A critical role for the programmed death ligand 1 in fetomaternal tolerance
Indira Guleria 1 , Arezou Khosroshahi, Mohammed Javeed Ansari, Antje Habicht, Miyuki Azuma, Hideo Yagita, Randolph J Noelle, Anthony Coyle, Andrew L Mellor, Samia J Khoury, Mohamed H Sayegh
J Exp Med
202(2)
231-7
2004
Afficher le résumé
Fetal survival during gestation implies that tolerance mechanisms suppress the maternal immune response to paternally inherited alloantigens. Here we show that the inhibitory T cell costimulatory molecule, programmed death ligand 1 (PDL1), has an important role in conferring fetomaternal tolerance in an allogeneic pregnancy model. Blockade of PDL1 signaling during murine pregnancy resulted in increased rejection rates of allogeneic concepti but not syngeneic concepti. Fetal rejection was T cell- but not B cell-dependent because PDL1-specific antibody treatment caused fetal rejection in B cell-deficient but not in RAG-1-deficient females. Blockade of PDL1 also resulted in a significant increase in the frequency of IFN-gamma-producing lymphocytes in response to alloantigen in an ELISPOT assay and higher IFN-gamma levels in placental homogenates by ELISA. Finally, PDL1-deficient females exhibited decreased allogeneic fetal survival rates as compared with littermate and heterozygote controls and showed evidence of expansion of T helper type 1 immune responses in vivo. These results provide the first evidence that PDL1 is involved in fetomaternal tolerance. | 16027236
 |
Expression of programmed death 1 ligands by murine T cells and APC
Tomohide Yamazaki 1 , Hisaya Akiba, Hideyuki Iwai, Hironori Matsuda, Mami Aoki, Yuka Tanno, Tahiro Shin, Haruo Tsuchiya, Drew M Pardoll, Ko Okumura, Miyuki Azuma, Hideo Yagita
J Immunol
169(10)
5538-45
2002
Afficher le résumé
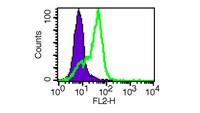
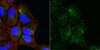
Programmed death 1 (PD-1) is a new member of the CD28/CTLA-4 family, which has been implicated in the maintenance of peripheral tolerance. Two ligands for PD-1, namely, B7-H1 (PD-L1) and B7-DC (PD-L2), have recently been identified as new members of the B7 family but their expression at the protein level remains largely unknown. To characterize the expression of B7-H1 and B7-DC, we newly generated an anti-mouse B7-H1 mAb (MIH6) and an anti-mouse B7-DC mAb (TY25). MIH6 and TY25 immunoprecipitated a single molecule of 43 and 42 kDa from the lysate of B7-H1 and B7-DC transfectants, respectively. Flow cytometric analysis revealed that B7-H1 was broadly expressed on the surface of mouse tumor cell lines while the expression of B7-DC was rather restricted. PD-1 was expressed on anti-CD3-stimulated T cells and anti-IgM plus anti-CD40-stimulated B cells at high levels but was undetectable on activated macrophages or DCs. B7-H1 was constitutively expressed on freshly isolated splenic T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells (DCs), and up-regulated on T cells by anti-CD3 stimulation on macrophages by LPS, IFN-gamma, GM-CSF, or IL-4, and on DCs by IFN-gamma, GM-CSF, or IL-4. In contrast, B7-DC expression was only inducible on macrophages and DCs upon stimulation with IFN-gamma, GM-CSF, or IL-4. The inducible expression of PD-1 ligands on both T cells and APCs may suggest new paradigms of PD-1-mediated immune regulation. | 12421930
 |