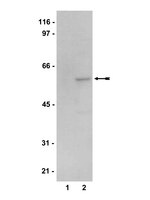
Data in support of 5'AMP-activated protein kinase alpha regulates stress granule biogenesis.
Mahboubi, H; Barisé, R; Stochaj, U
Data in brief
4
54-9
2015
Abstract anzeigen
This data article contains insights into the regulation of cytoplasmic stress granules (SGs) by 5'-AMP-activated kinase (AMPK). Our results verify the specific association of AMPK-α2, but not AMPK-α1, with SGs. We also provide validation data for the isoform-specific recruitment of the AMPK-α subunit to SGs using (i) different antibodies and (ii) a distinct cellular model system. In addition, we assess the SG association of the regulatory AMPK β- and γ-subunits. The interpretation of these data and further extensive insights into the regulation of SG biogenesis by AMPK can be found in "5'AMP-activated protein kinase alpha regulates stress granule biogenesis" [1]. | | 26217763
 |
AMPK-dependent phosphorylation of ULK1 regulates ATG9 localization.
Mack, HI; Zheng, B; Asara, JM; Thomas, SM
Autophagy
8
1197-214
2011
Abstract anzeigen
Autophagy is activated in response to a variety of cellular stresses including metabolic stress. While elegant genetic studies in yeast have identified the core autophagy machinery, the signaling pathways that regulate this process are less understood. AMPK is an energy sensing kinase and several studies have suggested that AMPK is required for autophagy. The biochemical connections between AMPK and autophagy, however, have not been elucidated. In this report, we identify a biochemical connection between a critical regulator of autophagy, ULK1, and the energy sensing kinase, AMPK. ULK1 forms a complex with AMPK, and AMPK activation results in ULK1 phosphorylation. Moreover, we demonstrate that the immediate effect of AMPK-dependent phosphorylation of ULK1 results in enhanced binding of the adaptor protein YWHAZ/14-3-3ζ; and this binding alters ULK1 phosphorylation in vitro. Finally, we provide evidence that both AMPK and ULK1 regulate localization of a critical component of the phagophore, ATG9, and that some of the AMPK phosphorylation sites on ULK1 are important for regulating ATG9 localization. Taken together these data identify an ULK1-AMPK signaling cassette involved in regulation of the autophagy machinery. | | 22932492
 |
Comparing the effects of nano-sized sugarcane fiber with cellulose and psyllium on hepatic cellular signaling in mice.
Wang, Zhong Q, et al.
Int J Nanomedicine, 7: 2999-3012 (2012)
2011
Abstract anzeigen
To compare the effects of dietary fibers on hepatic cellular signaling in mice. | | 22787396
 |
Transcriptome and translational signaling following endurance exercise in trained skeletal muscle: impact of dietary protein.
Rowlands, DS; Thomson, JS; Timmons, BW; Raymond, F; Fuerholz, A; Mansourian, R; Zwahlen, MC; Métairon, S; Glover, E; Stellingwerff, T; Kussmann, M; Tarnopolsky, MA
Physiological genomics
43
1004-20
2010
Abstract anzeigen
Postexercise protein feeding regulates the skeletal muscle adaptive response to endurance exercise, but the transcriptome guiding these adaptations in well-trained human skeletal muscle is uncharacterized. In a crossover design, eight cyclists ingested beverages containing protein, carbohydrate and fat (PTN: 0.4, 1.2, 0.2 g/kg, respectively) or isocaloric carbohydrate and fat (CON: 1.6, 0.2 g/kg) at 0 and 1 h following 100 min of cycling. Biopsies of the vastus lateralis were collected at 3 and 48 h following to determine the early and late transcriptome and regulatory signaling responses via microarray and immunoblot. The top gene ontology enriched by PTN were: muscle contraction, extracellular matrix--signaling and structure, and nucleoside, nucleotide, and nucleic acid metabolism (3 and 48 h); developmental processes, immunity, and defense (3 h); glycolysis, lipid and fatty acid metabolism (48 h). The transcriptome was also enriched within axonal guidance, actin cytoskeletal, Ca2+, cAMP, MAPK, and PPAR canonical pathways linking protein nutrition to exercise-stimulated signaling regulating extracellular matrix, slow-myofibril, and metabolic gene expression. At 3 h, PTN attenuated AMPKα1Thr172 phosphorylation but increased mTORC1Ser2448, rps6Ser240/244, and 4E-BP1-γ phosphorylation, suggesting increased translation initiation, while at 48 h AMPKα1Thr172 phosphorylation and PPARG and PPARGC1A expression increased, supporting the late metabolic transcriptome, relative to CON. To conclude, protein feeding following endurance exercise affects signaling associated with cell energy status and translation initiation and the transcriptome involved in skeletal muscle development, slow-myofibril remodeling, immunity and defense, and energy metabolism. Further research should determine the time course and posttranscriptional regulation of this transcriptome and the phenotype responding to chronic postexercise protein feeding. | | 21730029
 |
Myo1c regulates glucose uptake in mouse skeletal muscle.
