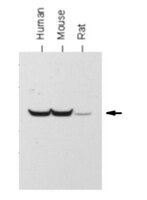
AMPK and GCN2-ATF4 signal the repression of mitochondria in colon cancer cells.
Martínez-Reyes, I; Sánchez-Aragó, M; Cuezva, JM
The Biochemical journal
444
249-59
2012
Show Abstract
Reprogramming of energetic metabolism is a phenotypic trait of cancer in which mitochondrial dysfunction represents a key event in tumour progression. In the present study, we show that the acquisition of the tumour-promoting phenotype in colon cancer HCT116 cells treated with oligomycin to inhibit ATP synthase is exerted by repression of the synthesis of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial proteins in a process that is regulated at the level of translation. Remarkably, the synthesis of glycolytic proteins is not affected in this situation. Changes in translational control of mitochondrial proteins are signalled by the activation of AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) and the GCN2 (general control non-derepressible 2) kinase, leading also to the activation of autophagy. Changes in the bioenergetic function of mitochondria are mimicked by the activation of AMPK and the silencing of ATF4 (activating transcription factor 4). These findings emphasize the relevance of translational control for normal mitochondrial function and for the progression of cancer. Moreover, they demonstrate that glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation are controlled at different levels of gene expression, offering the cell a mechanistic safeguard strategy for metabolic adaptation under stressful conditions. | 22435535
 |
Cancer abolishes the tissue type-specific differences in the phenotype of energetic metabolism.
Acebo, P; Giner, D; Calvo, P; Blanco-Rivero, A; Ortega, AD; Fernández, PL; Roncador, G; Fernández-Malavé, E; Chamorro, M; Cuezva, JM
Translational oncology
2
138-45
2009
Show Abstract
Nowadays, cellular bioenergetics has become a central issue of investigation in cancer biology. Recently, the metabolic activity of the cancer cell has been shown to correlate with a proteomic index that informs of the relative mitochondrial activity of the cell. Within this new field of investigation, we report herein the production and characterization of high-affinity monoclonal antibodies against proteins of the "bioenergetic signature" of the cell. The use of recombinant proteins and antibodies against the mitochondrial beta-F1-ATPase and Hsp60 proteins and the enzymes of the glycolytic pathway glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and pyruvate kinase M2 in quantitative assays provide, for the first time, the actual amount of these proteins in normal and tumor surgical specimens of breast, lung, and esophagus. The application of this methodology affords a straightforward proteomic signature that quantifies the variable energetic demand of human tissues. Furthermore, the results show an unanticipated finding: tumors from different tissues and/or histological types have the same proteomic signature of energetic metabolism. Therefore, the results indicate that cancer abolishes the tissue-specific differences in the bioenergetic phenotype of mitochondria. Overall, the results support that energetic metabolism represents an additional hallmark of the phenotype of the cancer cell and a promising target for the treatment of diverse neoplasias. | 19701498
 |