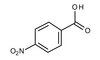
The forkhead transcription factor FOXM1 controls cell cycle-dependent gene expression through an atypical chromatin binding mechanism.
Chen, Xi, et al.
Mol. Cell. Biol., 33: 227-36 (2013)
2013
Show Abstract
There are nearly 50 forkhead (FOX) transcription factors encoded in the human genome and, due to sharing a common DNA binding domain, they are all thought to bind to similar DNA sequences. It is therefore unclear how these transcription factors are targeted to specific chromatin regions to elicit specific biological effects. Here, we used chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) to investigate the genome-wide chromatin binding mechanisms used by the forkhead transcription factor FOXM1. In keeping with its previous association with cell cycle control, we demonstrate that FOXM1 binds and regulates a group of genes which are mainly involved in controlling late cell cycle events in the G(2) and M phases. However, rather than being recruited through canonical RYAAAYA forkhead binding motifs, FOXM1 binding is directed via CHR (cell cycle genes homology region) elements. FOXM1 binds these elements through protein-protein interactions with the MMB transcriptional activator complex. Thus, we have uncovered a novel and unexpected mode of chromatin binding of a FOX transcription factor that allows it to specifically control cell cycle-dependent gene expression. | Western Blotting | 23109430
 |
The CHR promoter element controls cell cycle-dependent gene transcription and binds the DREAM and MMB complexes.
Müller, GA; Quaas, M; Schümann, M; Krause, E; Padi, M; Fischer, M; Litovchick, L; DeCaprio, JA; Engeland, K
Nucleic Acids Res
40
1561-78
2012
Show Abstract
Cell cycle-dependent gene expression is often controlled on the transcriptional level. Genes like cyclin B, CDC2 and CDC25C are regulated by cell cycle-dependent element (CDE) and cell cycle genes homology region (CHR) promoter elements mainly through repression in G(0)/G(1). It had been suggested that E2F4 binding to CDE sites is central to transcriptional regulation. However, some promoters are only controlled by a CHR. We identify the DREAM complex binding to the CHR of mouse and human cyclin B2 promoters in G(0). Association of DREAM and cell cycle-dependent regulation is abrogated when the CHR is mutated. Although E2f4 is part of the complex, a CDE is not essential but can enhance binding of DREAM. We show that the CHR element is not only necessary for repression of gene transcription in G(0)/G(1), but also for activation in S, G(2) and M phases. In proliferating cells, the B-myb-containing MMB complex binds the CHR of both promoters independently of the CDE. Bioinformatic analyses identify many genes which contain conserved CHR elements in promoters binding the DREAM complex. With Ube2c as an example from that screen, we show that inverse CHR sites are functional promoter elements that can bind DREAM and MMB. Our findings indicate that the CHR is central to DREAM/MMB-dependent transcriptional control during the cell cycle. | | 22064854
 |
A Lin-9 complex is recruited by B-Myb to activate transcription of G2/M genes in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells.
Knight, A S, et al.
Oncogene, 28: 1737-47 (2009)
2009
Show Abstract
It has recently been discovered that cell-cycle gene transcription is regulated by a core complex named LINC that switches from a transcriptionally repressive complex in G(0)-G(1) with the p130 or p107 pocket proteins and E2F4 to a transcriptionally active complex in S-G(2) containing B-Myb. We have studied the function of LINC in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells, which are distinguished by a rapid cell cycle resulting from an extremely short G(1) phase. We show that suppressing expression of the LINC component, Lin-9, in F9 cells causes arrest in mitosis, and we have used this system to screen for transcriptional targets. In these cells, B-Myb was found in complexes with Lin-9 and several other LINC constituents, however, the pocket proteins did not associate with LINC unless F9 cells were differentiated. Lin-9 and B-Myb were both required for transcription of G(2)/M genes such as Cyclin B1 and Survivin. Moreover, B-Myb was demonstrated to recruit Lin-9 to the Survivin promoter through multiple Myb-binding sites. The demonstration that a B-Myb/LINC complex is vital for progression through mitosis in cells lacking a G(1)/S checkpoint has implications for both undifferentiated embryonal cells and for cancers in which pocket protein function is compromised. | Western Blotting | 19252525
 |
Targeting an E2F site in the mouse genome prevents promoter silencing in quiescent and post-mitotic cells.
Tavner, F, et al.
Oncogene, 26: 2727-35 (2007)
2007
Show Abstract
Previous studies have shown that the cell cycle-regulated B-myb promoter contains a conserved E2F binding site that is critical for repressing transcription in quiescent cells. To investigate its significance for permanent promoter silencing, we have inactivated this binding site in the mouse genome. Mice homozygous for the mutant B-mybmE2F allele were fully viable, however, B-myb transcription was derepressed during quiescence in mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) derived from mutant animals. Moreover, it was found that mutation of the E2F site resulted in abnormal maintenance of B-myb expression in senescent MEFs and in differentiated brain tissue. These findings therefore reveal a direct and primary role for repressive E2F complexes in silencing gene expression in post-mitotic cells. Analysis of histone modifications at the promoter showed that histone H3 lysine 9 was constitutively acetylated throughout the cell cycle in homozygous mutant MEFs. This mouse system is the first description of an E2F site mutation in situ and will facilitate the study of E2F function in vivo. | | 17072340
 |