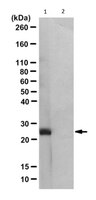
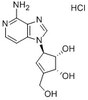
Monoclonal 1- and 3-Phosphohistidine Antibodies: New Tools to Study Histidine Phosphorylation.
Fuhs, SR; Meisenhelder, J; Aslanian, A; Ma, L; Zagorska, A; Stankova, M; Binnie, A; Al-Obeidi, F; Mauger, J; Lemke, G; Yates, JR; Hunter, T
Cell
162
198-210
2015
Show Abstract
Histidine phosphorylation (pHis) is well studied in bacteria; however, its role in mammalian signaling remains largely unexplored due to the lack of pHis-specific antibodies and the lability of the phosphoramidate (P-N) bond. Both imidazole nitrogens can be phosphorylated, forming 1-phosphohistidine (1-pHis) or 3-phosphohistidine (3-pHis). We have developed monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that specifically recognize 1-pHis or 3-pHis; they do not cross-react with phosphotyrosine or the other pHis isomer. Assays based on the isomer-specific autophosphorylation of NME1 and phosphoglycerate mutase were used with immunoblotting and sequencing IgG variable domains to screen, select, and characterize anti-1-pHis and anti-3-pHis mAbs. Their sequence independence was determined by blotting synthetic peptide arrays, and they have been tested for immunofluorescence staining and immunoaffinity purification, leading to putative identification of pHis-containing proteins. These reagents should be broadly useful for identification of pHis substrates and functional study of pHis using a variety of immunological, proteomic, and biological assays. | 26140597
 |