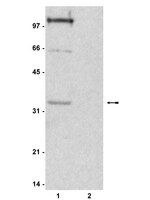
Global chromatin fibre compaction in response to DNA damage.
Hamilton, C; Hayward, RL; Gilbert, N
Biochemical and biophysical research communications
414
820-5
2010
Abstract anzeigen
DNA is protected by packaging it into higher order chromatin fibres, but this can impede nuclear processes like DNA repair. Despite considerable research into the factors required for signalling and repairing DNA damage, it is unclear if there are concomitant changes in global chromatin fibre structure. In human cells DNA double strand break (DSB) formation triggers a signalling cascade resulting in H2AX phosphorylation (γH2AX), the rapid recruitment of chromatin associated proteins and the subsequent repair of damaged sites. KAP1 is a transcriptional corepressor and in HCT116 cells we found that after DSB formation by chemicals or ionising radiation there was a wave of, predominantly ATM dependent, KAP1 phosphorylation. Both KAP1 and phosphorylated KAP1 were readily extracted from cells indicating they do not have a structural role and γH2AX was extracted in soluble chromatin indicating that sites of damage are not attached to an underlying structural matrix. After DSB formation we did not find a concomitant change in the sensitivity of chromatin fibres to micrococcal nuclease digestion. Therefore to directly investigate higher order chromatin fibre structures we used a biophysical sedimentation technique based on sucrose gradient centrifugation to compare the conformation of chromatin fibres isolated from cells before and after DNA DSB formation. After damage we found global chromatin fibre compaction, accompanied by rapid linker histone dephosphorylation, consistent with fibres being more regularly folded or fibre deformation being stabilized by linker histones. We suggest that following DSB formation, although there is localised chromatin unfolding to facilitate repair, the bulk genome becomes rapidly compacted protecting cells from further damage. | Western Blotting | 22020103
 |
Silencing of CDK5 reduces neurofibrillary tangles in transgenic alzheimer's mice.
Piedrahita, D; Hernández, I; López-Tobón, A; Fedorov, D; Obara, B; Manjunath, BS; Boudreau, RL; Davidson, B; Laferla, F; Gallego-Gómez, JC; Kosik, KS; Cardona-Gómez, GP
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
30
13966-76
2009
Abstract anzeigen
Alzheimer's disease is a major cause of dementia for which treatments remain unsatisfactory. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) is a relevant kinase that has been hypothesized to contribute to the tau pathology. Several classes of chemical inhibitors for CDK5 have been developed, but they generally lack the specificity to distinguish among various ATP-dependent kinases. Therefore, the efficacy of these compounds when tested in animal models cannot definitively be attributed to an effect on CDK5. However, RNA interference (RNAi) targeting of CDK5 is specific and can be used to validate CDK5 as a possible treatment target. We delivered a CDK5 RNAi by lentiviral or adenoassociated viral vectors and analyzed the results in vitro and in vivo. Silencing of CDK5 reduces the phosphorylation of tau in primary neuronal cultures and in the brain of wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Furthermore, the knockdown of CDK5 strongly decreased the number of neurofibrillary tangles in the hippocampi of triple-transgenic mice (3×Tg-AD mice). Our data suggest that this downregulation may be attributable to the reduction of the CDK5 availability in the tissue, without affecting the CDK5 kinase activity. In summary, our findings validate CDK5 as a reasonable therapeutic target for ameliorating tau pathology. | Western Blotting | 20962218
 |
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1-mediated Bcl-xL/Bcl-2 phosphorylation acts as a functional link coupling mitotic arrest and apoptosis.
David T Terrano,Meenakshi Upreti,Timothy C Chambers
Molecular and cellular biology
30
2009
Abstract anzeigen
Despite detailed knowledge of the components of the spindle assembly checkpoint, a molecular explanation of how cells die after prolonged spindle checkpoint activation, and thus how microtubule inhibitors and other antimitotic drugs ultimately elicit their lethal effects, has yet to emerge. Mitotically arrested cells typically display extensive phosphorylation of two key antiapoptotic proteins, Bcl-x(L) and Bcl-2, and evidence suggests that phosphorylation disables their antiapoptotic activity. However, the responsible kinase has remained elusive. In this report, evidence is presented that cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1)/cyclin B catalyzes mitotic-arrest-induced Bcl-x(L)/Bcl-2 phosphorylation. Furthermore, we show that CDK1 transiently and incompletely phosphorylates these proteins during normal mitosis. When mitosis is prolonged in the absence of microtubule inhibition, Bcl-x(L) and Bcl-2 become highly phosphorylated. Transient overexpression of nondegradable cyclin B1 caused apoptotic death, which was blocked by a phosphodefective Bcl-x(L) mutant but not by a phosphomimetic Bcl-x(L) mutant, confirming Bcl-x(L) as a key target of proapoptotic CDK1 signaling. These findings suggest a model whereby a switch in the duration of CDK1 activation, from transient during mitosis to sustained during mitotic arrest, dramatically increases the extent of Bcl-x(L)/Bcl-2 phosphorylation, resulting in inactivation of their antiapoptotic function. Thus, phosphorylation of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins acts as a sensor for CDK1 signal duration and as a functional link coupling mitotic arrest to apoptosis. Volltextartikel | | 19917720
 |
Activation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 is a consequence of cell death.
