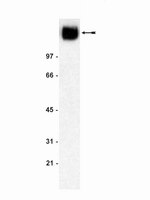
Dystroglycan controls dendritic morphogenesis of hippocampal neurons in vitro.
Bijata, M; Wlodarczyk, J; Figiel, I
Frontiers in cellular neuroscience
9
199
2015
Show Abstract
Dendritic outgrowth and arborization are important for establishing neural circuit formation. To date, little information exists about the involvement of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and its cellular receptors in these processes. In our studies, we focus on the role of dystroglycan (DG), a cell adhesion molecule that links ECM components to the actin cytoskeleton, in dendritic development and branching. Using a lentiviral vector to deliver short-hairpin RNA (shRNA) that specifically silences DG in cultured hippocampal neurons, we found that DG knockdown exerted an inhibitory effect on dendritic tree growth and arborization. The structural changes were associated with activation of the guanosine triphosphatase Cdc42. The overexpression of DG promoted dendritic length and branching. Furthermore, exposure of the cultures to autoactivating matrix metalloproteinase-9 (aaMMP-9), a β-DG-cleaving protease, decreased the complexity of dendritic arbors. This effect was abolished in neurons that overexpressed a β-DG mutant that was defective in MMP-9-mediated cleavage. Altogether, our results indicate that DG controls dendritic arborization in vitro in MMP-9-dependent manner. | | | 26074769
 |
Gephyrin clusters are absent from small diameter primary afferent terminals despite the presence of GABA(A) receptors.
Lorenzo, LE; Godin, AG; Wang, F; St-Louis, M; Carbonetto, S; Wiseman, PW; Ribeiro-da-Silva, A; De Koninck, Y
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
34
8300-17
2014
Show Abstract
Whereas both GABA(A) receptors (GABA(A)Rs) and glycine receptors (GlyRs) play a role in control of dorsal horn neuron excitability, their relative contribution to inhibition of small diameter primary afferent terminals remains controversial. To address this, we designed an approach for quantitative analyses of the distribution of GABA(A)R-subunits, GlyR α1-subunit and their anchoring protein, gephyrin, on terminals of rat spinal sensory afferents identified by Calcitonin-Gene-Related-Peptide (CGRP) for peptidergic terminals, and by Isolectin-B4 (IB4) for nonpeptidergic terminals. The approach was designed for light microscopy, which is compatible with the mild fixation conditions necessary for immunodetection of several of these antigens. An algorithm was designed to recognize structures with dimensions similar to those of the microscope resolution. To avoid detecting false colocalization, the latter was considered significant only if the degree of pixel overlap exceeded that expected from randomly overlapping pixels given a hypergeometric distribution. We found that both CGRP(+) and IB4(+) terminals were devoid of GlyR α1-subunit and gephyrin. The α1 GABA(A)R was also absent from these terminals. In contrast, the GABA(A)R α2/α3/α5 and β3 subunits were significantly expressed in both terminal types, as were other GABA(A)R-associated-proteins (α-Dystroglycan/Neuroligin-2/Collybistin-2). Ultrastructural immunocytochemistry confirmed the presence of GABA(A)R β3 subunits in small afferent terminals. Real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) confirmed the results of light microscopy immunochemical analysis. These results indicate that dorsal horn inhibitory synapses follow different rules of organization at presynaptic versus postsynaptic sites (nociceptive afferent terminals vs inhibitory synapses on dorsal horn neurons). The absence of gephyrin clusters from primary afferent terminals suggests a more diffuse mode of GABA(A)-mediated transmission at presynaptic than at postsynaptic sites. | | | 24920633
 |
Resistance exercise increases active MMP and β1-integrin protein expression in skeletal muscle.
Ogasawara, R; Nakazato, K; Sato, K; Boppart, MD; Fujita, S
Physiological reports
2
2014
Show Abstract
Recent studies indicate that matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and critical linkage proteins in the extracellular matrix (ECM) regulate skeletal muscle mass, although the effects of resistance training (RT) on protein expression and activity are unclear. Thus, the purpose of the present study was to investigate the effects of RT on MMP activity and expression of ECM-related proteins. Ten male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly assigned to 1 bout (1B) or 18 bouts (18B) of electrical stimulation. The right gastrocnemius muscle was isometrically contracted via percutaneous electrical stimulation (five sets of 5 sec stimulation × five contractions/set with 5 sec interval between contractions and 3 min rest between sets) once (1B) or every other day for 5 weeks (18B). The left leg served as a control. Activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9, determined via gelatin zymography, was increased (P less than 0.05) immediately after 1B. However, MMP activation was not evident following 18B. No changes in collagen IV, laminin α2, α7-integrin, or ILK protein expression were detected immediately following 1B or 18B. However, β1-integrin protein expression was significantly increased (P less than 0.05) with 18B. Our results suggest that resistance exercise activates MMPs during the initial phase of RT but this response is attenuated with continuation of RT. | | | 25413329
 |
ISPD gene mutations are a common cause of congenital and limb-girdle muscular dystrophies.
