Experimental traumatic brain injury induces rapid aggregation and oligomerization of amyloid-beta in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model.
Washington, PM; Morffy, N; Parsadanian, M; Zapple, DN; Burns, MP
Journal of neurotrauma
31
125-34
2014
Afficher le résumé
Soluble amyloid-beta (Aβ) oligomers are hypothesized to be the pathogenic species in Alzheimer's disease (AD), and increased levels of oligomers in the brain subsequent to traumatic brain injury (TBI) may exacerbate secondary injury pathways and underlie increased risk of developing AD in later life. To determine whether TBI causes Aβ aggregation and oligomerization in the brain, we exposed triple transgenic AD model mice to controlled cortical impact injury and measured levels of soluble, insoluble, and oligomeric Aβ by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) at 1, 3, and 7 days postinjury. TBI rapidly increased levels of both soluble and insoluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 in the injured cortex at 1 day postinjury. We confirmed previous findings that identified damaged axons as a major site of Aβ accumulation using both immunohistochemistry and biochemistry. We also report that soluble Aβ oligomers were significantly increased in the injured cortex, as demonstrated by both ELISA and Western blot. Interestingly, the mouse brain is able to rapidly clear trauma-induced Aβ, with both soluble and insoluble Aβ species returning to sham levels by 7 days postinjury. In conclusion, we demonstrate that TBI causes acute accumulation and aggregation of Aβ in the brain, including the formation of low- and high-molecular-weight Aβ oligomers. The formation and aggregation of Aβ into toxic species acutely after injury may play a role in secondary injury cascades after trauma and, chronically, may contribute to increased risk of developing AD in later life. | | | 24050316
 |
Dual cleavage of neuregulin 1 type III by BACE1 and ADAM17 liberates its EGF-like domain and allows paracrine signaling.
Fleck, D; van Bebber, F; Colombo, A; Galante, C; Schwenk, BM; Rabe, L; Hampel, H; Novak, B; Kremmer, E; Tahirovic, S; Edbauer, D; Lichtenthaler, SF; Schmid, B; Willem, M; Haass, C
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
33
7856-69
2013
Afficher le résumé
Proteolytic shedding of cell surface proteins generates paracrine signals involved in numerous signaling pathways. Neuregulin 1 (NRG1) type III is involved in myelination of the peripheral nervous system, for which it requires proteolytic activation by proteases of the ADAM family and BACE1. These proteases are major therapeutic targets for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease because they are also involved in the proteolytic generation of the neurotoxic amyloid β-peptide. Identification and functional investigation of their physiological substrates is therefore of greatest importance in preventing unwanted side effects. Here we investigated proteolytic processing of NRG1 type III and demonstrate that the ectodomain can be cleaved by three different sheddases, namely ADAM10, ADAM17, and BACE1. Surprisingly, we not only found cleavage by ADAM10, ADAM17, and BACE1 C-terminal to the epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain, which is believed to play a pivotal role in signaling, but also additional cleavage sites for ADAM17 and BACE1 N-terminal to that domain. Proteolytic processing at N- and C-terminal sites of the EGF-like domain results in the secretion of this domain from NRG1 type III. The soluble EGF-like domain is functionally active and stimulates ErbB3 signaling in tissue culture assays. Moreover, the soluble EGF-like domain is capable of rescuing hypomyelination in a zebrafish mutant lacking BACE1. Our data suggest that NRG1 type III-dependent myelination is not only controlled by membrane-retained NRG1 type III, but also in a paracrine manner via proteolytic liberation of the EGF-like domain. | | | 23637177
 |
Timosaponin-BII inhibits the up-regulation of BACE1 induced by ferric chloride in rat retina.