Yixia Ye,Antonella Tinari,Walter Malorni,Richard A Lockshin,Zahra Zakeri
Journal of biomedicine & biotechnology
2009
2009
Abstract anzeigen
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) is similar to other Cdks but is activated during cell differentiation and cell death rather than cell division. Since activation of Cdk5 has been reported in many situations leading to cell death, we attempted to determine if it was required for any form of cell death. We found that Cdk5 is activated during apoptotic deaths and that the activation can be detected even when the cells continue to secondary necrosis. This activation can occur in the absence of Bim, calpain, or neutral cathepsins. The kinase is typically activated by p25, derived from p35 by calpain-mediated cleavage, but inhibition of calpain does not affect cell death or the activation of Cdk5. Likewise, RNAi-forced suppression of the synthesis of Cdk5 does not affect the incidence or kinetics of cell death. We conclude that Cdk5 is activated as a consequence of metabolic changes that are common to many forms of cell death. Thus its activation suggests processes during cell death that will be interesting or important to understand, but activation of Cdk5 is not necessary for cells to die. Volltextartikel | | 19830249
 |
Cdk5 regulates STAT3 activation and cell proliferation in medullary thyroid carcinoma cells.
Lin, H; Chen, MC; Chiu, CY; Song, YM; Lin, SY
The Journal of biological chemistry
282
2776-84
2007
Abstract anzeigen
The biological behaviors of thyroid cancer are varied, and the pathological mechanisms remain unclear. Some reports indicated an apparent aggregation of amyloid accompanying medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC). Amyloid aggregation in neurodegeneration leads to hyperactivation of Cdk5 and subsequent neuronal death. Based on the connection with amyloid, the role of Cdk5 in MTC is worthy of investigation. Initially, the expression of Cdk5 and its activator, p35, in MTC cell lines was identified. Cdk5 inhibition by specific inhibitors or short interfering RNA decreased the proliferation of MTC cell lines, which reveals the importance of Cdk5 in MTC cell growth. Although p35 cleavage has been considered as an important element in neurodegeneration, it seems that p35 cleavage was not a major cause in Cdk5 activity-dependent MTC cell proliferation because neither Cdk5 activity nor cell growth was affected by the inhibition of p35 cleavage. Clearance of amyloid by antibody neutralization indicated that MTC cell proliferation was supported by calcitonin-derived extracellular amyloid and subsequent Her2 and Cdk5 activation. Significantly, the STAT3 pathway was involved in Cdk5-dependent proliferation of MTC cells through Ser-727 phosphorylation. In addition, Cdk5 inhibition reduced nuclear distributions of both the Cdk5-p35 complex and phospho-STAT3 in MTC cells. Finally, Cdk5 inhibition retarded tumor formation in vivo accompanying the reduction of phospho-STAT3. Our findings suggest the first demonstration of a novel and specific role for Cdk5 kinase in supporting the proliferation of the medullary thyroid carcinoma cells and could shed light on a new field for diagnosis and therapy of thyroid cancer. | | 17145757
 |
Characterization of vinblastine-induced Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 phosphorylation: evidence for a novel protein kinase and a coordinated phosphorylation/dephosphorylation cycle associated with apoptosis induction.
Du, L; Lyle, CS; Chambers, TC
Oncogene
24
107-17
2004
Abstract anzeigen
Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 are phosphorylated in response to microtubule inhibitors, but the kinase(s) responsible and the functional significance have remained unclear. In this study, we investigated the characteristics of Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 phosphorylation in KB-3 carcinoma cells treated with vinblastine. In both asynchronous and synchronous cell cultures, Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 underwent a well-defined and coordinated cycle of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, with a lengthy period of phosphorylation preceding apoptosis induction, and with dephosphorylation closely correlated with initiation of apoptosis. Internally, validated inhibitors of JNK, ERK, p38(MAPK), or CDK1 failed to inhibit vinblastine-induced phosphorylation of Bcl-xL or Bcl-2. In vitro, Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 were poor substrates relative to c-Jun and ATF2 for active recombinant JNK1. Both Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 were localized primarily to the mitochondrial fraction in both control and vinblastine-treated cells, indicating that phosphorylation did not promote subcellular redistribution. Bcl-xL kinase activity was demonstrated in mitochondrial extracts from vinblastine-treated, but not control, cells. These findings suggest that phosphorylation of these key antiapoptotic proteins may be catalysed by a novel or unsuspected kinase that is activated or induced in response to microtubule damage. Furthermore, the same kinase and phosphatase system may be operating in tandem on both proteins, and phosphorylation appears to maintain their antiapoptotic function, whereas dephosphorylation may trigger apoptosis. These results provide evidence for a novel signaling pathway connecting microtubule damage to apoptosis induction, and help to clarify some of the controversy concerning the role of Bcl-2 phosphorylation in microtubule inhibitor-induced apoptosis. | | 15531923
 |
Sulforaphane: a naturally occurring mammary carcinoma mitotic inhibitor, which disrupts tubulin polymerization.