Cirak, S; Foley, AR; Herrmann, R; Willer, T; Yau, S; Stevens, E; Torelli, S; Brodd, L; Kamynina, A; Vondracek, P; Roper, H; Longman, C; Korinthenberg, R; Marrosu, G; Nürnberg, P; , ; Michele, DE; Plagnol, V; Hurles, M; Moore, SA; Sewry, CA; Campbell, KP; Voit, T; Muntoni, F
Brain : a journal of neurology
136
269-81
2013
Show Abstract
Dystroglycanopathies are a clinically and genetically diverse group of recessively inherited conditions ranging from the most severe of the congenital muscular dystrophies, Walker-Warburg syndrome, to mild forms of adult-onset limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. Their hallmark is a reduction in the functional glycosylation of α-dystroglycan, which can be detected in muscle biopsies. An important part of this glycosylation is a unique O-mannosylation, essential for the interaction of α-dystroglycan with extracellular matrix proteins such as laminin-α2. Mutations in eight genes coding for proteins in the glycosylation pathway are responsible for ∼50% of dystroglycanopathy cases. Despite multiple efforts using traditional positional cloning, the causative genes for unsolved dystroglycanopathy cases have escaped discovery for several years. In a recent collaborative study, we discovered that loss-of-function recessive mutations in a novel gene, called isoprenoid synthase domain containing (ISPD), are a relatively common cause of Walker-Warburg syndrome. In this article, we report the involvement of the ISPD gene in milder dystroglycanopathy phenotypes ranging from congenital muscular dystrophy to limb-girdle muscular dystrophy and identified allelic ISPD variants in nine cases belonging to seven families. In two ambulant cases, there was evidence of structural brain involvement, whereas in seven, the clinical manifestation was restricted to a dystrophic skeletal muscle phenotype. Although the function of ISPD in mammals is not yet known, mutations in this gene clearly lead to a reduction in the functional glycosylation of α-dystroglycan, which not only causes the severe Walker-Warburg syndrome but is also a common cause of the milder forms of dystroglycanopathy. | Immunohistochemistry | Human | 23288328
 |
Pseudotype-dependent lentiviral transduction of astrocytes or neurons in the rat substantia nigra.
Cannon, JR; Sew, T; Montero, L; Burton, EA; Greenamyre, JT
Experimental neurology
228
41-52
2011
Show Abstract
Gene transfer to the central nervous system provides powerful methodology for the study of gene function and gene-environment interactions in vivo, in addition to a vehicle for the delivery of therapeutic transgenes for gene therapy. The aim of the present study was to determine patterns of tropism exhibited by pseudotyped lentiviral vectors in the rat substantia nigra, in order to evaluate their utility for gene transfer in experimental models of Parkinson's disease. Isogenic lentiviral vector particles encoding a GFP reporter were pseudotyped with envelope glycoproteins derived from vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), Mokola virus (MV), lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), or Moloney murine leukemia virus (MuLV). Adult male Lewis rats received unilateral stereotactic infusions of vector into the substantia nigra; three weeks later, patterns of viral transduction were determined by immunohistological detection of GFP. Different pseudotypes gave rise to transgene expression in restricted and distinct cellular populations. VSV and MV pseudotypes transduced midbrain neurons, including a subset of nigral dopaminergic neurons. In contrast, LCMV- and MuLV-pseudotyped lentivirus produced transgene expression exclusively in astrocytes; the restricted transduction of astroglial cells was not explained by the cellular distribution of receptors previously shown to mediate entry of LCMV or MuLV. These data suggest that pseudotyped lentiviral vectors will be useful for experimental gene transfer to the rat substantia nigra. In particular, the availability of neuronal and astrocytic-targeting vectors will allow dissociation of cell autonomous and cell non-autonomous functions of key gene products in vivo. | | | 21056560
 |
Renal collecting system growth and function depend upon embryonic γ1 laminin expression.