Huang, JF; Shang, L; Liu, P; Zhang, MQ; Chen, S; Chen, D; Fan, CL; Wang, H; Xiong, K
BMC complementary and alternative medicine
12
189
2011
Afficher le résumé
Our previous studies indicated that oxidative stress up-regulated the expression of β-amyloid precursor protein cleavage enzyme-1 (BACE1) in rat retina. Pharmacological reports have shown Timosaponin-BII, a purified extract originating from Chinese medical herb Rhizoma Anemarrhenae, is characterized as an antioxidant. Our present study aimed to determine whether Timosaponin-BII affected the expression of BACE1, β-amyloid precursor protein cleavage production of Aβ1-40 and β-C-terminal fragment (β-CTF) in rat retina, which were pre-treated with the oxidizing agent (solution of FeCl₃).Few distinctions of BACE1 distribution were observed among all groups (normal control group, model group, Timosaponin-BII treated and vehicle control groups). Rat retinas in model group and vehicle control group manifested an apparent up-regulation of BACE1 expression. Meanwhile, the level of malonaldehyde (MDA), Aβ1-40 and β-CTF were increased. However, when comparing with the vehicle control group, the retinas in Timosaponin-BII treated group showed significantly less BACE1 (pless than 0.05) and accumulated less Aβ1-40 or β-CTF (pless than 0.05). It also showed significantly decreased level of MDA (pless than 0.05) and prolonged partial thromboplastin time (pless than 0.05).Our data suggested that Timosaponin-BII remarkably inhibited the up-regulation of BACE1 and reduced the over-production of β-CTF and Aβ in rat retina, which was induced by FeCl₃. The mechanism of Timosaponin-BII on BACE1 expression may be related to its antioxidant property. | | | 23082924
 |
Delivery of Quantum Dot-siRNA Nanoplexes in SK-N-SH Cells for BACE1 Gene Silencing and Intracellular Imaging.
Li, S; Liu, Z; Ji, F; Xiao, Z; Wang, M; Peng, Y; Zhang, Y; Liu, L; Liang, Z; Li, F
Molecular therapy. Nucleic acids
1
e20
2011
Afficher le résumé
The fluorescent quantum dots (QDs) delivered small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) targeting β-secretase (BACE1) to achieve high transfection efficiency of siRNAs and reduction of β-amyloid (Aβ) in nerve cells. The CdSe/ZnS QDs with the conjugation of amino-polyethylene glycol (PEG) were synthesized. Negatively charged siRNAs were electrostatically adsorbed to the surface of QDs to develop QD-PEG/siRNA nanoplexes. The QD-PEG/siRNAs nanoplexes significantly promote the transfection efficiency of siRNA, and the siRNAs from non-packaged nanoplexes were widely distributed in cell bodies and processes and efficiently silenced BACE1 gene, leading to the reduction of Aβ. The biodegradable PEG polymer coating could protect QDs from being exposed to the intracellular environment and restrained the release of toxic Cd2(+). Therefore, the QD-PEG/siRNA nanoplexes reported here might serve as ideal carriers for siRNAs. We developed a novel method of siRNA delivery into nerve cells. We first reported that the QD-PEG/siRNA nanoplexes were generated by the electrostatic interaction and inhibited the Alzheimer's disease (AD)-associated BACE1 gene. We also first revealed the dynamics of QD-PEG/siRNAs within nerve cells via confocal microscopy and the ultrastructural evidences under transmission electron microscopy (TEM). This technology might hold promise for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as AD. | | | 23343930
 |
PPAR? co-activator-1? (PGC-1?) reduces amyloid-? generation through a PPAR?-dependent mechanism.
Loukia Katsouri,Callum Parr,Nenad Bogdanovic,Michael Willem,Magdalena Sastre
Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD
25
2010
Afficher le résumé
We have previously reported that the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-? (PPAR?) regulates the transcription of ?-secretase (BACE1), a key enzyme involved in amyloid-? (A?) generation. Here, we aimed to investigate the role of PPAR? coactivator-1? (PGC-1?), which controls major metabolic functions through the co-activation of PPAR? and other transcription factors. Western blotting experiments with nuclear extracts from brain cortex of AD cases and controls showed a reduction in the levels of PGC-1? in AD patients. PGC-1? overexpression in N2a neuroblastoma cells induced a decrease in the levels of secreted A? and an increase in the levels of non-amyloidogenic soluble A?PP?. The decrease in A? after exogenous expression of PGC-1? was a consequence of reduced BACE1 expression and transcription, together with a decrease in BACE1 promoter activity. In addition, we detected a significant reduction in ?-secretase activity by measuring the levels of ?-carboxy terminus fragment (?-CTFs) and by using a commercial assay for ?-secretase. In contrast, down-regulation of PGC-1? levels by transfection with PGC-1? siRNA increased BACE1 expression. These effects appeared to be dependent on PPAR?, because PGC-1? did not affect A? and BACE1 levels in N2a cells transfected with PPAR? siRNA or in PPAR? knockout fibroblasts. In conclusion, since PGC-1? appears to decrease A? generation, therapeutic modulation of PGC-1? could have real potential as a treatment for AD. | | | 21358044
 |
AGEs/RAGE complex upregulates BACE1 via NF-kappaB pathway activation.
