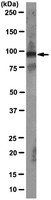
MABD55 Sigma-AldrichAnti-TERT (human) Antibody, clone 2C4
Anti-TERT (human) Antibody, clone 2C4 is an antibody against TERT (human) for use in WB, IC & IP.
More>> Anti-TERT (human) Antibody, clone 2C4 is an antibody against TERT (human) for use in WB, IC & IP. Less<<Produits recommandés
Aperçu
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Tableau de caractéristiques principal
| Species Reactivity | Key Applications | Host | Format | Antibody Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | WB, ICC, IP | M | Purified | Monoclonal Antibody |
| References |
|---|
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Format | Purified |
| Control |
|
| Presentation | Purified mouse monoclonal IgMκ in buffer containing PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Physicochemical Information |
|---|
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Storage and Shipping Information | |
|---|---|
| Storage Conditions | Stable for 1 year at 2-8°C from date of receipt. |
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Material Size | 100 µL |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Référence | GTIN |
| MABD55 | 04053252419591 |
Documentation
Anti-TERT (human) Antibody, clone 2C4 FDS
| Titre |
|---|
Anti-TERT (human) Antibody, clone 2C4 Certificats d'analyse
| Titre | Numéro de lot |
|---|---|
| Anti-TERT (human), clone 2C4 - 2432512 | 2432512 |
| Anti-TERT (human), clone 2C4 - 2050255 | 2050255 |
| Anti-TERT (human), clone 2C4 - 2328380 | 2328380 |
| Anti-TERT (human), clone 2C4 - 3193861 | 3193861 |
| Anti-TERT (human), clone 2C4 - 3443788 | 3443788 |
| Anti-TERT (human), clone 2C4 - 3796905 | 3796905 |
| Anti-TERT (human), clone 2C4 - NRG1897809 | NRG1897809 |
| Anti-TERT (human), clone 2C4 -2571286 | 2571286 |
| Anti-TERT (human), clone 2C4 -2581787 | 2581787 |
| Anti-TERT (human), clone 2C4 -2624975 | 2624975 |