Yang, DH; McKee, KK; Chen, ZL; Mernaugh, G; Strickland, S; Zent, R; Yurchenco, PD
Development (Cambridge, England)
138
4535-44
2011
Show Abstract
In order to understand the functions of laminins in the renal collecting system, the Lamc1 gene was inactivated in the developing mouse ureteric bud (UB). Embryos bearing null alleles exhibited laminin deficiency prior to mesenchymal tubular induction and either failed to develop a UB with involution of the mesenchyme, or developed small kidneys with decreased proliferation and branching, delayed renal vesicle formation and postnatal emergence of a water transport deficit. Embryonic day 12.5 kidneys revealed an almost complete absence of basement membrane proteins and reduced levels of α6 integrin and FGF2. mRNA levels for fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) and mediators of the GDNF/RET and WNT11 signaling pathway were also decreased. Furthermore, collecting duct cells derived from laminin-deficient kidneys and grown in collagen gels were found to proliferate and branch slowly. The laminin-deficient cells exhibited decreased activation of growth factor- and integrin-dependent pathways, whereas heparin lyase-treated and β1 integrin-null cells exhibited more selective decreases. Collectively, these data support a requirement of γ1 laminins for assembly of the collecting duct system basement membrane, in which immobilized ligands act as solid-phase agonists to promote branching morphogenesis, growth and water transport functions. | | | 21903675
 |
Conditional knockout of protein O-mannosyltransferase 2 reveals tissue-specific roles of O-mannosyl glycosylation in brain development.
Hu, H; Li, J; Gagen, CS; Gray, NW; Zhang, Z; Qi, Y; Zhang, P
The Journal of comparative neurology
519
1320-37
2011
Show Abstract
The meninges produce essential signaling molecules and major protein components of the pial basement membrane during normal brain development. Disruptions in the pial basement membrane underlie neural ectopia seen in those congenital muscular dystrophies (CMDs) caused by mutations in genes involved in O-mannosyl glycosylation. In mammals, biosynthesis of O-mannosyl glycans is initiated by a complex of mutually indispensable protein O-mannosyltransferases 1 and 2 (POMT1 and 2). To study the roles of O-mannosylation in brain development we generated a conditional allele of POMT2. POMT2 nulllizygosity resulted in embryonic lethality because of a defective Reichert's membrane. Brain-specific deletion of POMT2 resulted in hypoglycosylation of α-dystroglycan (DG) and abolished laminin binding activity. The effect of POMT2 deletion on brain development was dependent on timing, as earlier deletion resulted in more severe phenotypes. Multiple brain malformations including overmigration of neocortical neurons and migration failure of granule cells in the cerebellum were observed. Immunofluorescence staining and transmission electron microscopy revealed that these migration defects were closely associated with disruptions in the pial basement membrane. Interestingly, POMT2 deletion in the meninges (and blood vessels) did not disrupt the development of the neocortex. Thus, normal brain development requires protein O-mannosylation activity in neural tissue but not the meninges. These results suggest that gene therapy should be directed to the neural tissue instead of the meninges. | | Mouse | 21452199
 |
Transgenic overexpression of LARGE induces α-dystroglycan hyperglycosylation in skeletal and cardiac muscle.
Brockington, M; Torelli, S; Sharp, PS; Liu, K; Cirak, S; Brown, SC; Wells, DJ; Muntoni, F
PloS one
5
e14434
2010
Show Abstract
LARGE is one of seven putative or demonstrated glycosyltransferase enzymes defective in a common group of muscular dystrophies with reduced glycosylation of α-dystroglycan. Overexpression of LARGE induces hyperglycosylation of α-dystroglycan in both wild type and in cells from dystroglycanopathy patients, irrespective of their primary gene defect, restoring functional glycosylation. Viral delivery of LARGE to skeletal muscle in animal models of dystroglycanopathy has identical effects in vivo, suggesting that the restoration of functional glycosylation could have therapeutic applications in these disorders. Pharmacological strategies to upregulate Large expression are also being explored.In order to asses the safety and efficacy of long term LARGE over-expression in vivo, we have generated four mouse lines expressing a human LARGE transgene. On observation, LARGE transgenic mice were indistinguishable from the wild type littermates. Tissue analysis from young mice of all four lines showed a variable pattern of transgene expression: highest in skeletal and cardiac muscles, and lower in brain, kidney and liver. Transgene expression in striated muscles correlated with α-dystroglycan hyperglycosylation, as determined by immunoreactivity to antibody IIH6 and increased laminin binding on an overlay assay. Other components of the dystroglycan complex and extracellular matrix ligands were normally expressed, and general muscle histology was indistinguishable from wild type controls. Further detailed muscle physiological analysis demonstrated a loss of force in response to eccentric exercise in the older, but not in the younger mice, suggesting this deficit developed over time. However this remained a subclinical feature as no pathology was observed in older mice in any muscles including the diaphragm, which is sensitive to mechanical load-induced damage.This work shows that potential therapies in the dystroglycanopathies based on LARGE upregulation and α-dystroglycan hyperglycosylation in muscle should be safe. | Immunofluorescence | | 21203384
 |
Sub-physiological sarcoglycan expression contributes to compensatory muscle protection in mdx mice.