Guglielmotto, Michela, et al.
Neurobiology of aging, (2010)
2009
Afficher le résumé
Although the pathogenesis of sporadic Alzheimer disease (AD) is not clearly understood, it is likely dependent on several age-related factors. Diabetes is a risk factor for AD, and multiple mechanisms connecting the 2 diseases have been proposed. Hyperglycemia enhances the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) that result from the auto-oxidation of glucose and fructose. The interaction of AGEs with their receptor, named RAGE, elicits the formation of reactive oxygen species that are also believed to be an early event in AD pathology. To investigate a functional link between the disorders diabetes and AD, the effect of 2 AGEs, pentosidine and glyceraldehydes-derived pyridinium (GLAP), was studied on BACE1 expression both in vivo, in streptozotocin treated rats, and in vitro in differentiated neuroblastoma cells. We showed that pentosidine and GLAP were able to upregulate BACE1 expression through their binding with RAGE and the consequent activation of NF-kappaB. In addition, both pentosidine and GLAP were found to be increased in the brain in sporadic AD patients. Our findings demonstrate that activation of the AGEs/RAGE axis, by upregulating the key enzyme for amyloid-beta production, provides a pathologic link between diabetes mellitus and AD. | | | 20638753
 |
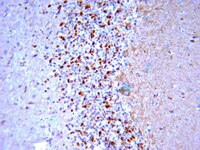
β-Secretase-1 elevation in aged monkey and Alzheimer's disease human cerebral cortex occurs around the vasculature in partnership with multisystem axon terminal pathogenesis and β-amyloid accumulation.
Cai, Y; Xiong, K; Zhang, XM; Cai, H; Luo, XG; Feng, JC; Clough, RW; Struble, RG; Patrylo, PR; Chu, Y; Kordower, JH; Yan, XX
The European journal of neuroscience
32
1223-38
2009
Afficher le résumé
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common dementia-causing disorder in the elderly; it may be related to multiple risk factors, and is characterized pathologically by cerebral hypometabolism, paravascular β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) plaques, neuritic dystrophy, and intra-neuronal aggregation of phosphorylated tau. To explore potential pathogenic links among some of these lesions, we examined β-secretase-1 (BACE1) alterations relative to Aβ deposition, neuritic pathology and vascular organization in aged monkey and AD human cerebral cortex. Western blot analyses detected increased levels of BACE1 protein and β-site-cleavage amyloid precursor protein C-terminal fragments in plaque-bearing human and monkey cortex relative to controls. In immunohistochemistry, locally elevated BACE1 immunoreactivity (IR) occurred in AD but not in control human cortex, with a trend for increased overall density among cases with greater plaque pathology. In double-labeling preparations, BACE1 IR colocalized with immunolabeling for Aβ but not for phosphorylated tau. In perfusion-fixed monkey cortex, locally increased BACE1 IR co-existed with intra-axonal and extracellular Aβ IR among virtually all neuritic plaques, ranging from primitive to typical cored forms. This BACE1 labeling localized to swollen/sprouting axon terminals that might co-express one or another neuronal phenotype markers (GABAergic, glutamatergic, cholinergic, or catecholaminergic). Importantly, these BACE1-labeled dystrophic axons resided near to or in direct contact with blood vessels. These findings suggest that plaque formation in AD or normal aged primates relates to a multisystem axonal pathogenesis that occurs in partnership with a potential vascular or metabolic deficit. The data provide a mechanistic explanation for why senile plaques are present preferentially near the cerebral vasculature. Article en texte intégral | Immunohistochemistry | | 20726888
 |
The up-regulation of BACE1 mediated by hypoxia and ischemic injury: role of oxidative stress and HIF1alpha.
