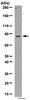
Neuronal inclusions of α-synuclein contribute to the pathogenesis of Krabbe disease.
Smith, BR; Santos, MB; Marshall, MS; Cantuti-Castelvetri, L; Lopez-Rosas, A; Li, G; van Breemen, R; Claycomb, KI; Gallea, JI; Celej, MS; Crocker, SJ; Givogri, MI; Bongarzone, ER
The Journal of pathology
232
509-21
2014
Abstract anzeigen
Demyelination is a major contributor to the general decay of neural functions in children with Krabbe disease. However, recent reports have indicated a significant involvement of neurons and axons in the neuropathology of the disease. In this study, we have investigated the nature of cellular inclusions in the Krabbe brain. Brain samples from the twitcher mouse model for Krabbe disease and from patients affected with the infantile and late-onset forms of the disease were examined for the presence of neuronal inclusions. Our experiments demonstrated the presence of cytoplasmic aggregates of thioflavin-S-reactive material in both human and murine mutant brains. Most of these inclusions were associated with neurons. A few inclusions were detected to be associated with microglia and none were associated with astrocytes or oligodendrocytes. Thioflavin-S-reactive inclusions increased in abundance, paralleling the development of neurological symptoms, and distributed throughout the twitcher brain in areas of major involvement in cognition and motor functions. Electron microscopy confirmed the presence of aggregates of stereotypic β-sheet folded proteinaceous material. Immunochemical analyses identified the presence of aggregated forms of α-synuclein and ubiquitin, proteins involved in the formation of Lewy bodies in Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative conditions. In vitro assays demonstrated that psychosine, the neurotoxic sphingolipid accumulated in Krabbe disease, accelerated the fibrillization of α-synuclein. This study demonstrates the occurrence of neuronal deposits of fibrillized proteins including α-synuclein, identifying Krabbe disease as a new α-synucleinopathy. | | 24415155
 |
Subventricular zone neural progenitors from rapid brain autopsies of elderly subjects with and without neurodegenerative disease.
Leonard, BW; Mastroeni, D; Grover, A; Liu, Q; Yang, K; Gao, M; Wu, J; Pootrakul, D; van den Berge, SA; Hol, EM; Rogers, J
The Journal of comparative neurology
515
269-94
2009
Abstract anzeigen
In mice and in young adult humans, the subventricular zone (SVZ) contains multipotent, dividing astrocytes, some of which, when cultured, produce neurospheres that differentiate into neurons and glia. It is unknown whether the SVZ of very old humans has this capacity. Here, we report that neural stem/progenitor cells can also be cultured from rapid autopsy samples of SVZ from elderly human subjects, including patients with age-related neurologic disorders. Histological sections of SVZ from these cases showed a glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-positive ribbon of astrocytes similar to the astrocyte ribbon in human periventricular white matter biopsies that is reported to be a rich source of neural progenitors. Cultures of the SVZ contained 1) neurospheres with a core of Musashi-1-, nestin-, and nucleostemin-immunopositive cells as well as more differentiated GFAP-positive astrocytes; 2) SMI-311-, MAP2a/b-, and beta-tubulin(III)-positive neurons; and 3) galactocerebroside-positive oligodendrocytes. Neurospheres continued to generate differentiated progeny for months after primary culturing, in some cases nearly 2 years postinitial plating. Patch clamp studies of differentiated SVZ cells expressing neuron-specific antigens revealed voltage-dependent, tetrodotoxin-sensitive, inward Na+ currents and voltage-dependent, delayed, slowly inactivating K+ currents, electrophysiologic characteristics of neurons. A subpopulation of these cells also exhibited responses consistent with the kinetics and pharmacology of the h-current. However, although these cells displayed some aspects of neuronal function, they remained immature, insofar as they did not fire action potentials. These studies suggest that human neural progenitor activity may remain viable throughout much of the life span, even in the face of severe neurodegenerative disease. Volltextartikel | | 19425077
 |
Olig2-induced neural stem cell differentiation involves downregulation of Wnt signaling and induction of Dickkopf-1 expression.
Ahn, SM; Byun, K; Kim, D; Lee, K; Yoo, JS; Kim, SU; Jho, EH; Simpson, RJ; Lee, B
PloS one
3
e3917
2008
Abstract anzeigen
Understanding stem cell-differentiation at the molecular level is important for clinical applications of stem cells and for finding new therapeutic approaches in the context of cancer stem cells. To investigate genome-wide changes involved in differentiation, we have used immortalized neural stem cell (NSC) line (HB1.F3) and Olig2-induced NSC differentiation model (F3.Olig2). Using microarray analysis, we revealed that Olig2-induced NSC differentiation involves downregulation of Wnt pathway, which was further confirmed by TOPflash/FOPflash reporter assay, RT-PCR analysis, immunoblots, and immunocytochemistry. Furthermore, we found that Olig2-induced differentiation induces the expression of Dickkopf-1(Dkk1), a potent antagonist of Wnt signaling. Dkk1 treatment blocked Wnt signaling in HB1.F3 in a dosage-dependent manner, and induced differentiation into astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and neurons. Our results support cancer stem cell hypothesis which implies that signaling pathway for self-renewal and proliferation of stem cells is maintained till the late stage of differentiation. In our proposed model, Dkk1 may play an important role in downregulating self-renewal and proliferation pathway of stem cells at the late stage of differentiation, and its failure may lead to carcinogenesis. | Immunocytochemistry | 19093005
 |