasion could undesirably lead to the growth of more vascular and proliferative tumors. | | 18350569
 |
MMP-21 is expressed by macrophages and fibroblasts in vivo and in culture.
Tiina Skoog, Katja Ahokas, Christina Orsmark, Leila Jeskanen, Keiichi Isaka, Ulpu Saarialho-Kere
Experimental dermatology
15
775-83
2005
Abstract anzeigen
Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-21 and MMP-26 (matrilysin-2) are two recently cloned epithelial metalloproteases. Here we examined their expression in various benign skin disorders, in which macrophages and fibroblasts have been implicated as well as in cultures of these cells. Expression of MMP-21 was detected by immunohistochemistry in a subset of macrophages of granulomatous skin lesions and in fibroblasts in dermatofibromas. MMP-21 mRNA was found in THP-1, U937, HEL 299 and Hs68 cells. Furthermore, MMP-21 protein was detected by immunohistochemistry in cultures of the same cell lines. In culture MMP-21 was upregulated by phorbol myristate acetate in THP-1 cells and by retinoic acid (RA) in U937 cells, and downregulated by transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-beta1) in HEL 299 as assessed by Taqman quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Expression of MMP-26 was detected by immunohistochemistry in granulomatous skin diseases and actinic elastosis. MMP-26 at both mRNA and protein levels was only found in HEL 299 cells. In culture it was downregulated by TGF-beta1, RA and IL-1beta as assessed by Taqman quantitative PCR. Our results suggest these two novel MMPs are not only associated with cancer but may be important in connective tissue remodelling and pathobiology of various benign skin disorders. | | 16984259
 |