Dejia Li, Chun Long, Yongping Yue, Dongsheng Duan, Dejia Li, Chun Long, Yongping Yue, Dongsheng Duan, Dejia Li, Chun Long, Yongping Yue, Dongsheng Duan, Dejia Li, Chun Long, Yongping Yue, Dongsheng Duan
Human molecular genetics
18
1209-20
2009
Show Abstract
Sarcoglycans are a group of single-pass transmembrane glycoproteins. In striated muscle, sarcoglycans interact with dystrophin and other dystrophin-associated proteins (DAPs) to form the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex (DGC). The DGC protects the sarcolemma from contraction-induced injury. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is caused by dystrophin gene mutations. In the absence of dystrophin, the DGC is disassembled from the sarcolemma. This initiates a chain reaction of muscle degeneration, necrosis, inflammation and fibrosis. In contrast to human patients, dystrophin-null mdx mice are only mildly affected. Enhanced muscle regeneration and the up-regulation of utrophin and integrin are thought to protect mdx muscle. Interestingly, trace amounts of sarcoglycans and other DAPs can be detected at the mdx sarcolemma. It is currently unclear whether sub-physiological sarcoglycan expression also contributes to the mild phenotype in mdx mice. To answer this question, we generated delta-sarcoglycan/dystrophin double knockout mice (delta-Dko) in which residual sarcoglycans were completely eliminated from the sarcolemma. Interestingly, utrophin levels were further increased in these mice. However, enhanced utrophin expression did not mitigate disease. The clinical manifestation of delta-Dko mice was worse than that of mdx mice. They showed characteristic dystrophic signs, body emaciation and more macrophage infiltration. Their lifespan was reduced by 60%. Furthermore, delta-Dko muscle generated significantly less absolute muscle force and became more susceptible to contraction-induced injury. Our results suggest that sub-physiological sarcoglycan expression plays a critical role in ameliorating muscle disease in mdx mice. We speculate that low-level sarcoglycan expression may represent a useful strategy to palliate DMD. Full Text Article | | | 19131360
 |
Mice Lacking Dystrophin or {alpha} Sarcoglycan Spontaneously Develop Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma with Cancer-Associated p53 Mutations and Alternatively Spliced or Mutant Mdm2 Transcripts.
Fernandez K, Serinagaoglu Y, Hammond S, Martin LT, Martin PT
The American journal of pathology
176
416-34
2009
Show Abstract
Altered expression of proteins in the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex results in muscular dystrophy and has more recently been implicated in a number of forms of cancer. Here we show that loss of either of two members of this complex, dystrophin in mdx mice or alpha sarcoglycan in Sgca(-/-) mice, results in the spontaneous development of muscle-derived embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) after 1 year of age. Many mdx and Sgca(-/-) tumors showed increased expression of insulin-like growth factor 2, retinoblastoma protein, and phosphorylated Akt and decreased expression of phosphatase and tensin homolog gene, much as is found in a human RMS. Further, all mdx and Sgca(-/-) RMS analyzed had increased expression of p53 and murine double minute (mdm)2 protein and contained missense p53 mutations previously identified in human cancers. The mdx RMS also contained missense mutations in Mdm2 or alternatively spliced Mdm2 transcripts that lacked an exon encoding a portion of the p53-binding domain. No Pax3:Fkhr or Pax7:Fkhr translocation mRNA products were evident in any tumor. Expression of natively glycosylated alpha dystroglycan and alpha sarcoglycan was reduced in mdx RMS, whereas dystrophin expression was absent in almost all human RMS, both for embryonal and alveolar RMS subtypes. These studies show that absence of members of the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex constitutes a permissive environment for spontaneous development of embryonal RMS associated with mutation of p53 and mutation or altered splicing of Mdm2. | | | 20019182
 |