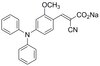
Sequential activation of soluble guanylate cyclase, protein kinase G and cGMP-degrading phosphodiesterase is necessary for proper induction of long-term potentiation in CA1 of hippocampus. Alterations in hyperammonemia.
Monfort, Pilar, et al.
Neurochem. Int., 45: 895-901 (2004)
2004
Show Abstract
Long-term potentiation (LTP) is a long-lasting enhancement of synaptic transmission efficacy and is considered the base for some forms of learning and memory. Nitric oxide (NO)-induced formation of cGMP is involved in hippocampal LTP. We have studied in hippocampal slices the effects of application of a tetanus to induce LTP on cGMP metabolism and the mechanisms by which cGMP modulates LTP. Tetanus application induced a transient rise in cGMP, reaching a maximum at 10s and decreasing below basal levels 5 min after the tetanus, remaining below basal levels after 60 min. Soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) activity increased 5 min after tetanus and returned to basal levels at 60 min. The decrease in cGMP was due to sustained tetanus-induced increase in cGMP-degrading phosphodiesterase activity, which remained activated 60 min after tetanus. Tetanus-induced activation of PDE and decrease of cGMP were prevented by inhibiting protein kinase G (PKG). This indicates that the initial increase in cGMP activates PKG that phosphorylates (and activates) cGMP-degrading PDE, which, in turn, degrades cGMP. Inhibition of sGC, of PKG or of cGMP-degrading phosphodiesterase impairs LTP, indicating that proper induction of LTP involves transient activation of sGC and increase in cGMP, followed by activation of cGMP-dependent protein kinase, which, in turn, activates cGMP-degrading phosphodiesterase, resulting in long-lasting reduction of cGMP content. Hyperammonemia is the main responsible for the neurological alterations found in liver disease and hepatic encephalopathy, including impaired intellectual function. Hyperammonemia impairs LTP in hippocampus by altering the modulation of this sGC-PKG-cGMP-degrading PDE pathway. Exposure of hippocampal slices to 1 mM ammonia completely prevents tetanus-induced decrease of cGMP by impairing PKG-mediated activation of cGMP-degrading phosphodiesterase. This impairment is responsible for the loss of the maintenance of LTP in hyperammonemia, and may be also involved in the cognitive impairment in patients with hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy. | 15312984
 |
A stimulatory role for cGMP-dependent protein kinase in platelet activation.
Li, Zhenyu, et al.
Cell, 112: 77-86 (2003)
2003
Show Abstract
It is currently accepted that cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) inhibits platelet activation. Here, we show that PKG plays an important stimulatory role in platelet activation. Expression of recombinant PKG in a reconstituted cell model enhanced von Willebrand factor (vWF)-induced activation of the platelet integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3). PKG knockout mice showed impaired platelet responses to vWF or low doses of thrombin and prolonged bleeding time. Human platelet aggregation induced by vWF or low-dose thrombin was inhibited by PKG inhibitors but enhanced by cGMP. Furthermore, a cGMP-enhancing agent, sildenafil, promoted vWF- or thrombin-induced platelet aggregation. The cGMP-stimulated platelet responses are biphasic, consisting of an initial transient stimulatory response that promotes platelet aggregation and a subsequent inhibitory response that limits the size of thrombi. | 12526795
 |