Downregulation of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling factor subunits modulates cisplatin cytotoxicity.
Kothandapani, Anbarasi, et al.
Exp. Cell Res., 318: 1973-86 (2012)
2012
Show Abstract
Chromatin remodeling complex SWI/SNF plays important roles in many cellular processes including transcription, proliferation, differentiation and DNA repair. In this report, we investigated the role of SWI/SNF catalytic subunits Brg1 and Brm in the cellular response to cisplatin in lung cancer and head/neck cancer cells. Stable knockdown of Brg1 and Brm enhanced cellular sensitivity to cisplatin. Repair kinetics of cisplatin DNA adducts revealed that downregulation of Brg1 and Brm impeded the repair of both intrastrand adducts and interstrand crosslinks (ICLs). Cisplatin ICL-induced DNA double strand break repair was also decreased in Brg1 and Brm depleted cells. Altered checkpoint activation with enhanced apoptosis as well as impaired chromatin relaxation was observed in Brg1 and Brm deficient cells. Downregulation of Brg1 and Brm did not affect the recruitment of DNA damage recognition factor XPC to cisplatin DNA lesions, but affected ERCC1 recruitment, which is involved in the later stages of DNA repair. Based on these results, we propose that SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex modulates cisplatin cytotoxicity by facilitating efficient repair of the cisplatin DNA lesions. | 22721696
 |
Novel role of base excision repair in mediating cisplatin cytotoxicity.
Kothandapani, Anbarasi, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 286: 14564-74 (2011)
2011
Show Abstract
Using isogenic mouse embryonic fibroblasts and human cancer cell lines, we show that cells defective in base excision repair (BER) display a cisplatin-specific resistant phenotype. This was accompanied by enhanced repair of cisplatin interstrand cross-links (ICLs) and ICL-induced DNA double strand breaks, but not intrastrand adducts. Cisplatin induces abasic sites with a reduced accumulation in uracil DNA glycosylase (UNG) null cells. We show that cytosines that flank the cisplatin ICLs undergo preferential oxidative deamination in vitro, and AP endonuclease 1 (APE1) can cleave the resulting ICL DNA substrate following removal of the flanking uracil. We also show that DNA polymerase β has low fidelity at the cisplatin ICL site after APE1 incision. Down-regulating ERCC1-XPF in BER-deficient cells restored cisplatin sensitivity. Based on our results, we propose a novel model in which BER plays a positive role in maintaining cisplatin cytotoxicity by competing with the productive cisplatin ICL DNA repair pathways. | 21357694
 |
BRG-1 is required for RB-mediated cell cycle arrest.
Strobeck, M W, et al.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 97: 7748-53 (2000)
2000
Show Abstract
The antiproliferative action of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein, RB, is disrupted in the majority of human cancers. Disruption of RB activity occurs through several disparate mechanisms, including viral oncoprotein binding, deregulated RB phosphorylation, and mutation of the RB gene. Here we report disruption of RB-signaling in tumor cells through loss of a critical cooperating factor. We have previously reported that C33A cells fail to undergo cell cycle inhibition in the presence of constitutively active RB (PSM-RB). To determine how C33A cells evade RB-mediated arrest, cell fusion experiments were performed with RB-sensitive cells. The resulting fusions were arrested by PSM-RB, indicating that C33A cells lack a factor required for RB-mediated cell cycle inhibition. C33A cells are deficient in BRG-1, a SWI/SNF family member known to stimulate RB activity. Consistent with BRG-1 deficiency underlying resistance to RB-mediated arrest, we identified two other BRG-1-deficient cell lines (SW13 and PANC-1) and demonstrate that these tumor lines are also resistant to cell cycle inhibition by PSM-RB and p16ink4a, which activates endogenous RB. In cell lines lacking BRG-1, we noted a profound defect in RB-mediated repression of the cyclin A promoter. This deficiency in RB-mediated transcriptional repression and cell cycle inhibition was rescued through ectopic coexpression of BRG-1. We also demonstrate that 3T3-derived cells, which inducibly express a dominant-negative BRG-1, arrest by PSM-RB and p16ink4a in the absence of dominant-negative BRG-1 expression; however, cell cycle arrest was abrogated on induction of dominant-negative BRG-1. These findings demonstrate that BRG-1 loss renders cells resistant to RB-mediated cell cycle progression, and that disruption of RB signaling through loss of cooperating factors occurs in cancer cells. | 10884406
 |










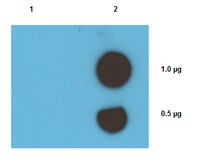


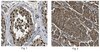

 Antibody[209787-ALL].jpg)