Jackson, SJ; Singletary, KW
Carcinogenesis
25
219-27
2004
Abstract anzeigen
Sulforaphane (SUL), an isothiocyanate found in broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables, has been shown to induce phase II detoxification enzymes, inhibit chemically induced mammary tumors in rats, and more recently to induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells of the colon. Here, we provide evidence that SUL also acts as a breast cancer anti-proliferative agent. The BALB/c mouse mammary carcinoma cell line F3II was treated with SUL at concentrations up to 15 microM and examined for markers of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Treatment of asynchronous F3II cells with 15 microM SUL resulted in G2/M cell cycle arrest, elevated p34cdc2 (cdc2) kinase activity, Bcl-2 down-regulation, evidence of caspase activation, and aggregation of condensed nuclear chromatin. Subsequent exposure of synchronized cells to 15 microM SUL resulted in elevated numbers of prophase/prometaphase mitotic figures, indicating cell cycle progression beyond G2 and arrest early within mitosis. Moreover, cells treated with 15 microM SUL displayed aberrant mitotic spindles, and higher doses of SUL inhibited tubulin polymerization in vitro. In addition, BALB/c mice injected s.c. with F3II cells and subsequently injected daily i.v. with SUL (15 nmol/day for 13 days) developed significantly smaller tumors (approximately 60% less in mass) than vehicle-treated controls. Western blot analysis of tumor proteins demonstrated significantly (Pless than 0.05) reduced PCNA and elevated PARP fragmentation in samples from animals dosed with SUL. Taken together, these results indicate that SUL has mammary cancer suppressive actions both in cell culture and in the whole animal. Inhibition of mammary carcinogenesis appears in part to involve perturbation of mitotic microtubules and early M-phase block associated with cdc2 kinase activation, indicating that cells arrest prior to metaphase exit. | Western Blotting | 14578157
 |
RLIP, an effector of the Ral GTPases, is a platform for Cdk1 to phosphorylate epsin during the switch off of endocytosis in mitosis
Rosse, C., et al
J Biol Chem, 278:30597-604 (2003)
2003
| Immunoblotting (Western) | 12775724
 |
Rapid activation of G2/M checkpoint after hypertonic stress in renal inner medullary epithelial (IME) cells is protective and requires p38 kinase.
Dmitrieva, NI; Bulavin, DV; Fornace, AJ; Burg, MB
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
99
184-9
2002
Abstract anzeigen
Cells in the kidney medulla are subject to variable and often extreme osmotic stress during concentration of the urine. Previous studies showed that renal inner medullary epithelial (IME) cells respond to hypertonicity by G(2) arrest. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the mechanisms involved in initiation and maintenance of G(2) arrest. Rapid initiation of G(2) arrest after UV radiation is mediated by p38 kinase. Here we find that p38 kinase is responsible for rapid initiation of the G(2) delay in IME cells after the hypertonic stress created by adding NaCl. High NaCl, but not high urea, rapidly initiates G(2) arrest. Inhibition of p38 kinase by SB202190 (10 microM) blocks the rapid initiation of this checkpoint both in an immortalized cell line (mIMCD3) and in second-passage IME cells from mouse renal inner medulla. p38 inhibition does not affect exit from G(2) arrest. The rapid initiation of G(2) arrest is followed by inhibition of cdc2 kinase, which is also prevented by SB202190. To assess the possible protective role of G(2) arrest, we measured DNA strand breaks as reflected by immunostaining against phospho-histone H2AX, which becomes phosphorylated on Ser-139 associated with DNA breaks. Abrogation of rapid G(2)/M checkpoint activation by SB202190 increases the histone H2AX phosphorylation in G(2)/M cells. We propose that the rapid initiation of G(2) delay by p38 kinase after hypertonicity protects the cells by decreasing the level of DNA breaks caused by aberrant mitosis entry. | | 11756692
 |
A novel regulatory element determines the timing of Mos mRNA translation during Xenopus oocyte maturation.
Amanda Charlesworth, John A Ridge, Leslie A King, Melanie C MacNicol, Angus M MacNicol
The EMBO journal
21
2798-806
2002
Abstract anzeigen
Progression through vertebrate oocyte maturation requires that pre-existing, maternally derived mRNAs be translated in a strict temporal order. The mechanism that controls the timing of oocyte mRNA translation is unknown. In this study we show that the early translational induction of the mRNA encoding the Mos proto-oncogene is mediated through a novel regulatory element within the 3' untranslated region of the Mos mRNA. This novel element is responsive to the MAP kinase signaling pathway and is distinct from the late acting, cdc2-responsive, cytoplasmic polyadenylation element. Our findings suggest that the timing of maternal mRNA translation is controlled through signal transduction pathways targeting distinct 3' UTR mRNA elements. Volltextartikel | | 12032092
 |