Toyoda, T; An, D; Witczak, CA; Koh, HJ; Hirshman, MF; Fujii, N; Goodyear, LJ
The Journal of biological chemistry
286
4133-40
2010
Abstract anzeigen
Contraction and insulin promote glucose uptake in skeletal muscle through GLUT4 translocation to cell surface membranes. Although the signaling mechanisms leading to GLUT4 translocation have been extensively studied in muscle, the cellular transport machinery is poorly understood. Myo1c is an actin-based motor protein implicated in GLUT4 translocation in adipocytes; however, the expression profile and role of Myo1c in skeletal muscle have not been investigated. Myo1c protein abundance was higher in more oxidative skeletal muscles and heart. Voluntary wheel exercise (4 weeks, 8.2 ± 0.8 km/day), which increased the oxidative profile of the triceps muscle, significantly increased Myo1c protein levels by ∼2-fold versus sedentary controls. In contrast, high fat feeding (9 weeks, 60% fat) significantly reduced Myo1c by 17% in tibialis anterior muscle. To study Myo1c regulation of glucose uptake, we expressed wild-type Myo1c or Myo1c mutated at the ATPase catalytic site (K111A-Myo1c) in mouse tibialis anterior muscles in vivo and assessed glucose uptake in vivo in the basal state, in response to 15 min of in situ contraction, and 15 min following maximal insulin injection (16.6 units/kg of body weight). Expression of wild-type Myo1c or K111A-Myo1c had no effect on basal glucose uptake. However, expression of wild-type Myo1c significantly increased contraction- and insulin-stimulated glucose uptake, whereas expression of K111A-Myo1c decreased both contraction-stimulated and insulin-stimulated glucose uptake. Neither wild-type nor K111A-Myo1c expression altered GLUT4 expression, and neither affected contraction- or insulin-stimulated signaling proteins. Myo1c is a novel mediator of both insulin-stimulated and contraction-stimulated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. | | 21127070
 |
TBC1D1 regulates insulin- and contraction-induced glucose transport in mouse skeletal muscle.
An, D; Toyoda, T; Taylor, EB; Yu, H; Fujii, N; Hirshman, MF; Goodyear, LJ
Diabetes
59
1358-65
2009
Abstract anzeigen
TBC1D1 is a member of the TBC1 Rab-GTPase family of proteins and is highly expressed in skeletal muscle. Insulin and contraction increase TBC1D1 phosphorylation on phospho-Akt substrate motifs (PASs), but the function of TBC1D1 in muscle is not known. Genetic linkage analyses show a TBC1D1 R125W missense variant confers risk for severe obesity in humans. The objective of this study was to determine whether TBC1D1 regulates glucose transport in skeletal muscle.In vivo gene injection and electroporation were used to overexpress wild-type and several mutant TBC1D1 proteins in mouse tibialis anterior muscles, and glucose transport was measured in vivo.Expression of the obesity-associated R125W mutant significantly decreased insulin-stimulated glucose transport in the absence of changes in TBC1D1 PAS phosphorylation. Simultaneous expression of an inactive Rab-GTPase (GAP) domain of TBC1D1 in the R125W mutant reversed this decrease in glucose transport caused by the R125W mutant. Surprisingly, expression of TBC1D1 mutated to Ala on four conserved Akt and/or AMP-activated protein kinase predicted phosphorylation sites (4P) had no effect on insulin-stimulated glucose transport. In contrast, expression of the TBC1D1 4P mutant decreased contraction-stimulated glucose transport, an effect prevented by concomitant disruption of TBC1D1 Rab-GAP activity. There was no effect of the R125W mutation on contraction-stimulated glucose transport.TBC1D1 regulates both insulin- and contraction-stimulated glucose transport, and this occurs via distinct mechanisms. The R125W mutation of TBC1D1 impairs skeletal muscle glucose transport, which could be a mechanism for the obesity associated with this mutation. Volltextartikel | Western Blotting, Immunoprecipitation | 20299473
 |
Alpha2-AMPK activity is not essential for an increase in fatty acid oxidation during low-intensity exercise.
