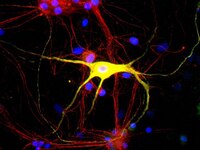
Vitamin D receptor and enzyme expression in dorsal root ganglia of adult female rats: modulation by ovarian hormones.
Tague, SE; Smith, PG
Journal of chemical neuroanatomy
41
1-12
2011
Show Abstract
Vitamin D insufficiency impacts sensory processes including pain and proprioception, but little is known regarding vitamin D signaling in adult sensory neurons. We analyzed female rat dorsal root ganglia (DRG) for vitamin receptor (VDR) and the vitamin D metabolizing enzymes CYP27B1 and CYP24. Western blots and immunofluorescence revealed the presence of these proteins in sensory neurons. Nuclear VDR immunoreactivity was present within nearly all neurons, while cytoplasmic VDR was found preferentially in unmyelinated calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-positive neurons, colocalizing with CYP27B1 and CYP24. These data suggest that 1,25(OH)(2)D3 may affect sensory neurons through nuclear or extranuclear signaling pathways. In addition, local vitamin D metabolite concentrations in unmyelinated sensory neurons may be controlled through expression of CYP27B1 and CYP24. Because vitamin D deficiency appears to exacerbate some peri-menopausal pain syndromes, we assessed the effect of ovariectomy on vitamin D-related proteins. Two weeks following ovariectomy, total VDR expression in DRG dropped significantly, owing to a slight decrease in the percentage of total neurons expressing nuclear VDR and a large drop in unmyelinated CGRP-positive neurons expressing cytoplasmic VDR. Total CYP27B1 expression dropped significantly, predominantly due to decreased expression within unmyelinated CGRP-positive neurons. CYP24 expression remained unchanged. Therefore, unmyelinated CGRP-positive neurons appear to have a distinct vitamin D phenotype with hormonally-regulated ligand and receptor levels. These findings imply that vitamin D signaling may play a specialized role in a neural cell population that is primarily nociceptive. | 20969950
 |
Syncoilin modulates peripherin filament networks and is necessary for large-calibre motor neurons
W Thomas Clarke 1 , Ben Edwards, Karl J A McCullagh, Matthew W Kemp, Catherine Moorwood, Diane L Sherman, Matthew Burgess, Kay E Davies
J Cell Sci
123(Pt 15)
2543-52
2010
Show Abstract
Syncoilin is an atypical type III intermediate filament (IF) protein, which is expressed in muscle and is associated with the dystrophin-associated protein complex. Here, we show that syncoilin is expressed in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. Isoform Sync1 is dominant in the brain, but isoform Sync2 is dominant in the spinal cord and sciatic nerve. Peripherin is a type III IF protein that has been shown to colocalise and interact with syncoilin. Our analyses suggest that syncoilin might function to modulate formation of peripherin filament networks through binding to peripherin isoforms. Peripherin is associated with the disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), thus establishing a link between syncoilin and ALS. A neuronal analysis of the syncoilin-null mouse (Sync(-/-)) revealed a reduced ability in accelerating treadmill and rotarod tests. This phenotype might be attributable to the impaired function of extensor digitorum longus muscle and type IIb fibres caused by a shift from large- to small-calibre motor axons in the ventral root. | 20587592
 |
Evidence for the direct binding of phosphorylated p53 to sites of DNA breaks in vivo.
Al Rashid, ST; Dellaire, G; Cuddihy, A; Jalali, F; Vaid, M; Coackley, C; Folkard, M; Xu, Y; Chen, BP; Chen, DJ; Lilge, L; Prise, KM; Bazett Jones, DP; Bristow, RG
Cancer research
65
10810-21
2005
Show Abstract
Despite a clear link between ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM)-dependent phosphorylation of p53 and cell cycle checkpoint control, the intracellular biology and subcellular localization of p53 phosphoforms during the initial sensing of DNA damage is poorly understood. Using G0-G1 confluent primary human diploid fibroblast cultures, we show that endogenous p53, phosphorylated at Ser15 (p53Ser15), accumulates as discrete, dose-dependent and chromatin-bound foci within 30 minutes following induction of DNA breaks or DNA base damage. This biologically distinct subpool of p53Ser15 is ATM dependent and resistant to 26S-proteasomal degradation. p53Ser15 colocalizes and coimmunoprecipitates with gamma-H2AX with kinetics similar to that of biochemical DNA double-strand break (DNA-dsb) rejoining. Subnuclear microbeam irradiation studies confirm p53Ser15 is recruited to sites of DNA damage containing gamma-H2AX, ATM(Ser1981), and DNA-PKcs(Thr2609) in vivo. Furthermore, studies using isogenic human and murine cells, which express Ser15 or Ser18 phosphomutant proteins, respectively, show defective nuclear foci formation, decreased induction of p21WAF, decreased gamma-H2AX association, and altered DNA-dsb kinetics following DNA damage. Our results suggest a unique biology for this p53 phosphoform in the initial steps of DNA damage signaling and implicates ATM-p53 chromatin-based interactions as mediators of cell cycle checkpoint control and DNA repair to prevent carcinogenesis. | 16322227
 |