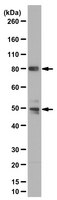
Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of adipocyte differentiation by Jumonji domain-containing protein 6.
Hu, YJ; Belaghzal, H; Hsiao, WY; Qi, J; Bradner, JE; Guertin, DA; Sif, S; Imbalzano, AN
Nucleic acids research
43
7790-804
2015
Afficher le résumé
Jumonji domain-containing protein 6 (JMJD6) is a nuclear protein involved in histone modification, transcription and RNA processing. Although JMJD6 is crucial for tissue development, the link between its molecular functions and its roles in any given differentiation process is unknown. We report that JMJD6 is required for adipogenic gene expression and differentiation in a manner independent of Jumonji C domain catalytic activity. JMJD6 knockdown led to a reduction of C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ protein expression without affecting mRNA levels in the early phase of differentiation. However, ectopic expression of C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ did not rescue differentiation. Further analysis demonstrated that JMJD6 was associated with the Pparγ2 and Cebpα loci and putative enhancers. JMJD6 was previously found associated with bromodomain and extra-terminal domain (BET) proteins, which can be targeted by the bromodomain inhibitor JQ1. JQ1 treatment prevented chromatin binding of JMJD6, Pparγ2 and Cebpα expression, and adipogenic differentiation, yet had no effect on C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ expression or chromatin binding. These results indicate dual roles for JMJD6 in promoting adipogenic gene expression program by post-transcriptional regulation of C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ and direct transcriptional activation of Pparγ2 and Cebpα during adipocyte differentiation. | 26117538
 |
KIM-1-mediated phagocytosis reduces acute injury to the kidney.
Yang, L; Brooks, CR; Xiao, S; Sabbisetti, V; Yeung, MY; Hsiao, LL; Ichimura, T; Kuchroo, V; Bonventre, JV
The Journal of clinical investigation
125
1620-36
2015
Afficher le résumé
Kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1, also known as TIM-1) is markedly upregulated in the proximal tubule after injury and is maladaptive when chronically expressed. Here, we determined that early in the injury process, however, KIM-1 expression is antiinflammatory due to its mediation of phagocytic processes in tubule cells. Using various models of acute kidney injury (AKI) and mice expressing mutant forms of KIM-1, we demonstrated a mucin domain-dependent protective effect of epithelial KIM-1 expression that involves downregulation of innate immunity. Deletion of the mucin domain markedly impaired KIM-1-mediated phagocytic function, resulting in increased proinflammatory cytokine production, decreased antiinflammatory growth factor secretion by proximal epithelial cells, and a subsequent increase in tissue macrophages. Mice expressing KIM-1Δmucin had greater functional impairment, inflammatory responses, and mortality in response to ischemia- and cisplatin-induced AKI. Compared with primary renal proximal tubule cells isolated from KIM-1Δmucin mice, those from WT mice had reduced proinflammatory cytokine secretion and impaired macrophage activation. The antiinflammatory effect of KIM-1 expression was due to the interaction of KIM-1 with p85 and subsequent PI3K-dependent downmodulation of NF-κB. Hence, KIM-1-mediated epithelial cell phagocytosis of apoptotic cells protects the kidney after acute injury by downregulating innate immunity and inflammation. | 25751064
 |
Prmt7 is dispensable in tissue culture models for adipogenic differentiation.
Hu, YJ; Sif, S; Imbalzano, AN
F1000Research
2
279
2013
Afficher le résumé
Protein arginine methylation is a common posttranslational modification that has been implicated in numerous biological processes including gene expression. The mammalian genome encodes nine protein arginine methyltransferases (Prmts) that catalyze monomethylation, asymmetric dimethylation, and symmetric dimethylation on arginine residues. Protein arginine methyltransferase 7 (Prmt7) is categorized as a type II and type III enzyme that produces symmetric dimethylated arginine and monomethylated arginine, respectively. However, the biological role of Prmt7 is not well characterized. We previously showed that Prmt5, a type II Prmt that associates with Brg1-based SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, is required for adipocyte differentiation. Since Prmt7 also associates with Brg1-based SWI/SNF complex and modifies core histones, we hypothesized that Prmt7 might play a role in transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. In the present study, we determined that the expression of Prmt7 did not change throughout adipogenic differentiation of C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal cells. Knockdown or over-expression of Prmt7 had no effect on lipid accumulation or adipogenic gene expression in differentiating C3H10T1/2 cells or in C/EBPα-reprogrammed NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Based on these results, we conclude that Prmt7, unlike Prmt5, is dispensable for adipogenic differentiation in tissue culture models. | 24715966
 |