203389 Sigma-AldrichInSolution™Blebbistatin, Racemic - Calbiochem
InSolution™Blebbistatin, Racemic, is a 50 mM in 90% DMSO. A cell-permeable, selective, and reversible inhibitor of nonmuscle myosin II. Blocks cell blebbing and disrupts cell migration & cytoKinesis.
More>> InSolution™Blebbistatin, Racemic, is a 50 mM in 90% DMSO. A cell-permeable, selective, and reversible inhibitor of nonmuscle myosin II. Blocks cell blebbing and disrupts cell migration & cytoKinesis. Less<<Empfohlene Produkte
Übersicht
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Key Spec Table
| Empirical Formula |
|---|
| C₁₈H₁₆N₂O₂ |
Preis & Verfügbarkeit
| Bestellnummer | Verfügbarkeit | Verpackung | St./Pkg. | Preis | Menge | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 203389-5MG |
|
Kst.-Ampulle | 5 mg |
|
— |
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | 203389 |
| Brand Family | Calbiochem® |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| ATP Competitive | N |
| Form | Liquid |
| Formulation | A 50 mM (5 mg/342 µl) solution of (±)-Blebbistatin (Cat. No. 203390) in 90% DMSO. |
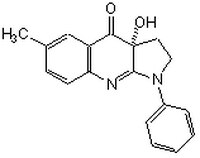
| Hill Formula | C₁₈H₁₆N₂O₂ |
| Chemical formula | C₁₈H₁₆N₂O₂ |
| Hygroscopic | Hygroscopic |
| Reversible | Y |
| Structure formula Image | |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Biological Information | |
|---|---|
| Primary Target | ATPase |
| Primary Target IC<sub>50</sub> | <100 µM inhibiting the ATPase and gliding motility of human platelets |
| Purity | ≥97% by HPLC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
|---|---|
| Cell permeable | Y |
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Product Usage Statements |
|---|
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Packaged under inert gas | Packaged under inert gas |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Bestellnummer | GTIN |
| 203389-5MG | 04055977221251 |
Documentation
InSolution™Blebbistatin, Racemic - Calbiochem SDB
| Titel |
|---|
InSolution™Blebbistatin, Racemic - Calbiochem Analysenzertifikate
| Titel | Chargennummer |
|---|---|
| 203389 |
Literatur
| Übersicht |
|---|
| Shu, S., et al. 2005. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 1472. Kovacs, M., et al. 2004. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 35557. Straight, A.F., et al. 2003. Science 299, 1743. Cheung, A., et al. 2001. Mol. Biol. Cell Suppl. 12, 271a. |
| Datenblatt | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Note that this data sheet is not lot-specific and is representative of the current specifications for this product. Please consult the vial label and the certificate of analysis for information on specific lots. Also note that shipping conditions may differ from storage conditions.
|