Guglielmotto, Michela, et al.
J. Neurochem., 108: 1045-56 (2009)
2009
Afficher le résumé
While it is well established that stroke and cerebral hypoperfusion are both significant risk factors for Alzheimer's disease, the molecular link between ischemia and amyloid precursor protein processing has only been recently established. Specifically, hypoxia significantly increases beta-site APP cleaving enzyme (BACE1) gene transcription through the over-expression of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha, resulting in increased BACE1 secretase activity and amyloid-beta production. In this study, we significantly extend these findings both in vitro, in differentiated SK-N-BE neuroblastoma cells, and in vivo, in rats subjected to cerebral ischemia, showing that hypoxia up-regulates BACE1 expression through a biphasic mechanism. The early post-hypoxic up-regulation of BACE1 depends on the production of reactive oxygen species mediated by the sudden interruption of the mitochondrial electron transport chain, while the later expression of BACE1 is caused by hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha activation. The involvement of reactive oxygen species released by mitochondria in the BACE1 up-regulation was confirmed by the complete protection exerted by complex I inhibitors such as rotenone and diphenyl-phenylen iodonium. Moreover, the oxidative stress-mediated up-regulation of BACE1 is mediated by c-jun N terminal kinase pathway as demonstrated by the protection exerted by the silencing of c-jun N-terminal kinase isoforms 1 and 2. Our study strengthens the hypothesis that oxidative stress is a basic common mechanism of amyloid-beta accumulation. | | Rat | 19196431
 |
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), but not morphine, alters APP processing in the rat brain.
Kálmán, János, et al.
Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol., 10: 183-90 (2007)
2007
Afficher le résumé
The abuse of drugs such as opioids and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA or 'ecstasy') can have detrimental effects on the cognitive functions, but the exact molecular mechanism whereby these drugs promote neurodegeneration remains to be elucidated. The major purpose of the present pilot study was to determine whether the chronic in-vivo administration of morphine (10 mg/kg) or MDMA (1 mg/kg) to rats can alter the expression and processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP), the central molecule in the proposed pathomechanism of Alzheimer's disease. MDMA treatment significantly decreased the production of APP in the cytosolic fraction of the brain cortex. A concomitant 25% increase was found both in the beta-secretase (BACE) and APP mRNA levels (108%). In contrast, in the applied single dosage chronic morphine treatment did not influence either the APP and BACE protein levels or the APP mRNA production. These results indicate that the chronic use of 'ecstasy', but not morphine, may be harmful via a novel mode of action, i.e. by altering the APP expression and processing in the brain. | | | 16487451
 |
Human apoB overexpression and a high-cholesterol diet differently modify the brain APP metabolism in the transgenic mouse model of atherosclerosis.
Bjelik, Annamária, et al.
Neurochem. Int., 49: 393-400 (2006)
2005
Afficher le résumé
Epidemiological and biochemical data suggest a link between the cholesterol metabolism, the amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing and the increased cerebral beta-amyloid (Abeta) deposition in Alzheimer's disease (AD). The individual and combined effects of a high-cholesterol (HC) diet and the overexpression of the human apoB-100 gene were therefore examined on the cerebral expression and processing of APP in homozygous apoB-100 transgenic mice [Tg (apoB(+/+))], a validated model of atherosclerosis. When fed with 2% cholesterol for 17 weeks, only the wild-type mice exhibited significantly increased APP695 (123%) and APP770 (138%) mRNA levels in the cortex. The HC diet-induced hypercholesterolemia significantly increased the APP isoform levels in the membrane-bound fraction, not only in the wild-type animals (114%), but also in the Tg apoB(+/+) group (171%). The overexpression of human apoB-100 gene by the liver alone reduced the brain APP isoform levels in the membrane-bound fraction (78%), whereas the levels were increased by the combined effect of HC and the overexpression of the human apoB-100 gene (134%). The protein kinase C and beta-secretase protein levels were not altered by the individual or combined effects of these two factors. Our data indicate that the two atherogenic factors, the HC diet and the overexpression of the human apoB-100 gene by the liver, could exert different effects on the processing and expression of APP in the mice brain. | | | 16546298
 |