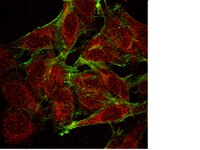
05-1469 Sigma-AldrichAnti-NFĸB Antibody, p65, clone 1G10.2
Anti-NFĸB Antibody, p65, clone 1G10.2 detects level of NFĸB & has been published & validated for use in WB, IF & IC.
More>> Anti-NFĸB Antibody, p65, clone 1G10.2 detects level of NFĸB & has been published & validated for use in WB, IF & IC. Less<<Recommended Products
Overview
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Key Spec Table
| Species Reactivity | Key Applications | Host | Format | Antibody Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H, M, R, B | WB, IF, ICC | M | Purified | Monoclonal Antibody |
| References |
|---|
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Format | Purified |
| HS Code | 3002 15 90 |
| Presentation | Purified mouse monoclonal in 0.1M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4) with 150mM NaCl and 0.05% NaN3. |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Physicochemical Information |
|---|
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Material Size | 200 µg |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | GTIN |
| 05-1469 | 04053252473333 |
Documentation
Anti-NFĸB Antibody, p65, clone 1G10.2 SDS
| Title |
|---|
Anti-NFĸB Antibody, p65, clone 1G10.2 Certificates of Analysis
| Title | Lot Number |
|---|---|
| Anti-NFkB, p65, clone 1G10.2 - 2181277 | 2181277 |
| Anti-NFkB, p65, clone 1G10.2 - 2278555 | 2278555 |
| Anti-NFkB, p65, clone 1G10.2 - NG1726940 | NG1726940 |
| Anti-NFkB, p65, clone 1G10.2 - NG1853752 | NG1853752 |
| Anti-NFkB, p65, clone 1G10.2 -2851198 | 2851198 |
| Anti-NFkB, p65, clone 1G10.2 -2858456 | 2858456 |
| Anti-NFκB, p65, clone 1G10.2 - 2452691 | 2452691 |
| Anti-NFκB, p65, clone 1G10.2 - 3351205 | 3351205 |
| Anti-NFκB, p65, clone 1G10.2 - 3974881 | 3974881 |
| Anti-NFκB, p65, clone 1G10.2 -2680242 | 2680242 |
Brochure
| Title |
|---|
| Pathways and Biomarkers of Toll-like Receptor (TLR) Signaling |