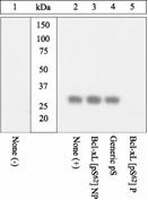
AB3573 Sigma-AldrichAnti-BCL-XL (pS62) Antibody
Anti-BCL-XL (pS62) Antibody detects level of BCL-XL (pS62) & has been published & validated for use in WB.
More>> Anti-BCL-XL (pS62) Antibody detects level of BCL-XL (pS62) & has been published & validated for use in WB. Less<<Empfohlene Produkte
Übersicht
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Key Spec Table
| Species Reactivity | Key Applications | Host | Format | Antibody Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | WB | Rb | Affinity Purified | Polyclonal Antibody |
| References |
|---|
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Format | Affinity Purified |
| HS Code | 3002 15 90 |
| Control |
|
| Presentation | Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline (without Mg2+ and Ca2+), pH 7.3 (+/- 0.1), 50% glycerol, with 1.0 mg/mL BSA (IgG, protease free) as a carrier. 0.05% sodium azide. |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Physicochemical Information |
|---|
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Material Size | 100 µL |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Bestellnummer | GTIN |
| AB3573 | 04053252327827 |
Documentation
Anti-BCL-XL (pS62) Antibody SDB
| Titel |
|---|
Anti-BCL-XL (pS62) Antibody Analysenzertifikate
Literatur
| Übersicht | Anwendung | Pub Med ID |
|---|---|---|
| Bcl-xL controls a switch between cell death modes during mitotic arrest. Bah, N; Maillet, L; Ryan, J; Dubreil, S; Gautier, F; Letai, A; Juin, P; Barillé-Nion, S Cell death & disease 5 e1291 2014 Abstract anzeigen | Western Blotting | 24922075
 |
| Enhanced chemosensitivity of drug-resistant osteosarcoma cells by lentivirus-mediated Bcl-2 silencing. Yao Zhao,Chun-lin Zhang,Bing-fang Zeng,Xiao-san Wu,Tian-tian Gao,Yoshino Oda Biochemical and biophysical research communications 390 2009 Abstract anzeigen | 19818735
 | |
| The MUC1 oncoprotein activates the anti-apoptotic phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt and Bcl-xL pathways in rat 3Y1 fibroblasts. Raina, D., et al. J. Biol. Chem., 279(20):20607-20612 (2004) 2004 | 14999001
 | |
| Ochratoxin A induces apoptosis in human lymphocytes through down regulation of Bcl-xL. Assaf, Hind, et al. Toxicol. Sci., 79: 335-44 (2004) 2004 Abstract anzeigen | 15056805
 | |
| Anti-HLA class I antibody-mediated activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and induction of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL expression in endothelial cells. Jin, Y.P., et al. Hum. Immunol., 65(4):291-302 (2004) 2004 | 15120184
 | |
| Selective induction of apoptosis by PBOX-6 in leukemia cells occurs via the JNK dependent phosphorylation and inactivation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL. Mc Gee, M.M., et al. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 310(3):1084-1095 (2004) 2004 | 15143129
 | |
| Identification of a novel Bcl-xL phosphorylation site regulating the sensitivity of taxol- or 2-methoxyestradiol-induced apoptosis Basu, A. and Haldar, S. FEBS Letters, 538:41-47 (2003) 2003 | 12633850
 | |
| Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL with nonpeptidic small-molecule antagonists. Wang, S., et al. Targeting Semin. Oncol., 30(5 Suppl 16):133-142 (2003) 2003 | 14613034
 | |
| Decrease in susceptibility toward induction of apoptosis and alteration in G1 checkpoint function as determinants of resistance of human lung cancer cells against the antisignaling drug UCN-01 (7-Hydroxystaurosporine). Sugiyama, K., et al. Cancer Res. , 59(17):4406-4412 (1999) 1998 | 10485490
 |