Miura, S; Kai, Y; Kamei, Y; Bruce, CR; Kubota, N; Febbraio, MA; Kadowaki, T; Ezaki, O
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism
296
E47-55
2009
Abstract anzeigen
A single bout of exercise increases glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle, with a corresponding activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). While the exercise-induced increase in glucose uptake is partly due to activation of AMPK, it is unclear whether the increase of fatty acid oxidation is dependent on activation of AMPK. To examine this, transgenic mice were produced expressing a dominant-negative (DN) mutant of alpha(1)-AMPK (alpha(1)-AMPK-DN) in skeletal muscle and subjected to treadmill running. alpha(1)-AMPK-DN mice exhibited a 50% reduction in alpha(1)-AMPK activity and almost complete loss of alpha(2)-AMPK activity in skeletal muscle compared with wild-type littermates (WT). The fasting-induced decrease in respiratory quotient (RQ) ratio and reduced body weight were similar in both groups. In contrast with WT mice, alpha(1)-AMPK-DN mice could not perform high-intensity (30 m/min) treadmill exercise, although their response to low-intensity (10 m/min) treadmill exercise was not compromised. Changes in oxygen consumption and the RQ ratio during sedentary and low-intensity exercise were not different between alpha(1)-AMPK-DN and WT. Importantly, at low-intensity exercise, increased fatty acid oxidation in response to exercise in soleus (type I, slow twitch muscle) or extensor digitorum longus muscle (type II, fast twitch muscle) was not impaired in alpha(1)-AMPK-DN mice, indicating that alpha(1)-AMPK-DN mice utilize fatty acid in the same manner as WT mice during low-intensity exercise. These findings suggest that an increased alpha(2)-AMPK activity is not essential for increased skeletal muscle fatty acid oxidation during endurance exercise. | | 18940938
 |
TBC 11251. IPI 1040.
[No authors listed]
Drugs in RD
2
38-9
2001
| | 10610280
 |
Dealing with energy demand: the AMP-activated protein kinase.
Kemp, B E, et al.
Trends Biochem. Sci., 24: 22-5 (1999)
1998
Abstract anzeigen
The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a member of a metabolite-sensing protein kinase family that is found in all eukaryotes. AMPK activity is regulated by vigorous exercise, nutrient starvation and ischemia/hypoxia, and modulates many aspects of mammalian cell metabolism. The AMPK yeast homolog, Snf1p, plays a major role in adaption to glucose deprivation. In mammals, AMPK also has diverse roles that extend from energy metabolism through to transcriptional control. | | 10087918
 |
Isoform-specific purification and substrate specificity of the 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase.
Michell, B J, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 271: 28445-50 (1996)
1996
Abstract anzeigen
The 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) mediates several cellular responses to metabolic stress. Rat liver contains at least two isoforms of this enzyme, either alpha1 or alpha2 catalytic subunits together with beta and gamma noncatalytic subunits in a trimeric complex. The alpha1 isoform is purified using a peptide substrate affinity chromatography column with ADR1 (222-234)P229 (LKKLTRRPSFSAQ), corresponding to the cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation site in the yeast transcriptional activator of the ADH2 gene, ADR1. This peptide is phosphorylated at Ser230 by AMPK alpha1 with a Km of 3.8 microM and a Vmax of 4.8 micromol/min/mg compared to the commonly used rat acetyl-CoA carboxylase (73-87)A77R86-87 peptide substrate, HMRSAMSGLHLVKRR, with a Km of 33.3 microM and a Vmax of 8.1 micromol/min/mg. Thus, the AMPK exhibits some overlapping specificity with the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. The rat liver AMPK alpha1 isoform has a Kcat approximately 250-fold higher than the AMPK alpha2 isoform isolated from rat liver. The AMPK alpha1 isoform readily phosphorylates peptides corresponding to the reported AMPK phosphorylation sites in rat, chicken, and yeast acetyl-CoA carboxylase and rat hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase but not phosphorylase kinase. Based on previous peptide substrate specificity studies (Dale, S., Wilson, W. A., Edelman, A. M., and Hardie, G. (1995) FEBS Lett. 361, 191-195) using partially purified enzyme and variants of the peptide AMARAASAAALARRR, it was proposed that the AMPK preferred the phosphorylation site motif Phi(X, beta)XXS/TXXXPhi (Phi, hydrophobic; beta, basic). In good AMPK alpha1 peptide substrates, a hydrophobic residue at the P-5 position is conserved but not at the P+4 position. Oxidation of the Met residues in the rat acetyl-CoA carboxylase (73-87)A77R86-87 peptide increased the Km 6-fold and reduced the Vmax to 4% of the reduced peptide. | | 8910470
 |